Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway: Difference between revisions
HughWilding (talk | contribs) Content added |
‘Stations’ heading revised and corrections to ‘Textboxes’ |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|stations= [[Ahmedabad]], [[Baroda]], [[Broach]], [[Surat]] | |stations= [[Ahmedabad]], [[Baroda]], [[Broach]], [[Surat]] | ||
|system1date= 1906 | |system1date= 1906 | ||
|system1details= Worked by reformed | |system1details= Worked by reformed BB&CIR | ||
|system2date= | |system2date= | ||
|system2details= | |system2details= | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
{{System_Railways_Infobox | {{System_Railways_Infobox | ||
|image= | |image= Bombay Baroda Central India Railway logo.jpg | ||
|caption= '' | |caption= ''Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway device'' | ||
|timeline1date= 1906 | |timeline1date= 1906 | ||
|timeline1details= BBCIR contracted to work State line | |timeline1details= BBCIR contracted to work State line | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
|company4details= [[Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway]] | |company4details= [[Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway]] | ||
|company5= | |company5= | ||
|company5details= [[Godhra- | |company5details= [[Godhra-Ratlam-Nagda Railway]] | ||
|company6= | |company6= | ||
|company6details= [[Nagda-Ujjain Railway]] | |company6details= [[Nagda-Ujjain Railway]] | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
|company12details= [[Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway]] | |company12details= [[Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway]] | ||
|headquarters= [[Bombay]] (BG), [[Ajmer]] (MG) | |headquarters= [[Bombay]] (BG), [[Ajmer]] (MG) | ||
|workshop= [[Ajmer]] | |workshop= [[Parel]] (BG) see also [[Parel Railway Workshops]] <br>[[Ajmer]] (MG) | ||
|stations= [[Agra]], [[Ajmer]], [[Ahmedabad]], [[Baroda]], [[Cawnpore]], [[Delhi]], [[Indore]], [[Jaipur]], [[Rutlam]], [[Surat]] | |stations= '''[[Agra]]''', [[Ajmer]], [[Ahmedabad]], [[Baroda]],'''[[Bombay]]''', '''[[Cawnpore]]''', '''[[Delhi]]''', [[Indore]], [[Jaipur]], [[Rutlam]], [[Surat]] | ||
''See also heading '''Stations''' for major stations marked'' '''bold''' | |||
|system1date= | |system1date= | ||
|system1details= | |system1details= | ||
| Line 79: | Line 80: | ||
|system3details= | |system3details= | ||
|gauge1= Broad gauge | |gauge1= Broad gauge | ||
|gauge1details= 868 miles (1905) | |gauge1details= 868 miles (1905)<br>1233 miles (1943) | ||
|gauge2= Metre gauge | |gauge2= Metre gauge | ||
|gauge2details= 2022 miles (1905) | |gauge2details= 2022 miles (1905)<br>1985 miles (1943) | ||
|gauge3= 2'6" NG | |gauge3= 2'6" NG | ||
|gauge3details= 132 miles (1905) | |gauge3details= 132 miles (1905)<br>152 miles (1943) | ||
|gauge4= | |gauge4= | ||
|gauge4details= | |gauge4details= | ||
| Line 89: | Line 90: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File: Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Map 1909, north section.png|thumb| Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Map 1909 – north/east section]] | |||
[[File: Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Map 1909, south section.png|thumb| Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Map 1909 – south/west section]] | |||
[[File:BB&CI Railway System Map 1937.png|thumb| BB&CIR System 1937 Map]] | |||
The '''Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Company''' (BB&CIR) was incorporated in 1855 for "the construction and working of a line from Bombay, ''via'' Surat and Baroda, to Ahmedabad - total about 320 miles. Capital 2,300,000''l''. Rate of Interest Guaranteed - 5 per cent on 2,000,000''l''. capital and 4½ per cent . on 300,000''l''. debentures." <ref>"Money Market and City Intelligence", ''The Times'', Wednesday, 15 June 1859, #23333, 7a.</ref> | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
In 1852 [[John Pitt Kennedy]] was introduced in London to Lieutenant-Colonel French, who had been Acting Resident at the Court of the Guicowar of Baroda. Colonel French wanted to get up a company to construct a line of railway from [[Baroda]] to Tankaria Bunda, in the gulf of Cambay, a distance of about 45 miles. Colonel Kennedy joined him, but instead of the original line proposed, they projected what became the '''Bombay, Baroda, and Central India railway''' <ref name=grace>[http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/John_Pitt_Kennedy_(1796-1879) Grace's Guide "John Pitt Kennedy"]Retrieved on 21 Apr 2016</ref>. | |||
