Difference between revisions of "Rail gauge"
(→Standard Gauge(SG): 'Bombay City Improvement Trust Railways' and 'Salsette Trombay Railway' added) |
m |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
*'''[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]''' The records show that eight SG locomotives dating from 1921-22 were supplied for the '[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]' which did not commence operations until 1928. | *'''[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]''' The records show that eight SG locomotives dating from 1921-22 were supplied for the '[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]' which did not commence operations until 1928. | ||
<blockquote>''It is interesting to speculate how, in the 1920's when BG was becoming the norm, both the 'Bombay City Improvement Trust' and the '[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]' came to use the Standard Gauge (SG)''</blockquote> | <blockquote>''It is interesting to speculate how, in the 1920's when BG was becoming the norm, both the 'Bombay City Improvement Trust' and the '[[Salsette Trombay Railway]]' came to use the Standard Gauge (SG)''</blockquote> | ||
| − | + | ====Unique rail Gauges==== | |
| − | |||
*'''[[Nalhati-Azimganj Railway]]''', the original name for the [[Indian Branch Railway]]; constructed in 1863 used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge, later converted to BG. | *'''[[Nalhati-Azimganj Railway]]''', the original name for the [[Indian Branch Railway]]; constructed in 1863 used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge, later converted to BG. | ||
*'''[[Sone Canal Construction Railway/Tramway]]''' used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge during the construction 1868-74 | *'''[[Sone Canal Construction Railway/Tramway]]''' used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge during the construction 1868-74 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
| − | + | ====Gauge conversion==== | |
Following the introduction of the metre gauge, the Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) occasionally allowed existing broad gauge lines to be converted to metre gauge and ''vice versa'' where expedient. | Following the introduction of the metre gauge, the Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) occasionally allowed existing broad gauge lines to be converted to metre gauge and ''vice versa'' where expedient. | ||
| − | + | ====Transhipment==== | |
Despite four Commissions of Inquiry, the GoI did little te resolve the continuing problem of transhipment wherever there was a break-of-gauge. | Despite four Commissions of Inquiry, the GoI did little te resolve the continuing problem of transhipment wherever there was a break-of-gauge. | ||
Revision as of 06:19, 1 September 2017
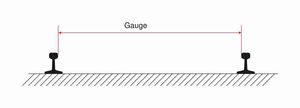
Rail gauge, sometimes track gauge, is the distance between the inner sides of the two parallel rails that make up a single railway line. Sixty percent of the world's railways use a standard gauge of 1,435 mm (4' 8½" in). Wider gauges are called broad gauge ; smaller gauges, narrow gauge. Break-of-gauge refers to a place where different gauges meet; sometimes this may involve transhipment and there may be extensive sheds to facilitate this. Some stretches of track are dual or mixed gauge, with three (or sometimes four) rails in place of the usual two, to allow trains of two or more different gauges to share the same path. Gauge conversion can be used to reduce break-of-gauge situations.
Abbreviations
- BG - Broad Gauge
- MG - Metre Gauge
- NG - Narrow Gauge
- SG - Standard Gauge
Contents
History
Broad Gauge (BG)
The first gauge used in India was one of 5' 6" (1676mm), settled upon in the belief that it offered greater stability in the face of Indian weather and the perceived threat of cyclonic winds, and offered economies in freight haulage.
Metre Gauge (MG)
In 1868, a decision was taken to permit the introduction of a smaller gauge in order to increase quickly the construction of railways in India.
Narrow Gauge (NG)
Later, two even narrower gauges (2' and 2' 6") were allowed to be used for feeder lines.
Standard Gauge(SG)
Although this 4 ft 8½ in (1,435 mm) gauge was the most usual throughout the world it was not adopted in India. There were a few exceptions:-
- Yamuna River, Okhla Canal Construction Tramway used from 1869 to 1874 to build the headworks from the Yamuna River at Okhla. It was Standard Gauge tramway used to carry stone.
- Calcutta Tramways Company adopted the Standard Gauge on its electric tramcars from 1900 onwards, on conversion from the MG horse drawn tram system.
- Bombay City Improvement Trust Railways The records show a total of twenty-one standard gauge (SG) locomotives dating from 1920-23 that were supplied to the Bombay City Improvement Trust Schemes. The destiny of these locomotives on completion of the schemes in the mid 1920's is unknown.
- Salsette Trombay Railway The records show that eight SG locomotives dating from 1921-22 were supplied for the 'Salsette Trombay Railway' which did not commence operations until 1928.
It is interesting to speculate how, in the 1920's when BG was becoming the norm, both the 'Bombay City Improvement Trust' and the 'Salsette Trombay Railway' came to use the Standard Gauge (SG)
Unique rail Gauges
- Nalhati-Azimganj Railway, the original name for the Indian Branch Railway; constructed in 1863 used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge, later converted to BG.
- Sone Canal Construction Railway/Tramway used a 4ft(1222cm) gauge during the construction 1868-74
- Arakkonam-Conjeevaram Tramway, absorbed into the Indian Tramway Co. was a 3'6"(1067mm) gauge line which opened in 1865, converted in 1878 to MG.
- Chirimiri Colliery Railway used a 3ft 0in(915mm) gauge locomotives operational from 1932.
Gauge conversion
Following the introduction of the metre gauge, the Government of India(GoI) occasionally allowed existing broad gauge lines to be converted to metre gauge and vice versa where expedient.
Transhipment
Despite four Commissions of Inquiry, the GoI did little te resolve the continuing problem of transhipment wherever there was a break-of-gauge.
Project Unigauge
Starting about 1980, Indian Railways resolved to convert its legacy of metre and narrow gauge lines to broad gauge standards. This project is ongoing.