Their object was to open the most effectual line from Bombay, through the central and north-western districts, to meet the railway in progress of construction from [[Calcutta]] to [[Delhi]], together with all the branches that such a line could require. In 1853 the '''[[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]] Company'''(BB&CIR) was formed with Colonel [[John Pitt Kennedy]] appointed as consulting engineer and managing director. A staff of engineers was sent to Bombay, and during the cold season of 1853, comparative surveys, sufficient to lay a well-considered scheme before the Government, were made <ref name=grace/>. | |||
On the 3rd of November, 1854, the Governor-General, Lord Dalhousie, sanctioned the construction of the sections [[Broach]], and [[Baroda]], to [[Ahmedabad]], leaving the remainder of the scheme for future decision, and the work to be commenced at [[Bombay]]. The Home Government, however, decided that the work should be commenced at [[Surat]] <ref name=grace/>. Although on flat country, this. line had to traverse some of the mightiest rivers and water channels in the country including the [[Nerbudda (Broach) Bridge BB&CIR| Nerbudda Bridge near Broach]] and the [[Taptee (Surat) Bridge BB&CIR|Taptee Bridge near Surat]] | |||
Construction commenced in 1855 and began work on track from [[Baroda]] to [[Surat]]. By 1865, the [[Bombay]]-[[Surat]]-[[Baroda]]-[[Ahmedabad]] route was complete in 1867. The [[Bombay Back Bay Reclamation Scheme Railway|Bombay Back Bay]] suburban service commenced in 1870 with one train in each direction each day. In 1871 the [[Bombay-Ahmadabad BB&CIR Main Line|Bombay-Ahmadabad Main Line]] was extended north to [[Viramgam]] to 350 miles (563km). | |||
The [[1870-71_Report_on_Railways#Progress_on_State_lines._Paragraphs_5-10.3B_Pages_3-4| “1870-71 Annual Report for Indian Railways for the BB&CIR“]] gives:- [[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|‘Broad Gauge (BG)]] Line sanctioned 391 miles(629km), total line opened 312 miles(502km) and 72 miles(116km) to be finished’. The Report also details of the [[1870-71_Report_on_Railways#Bombay.2C_Baroda_and_Central_India_Railway._Paragraphs_67.2C68.3B_Page_35|‘progress of the railway and the commercial summery’]] - ''see separate pages for details.'' | |||
On 31 December 1905, ownership of the BB&CIR passed to the Government of India [[Government of India |(GoI)]] and a new company formed to manage the BB&CIR under a contract agreed in 1907 and revised in 1913<ref>[https://ia801009.us.archive.org/8/items/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System.pdf " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 12-22]; Retrieved 17 Dec 2015</ref> | |||
<ref>[https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/228649/8330.pdf H.M. Government “Statute Law Repeals: Nineteenth Report : Draft Statute Law (Repeals) Bill; April 2012"; page 118-120, paragraph 3.18-3.25] Retrieved on 2 January 2016</ref>. | |||
Management of the BB&CIR passed to the GoI on 1 January 1942. | |||
In 1951, the BB&CIR was split to form three Zones of [[Indian Railways]]:- | |||
*‘[[Western Railway]] Zone’ comprised most of the BB&CIR (less the Delhi-Rewari-Fazilka and Kanpur/Cawnpore-Achnera sections) , which were added to other railways [[Western Railway|- ''see separate page'']] | |||
*‘[[Northern Railway]] Zone’ comprised the ‘Delhi-Rewari-Fazilka Section’ , which were added to other railways [[Northern Railway| - ''see separate page'']] | |||
*‘[[North Eastern Railway]] Zone’ comprised the ‘Kanpur/Cawnpore-Achnera Section’ , which were added to other railways [[North Eastern Railway| - ''see separate page'']] | |||
==BB&CIR Collieries and Coal Supplies== | |||
''See separate pages'' | |||
* ‘[[Jarangdih Colliery]] was a 'Joint BB&CIR and [[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway| 'Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway']] Colliery | |||
* ‘[[Kurasia Colliery]] near Chirimiri was a 'BB&CIR Colliery’ | |||
== | ==BB&CIR Bridges and Constructions== | ||
See [[Bombay,_Baroda_%26_Central_India_Railway_Bridges_and_Constructions| '''BB&CIR Bridges and Constructions''']] | |||
==BB&CIR Main line, Branches and Extensions== | |||
The BB&CIR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge | |||
* Broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) - 868 miles/1397km (1905); 997 miles/1604km (1918); 1233 miles/1984km (1943) | |||
* Metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) - 2022 miles/3254km (1905); 1822 miles/2931km (1918); 1985/3195km miles (1943) | |||
* Narrow gauge 2ft 6in([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) - 132 miles/212km (1905); 326 miles/523km (1918); 152 miles/245km (1943) | |||
In 1918 the total length of line being worked as the BB&CIR system (both owned lines and managed/worked lines) was 3823 miles(6150km) opened plus a further 254 miles(407km) under construction or sanctioned for construction <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n21/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 12, pdf page 21]; Retrieved 4 Nov 2016</ref> . | |||
See separate page '''[[Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Network - Lines owned and worked]]''' for details. | |||
==Lines worked by BB&CIR== | |||
The BB&CIR also managed, worked and maintained a number of mixed gauge lines on behalf of other parties. | |||
* Broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) - 1918 Total 202 miles(325km) <ref name=Admin/>. | |||
* Metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) - 1918 Total 456 miles(733km) <ref name=Admin/>. | |||
* Narrow gauge 2ft 6in([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) - 1918 Total 326 miles(523km) <ref name=Admin/>. | |||
See separate page '''[[Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Network - Lines owned and worked]]''' for details. | |||
==Stations== | |||
See separate pages for details of the Stations and Rail System into the following major Cities:- | |||
* [[Agra_Railways_%26_Stations#Agra_Stations| ‘Agra Stations’]] | |||
* [[Bombay_Churchgate_HQ_and_Station_BB%26CIR| ‘ Bombay Churchgate Stations’]] | |||
*[[Bombay_Central_Station_BB%26CIR| ‘Bombay Central Station’ from 1930]] | |||
* [[Cawnpore_Railways_and_Stations#Cawnpore_Stations| ‘Cawnpore Stations’]] | |||
* [[Delhi_Railways_%26_Stations#Delhi_Stations| ‘Delhi Stations’]] | |||
==Records== | |||
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the [http://www.fibis.org/store/fibis-books-and-publications/bff-0004-research-sources-for-indian-railways-1845-1947/ Fibis shop]. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the [[India Office Records]] (IOR) held at the [[British Library]] | |||
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway | |||
<ref>[http://searcharchives.bl.uk/primo_library/libweb/action/search.do?vid=IAMS_VU2 “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search"]; Retrieved 21 Jan 2016</ref> gives a large number of references. The most important being:- | |||
*'''L /AG/46/6''' “Records of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Company; 1856-1947” | |||
==Personnel Records== | |||
Unfortunately, there are no BB&CIR staff records held in the [[India Office Records]] at the [[British Library]]. | |||
Only some records that have been found from different sources:- | |||
See separate page '''[[Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Personnel]]''' for details. | |||
==Historical books online== | |||
*[https://archive.org/details/throughrajputan00stubgoog ''Through Rajputana to Delhi : An Ilustrated Guide to the Districts Reached by the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway''] by Carlton Stubbs 1907 Archive.org | |||
*[https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.57412 ''Bombay Baroda Central India Railway Company: Traffic Statistics''] 1920. Archive.org, mirror from Digital Library of India. | |||
:[https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.57589 ''Bombay Baroda Central India Railway Company: Traffic Statistics''] 1921. Archive.org, mirror from Digital Library of India. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
{{#widget:Google PlusOne | |||
|size=small | |||
|count=true | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Guaranteed Railways]] | [[Category:Guaranteed Railways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:12, 28 February 2021
| Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Churchgate Terminus & Offices, BBCIR, Bombay | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Bombay to Viramgam | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 504 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1855 | Formed as Guaranteed company | |
| 1905 | Line acquired by State | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Ahmedabad, Baroda, Broach, Surat | |
| System agency | ||
| 1906 | Worked by reformed BB&CIR | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway device | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1906 | BBCIR contracted to work State line | |
| 1942 | Working of system taken over by State | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Ahmedabad-Dholka Railway | ||
| Ahmedabad-Parantij Railway | ||
| Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway | ||
| Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway | ||
| Godhra-Ratlam-Nagda Railway | ||
| Nagda-Ujjain Railway | ||
| Palanpur-Deesa Railway | ||
| Petlad-Cambay Railway | ||
| Rajpipla Railway | ||
| Rajputana-Malwa Railway | ||
| Tapti Valley Railway | ||
| Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Bombay (BG), Ajmer (MG) | |
| Workshops | Parel (BG) see also Parel Railway Workshops Ajmer (MG) | |
| Major Stations | Agra, Ajmer, Ahmedabad, Baroda,Bombay, Cawnpore, Delhi, Indore, Jaipur, Rutlam, Surat
See also heading Stations for major stations marked bold | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1951 | Western Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 868 miles (1905) 1233 miles (1943) | |
| Metre gauge | 2022 miles (1905) 1985 miles (1943) | |
| 2'6" NG | 132 miles (1905) 152 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Regiment | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
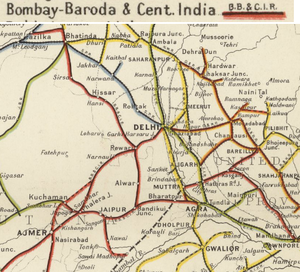
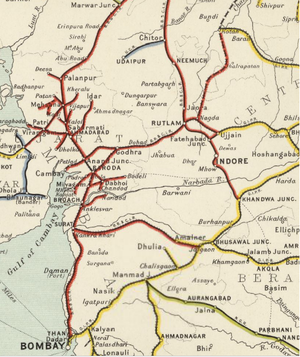
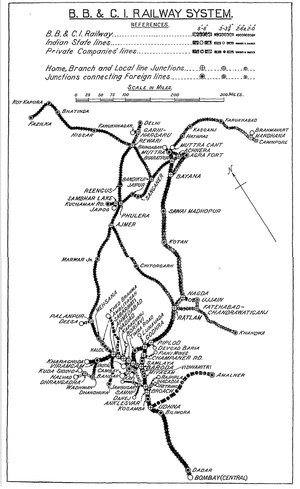
The Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Company (BB&CIR) was incorporated in 1855 for "the construction and working of a line from Bombay, via Surat and Baroda, to Ahmedabad - total about 320 miles. Capital 2,300,000l. Rate of Interest Guaranteed - 5 per cent on 2,000,000l. capital and 4½ per cent . on 300,000l. debentures." [1]
History
In 1852 John Pitt Kennedy was introduced in London to Lieutenant-Colonel French, who had been Acting Resident at the Court of the Guicowar of Baroda. Colonel French wanted to get up a company to construct a line of railway from Baroda to Tankaria Bunda, in the gulf of Cambay, a distance of about 45 miles. Colonel Kennedy joined him, but instead of the original line proposed, they projected what became the Bombay, Baroda, and Central India railway [2].
Their object was to open the most effectual line from Bombay, through the central and north-western districts, to meet the railway in progress of construction from Calcutta to Delhi, together with all the branches that such a line could require. In 1853 the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Company(BB&CIR) was formed with Colonel John Pitt Kennedy appointed as consulting engineer and managing director. A staff of engineers was sent to Bombay, and during the cold season of 1853, comparative surveys, sufficient to lay a well-considered scheme before the Government, were made [2].
On the 3rd of November, 1854, the Governor-General, Lord Dalhousie, sanctioned the construction of the sections Broach, and Baroda, to Ahmedabad, leaving the remainder of the scheme for future decision, and the work to be commenced at Bombay. The Home Government, however, decided that the work should be commenced at Surat [2]. Although on flat country, this. line had to traverse some of the mightiest rivers and water channels in the country including the Nerbudda Bridge near Broach and the Taptee Bridge near Surat
Construction commenced in 1855 and began work on track from Baroda to Surat. By 1865, the Bombay-Surat-Baroda-Ahmedabad route was complete in 1867. The Bombay Back Bay suburban service commenced in 1870 with one train in each direction each day. In 1871 the Bombay-Ahmadabad Main Line was extended north to Viramgam to 350 miles (563km).
The “1870-71 Annual Report for Indian Railways for the BB&CIR“ gives:- ‘Broad Gauge (BG) Line sanctioned 391 miles(629km), total line opened 312 miles(502km) and 72 miles(116km) to be finished’. The Report also details of the ‘progress of the railway and the commercial summery’ - see separate pages for details.
On 31 December 1905, ownership of the BB&CIR passed to the Government of India (GoI) and a new company formed to manage the BB&CIR under a contract agreed in 1907 and revised in 1913[3] [4].
Management of the BB&CIR passed to the GoI on 1 January 1942.
In 1951, the BB&CIR was split to form three Zones of Indian Railways:-
- ‘Western Railway Zone’ comprised most of the BB&CIR (less the Delhi-Rewari-Fazilka and Kanpur/Cawnpore-Achnera sections) , which were added to other railways - see separate page
- ‘Northern Railway Zone’ comprised the ‘Delhi-Rewari-Fazilka Section’ , which were added to other railways - see separate page
- ‘North Eastern Railway Zone’ comprised the ‘Kanpur/Cawnpore-Achnera Section’ , which were added to other railways - see separate page
BB&CIR Collieries and Coal Supplies
See separate pages
- ‘Jarangdih Colliery was a 'Joint BB&CIR and 'Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway' Colliery
- ‘Kurasia Colliery near Chirimiri was a 'BB&CIR Colliery’
BB&CIR Bridges and Constructions
See BB&CIR Bridges and Constructions
BB&CIR Main line, Branches and Extensions
The BB&CIR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge
- Broad gauge(BG) - 868 miles/1397km (1905); 997 miles/1604km (1918); 1233 miles/1984km (1943)
- Metre gauge(MG) - 2022 miles/3254km (1905); 1822 miles/2931km (1918); 1985/3195km miles (1943)
- Narrow gauge 2ft 6in(NG) - 132 miles/212km (1905); 326 miles/523km (1918); 152 miles/245km (1943)
In 1918 the total length of line being worked as the BB&CIR system (both owned lines and managed/worked lines) was 3823 miles(6150km) opened plus a further 254 miles(407km) under construction or sanctioned for construction [5] .
See separate page Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Network - Lines owned and worked for details.
Lines worked by BB&CIR
The BB&CIR also managed, worked and maintained a number of mixed gauge lines on behalf of other parties.
- Broad gauge(BG) - 1918 Total 202 miles(325km) [5].
- Metre gauge(MG) - 1918 Total 456 miles(733km) [5].
- Narrow gauge 2ft 6in(NG) - 1918 Total 326 miles(523km) [5].
See separate page Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Network - Lines owned and worked for details.
Stations
See separate pages for details of the Stations and Rail System into the following major Cities:-
- ‘Agra Stations’
- ‘ Bombay Churchgate Stations’
- ‘Bombay Central Station’ from 1930
- ‘Cawnpore Stations’
- ‘Delhi Stations’
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [6] gives a large number of references. The most important being:-
- L /AG/46/6 “Records of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway Company; 1856-1947”
Personnel Records
Unfortunately, there are no BB&CIR staff records held in the India Office Records at the British Library.
Only some records that have been found from different sources:-
See separate page Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Personnel for details.
Historical books online
- Through Rajputana to Delhi : An Ilustrated Guide to the Districts Reached by the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway by Carlton Stubbs 1907 Archive.org
- Bombay Baroda Central India Railway Company: Traffic Statistics 1920. Archive.org, mirror from Digital Library of India.
- Bombay Baroda Central India Railway Company: Traffic Statistics 1921. Archive.org, mirror from Digital Library of India.
References
- ↑ "Money Market and City Intelligence", The Times, Wednesday, 15 June 1859, #23333, 7a.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Grace's Guide "John Pitt Kennedy"Retrieved on 21 Apr 2016
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 12-22; Retrieved 17 Dec 2015
- ↑ H.M. Government “Statute Law Repeals: Nineteenth Report : Draft Statute Law (Repeals) Bill; April 2012"; page 118-120, paragraph 3.18-3.25 Retrieved on 2 January 2016
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 12, pdf page 21; Retrieved 4 Nov 2016
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search"; Retrieved 21 Jan 2016