Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway
| Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| MG | 308 miles (1944) | |
| 2' 6" NG | 356 miles (1944) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1949 | Nationalised & merged into BB&CIR | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Baroda | |
| System agency | ||
| Own agency | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway(GBSR) was formed in 1921 from the original Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway(GDR) that had started 1862 and progressively expanded as a narrow gauge(NG) network. The Gaekwars of the Princely Baroda State were responsible for building several narrow and metre gauge lines in and around Baroda State and the eastern Gujerat.
The ‘Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway’(BB&CIR) had been working the’ Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway’ on behalf of the Baroda Durbar together with the ‘Gaekwar's Petlad Railway’, the ‘Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway’, the Petlad-Vaso Railway and the ‘Bodeli-Chhota Udaipur Railway’.The working arrangements of all these lines were transferred to the newly formed GBSR in 1921.
Contents
Origins of GBSR
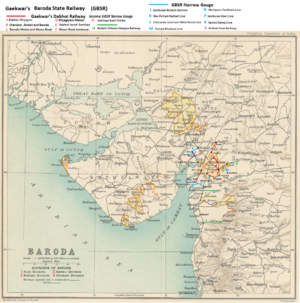
The 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) railway network, known as the Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway commenced with an oxen driven line between Dabhoi and Miyagam, a distance of 20 miles(33km), that first opened in 1862. The rails were inadequate for steam locomotives and the upgraded railway was reopened to traffic in 1873. The network expanded and by 1909 Dabhoi had become an NG railway junction, it had become the centre where the lines from Miyagam, Chandod , Bodeli and Baroda converged with a line length of 92 miles(147km). By 1918 the NG network had expanded to 154 miles(246km) [1]. By 1921, when the network was renamed the GBSR, there was approximately 246 miles(393km) of track. The network on handover in 1921 is shown in "Red" on Route Map
See Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway for details and references
Development of GBSR
Additional lines were constructed up to 1929, creating a complex network using two railgauges:-
These are detailed separately:-
GBSR Narrow Gauge Expansion in chronological order
The GBSR took over the Gaekwar's Dabhoi Railway(GDR) network shown in “Red” on Route Map. A number of projects had been sanctioned for construction by the GDR and some were in progress, these were taken over and completed by GBSR. Some lines previously sanctioned were apparently never constructed.
Narrow Gauge First Division – Headquarters Dabhoi
From 1921 GBSR continued to develop their NG system :-
- ‘Dabhoi-Miyagam Line’ (“Red Line A”); 20 miles(32km) NG, first opened 1862, re-opened 1873 by GDR; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Dabhoi-Chandod Line’ (“Red Line B”); 11 miles(17km) NG, opened by GDR 1879; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Dabhoi-Baroda Line’ (“Red Line B”); 19 miles(34km) NG, opened by GDR 1879-90; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Baroda-Masor Road Line’ (“Red Line C”); 20 miles(32km) NG, opened by GDR 1897-1904; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Miyaram Karjan-Malsar Line’ (“Red Line D”); 24 miles(44km) NG, opened by GDR 1912; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Dabhoi-Timba Line’ (“Red Line E”) 62 miles(100km) NG; opened by GDR 1913-19; transferred from DDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Masor Road-Jambusar Junction Line’ (“Red Line F”) 7 miles(11km) NG; opened by GDR 1917; transferred from GDR to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Bodeli-Chhota Udaipur Railway’ (“Green Line H”) 22.5 miles(36km) NG; opened 1917. This was a separate Company worked by BB&CIR and transferred to GBSR, 1921.
- ‘Broach-Jambusar Railway’, (“Blue Line J”) 30 miles(48km) NG; from Jambusar via Samni to Broach; was constructed by the BB&CIR and opened in Nov 1914 as a branch of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) [2]. The line had been proposed in 1903 as the ‘Broach-Jambusar-Masor Road(Kangat) Branch’, 31 miles (50km) NG: proposed 1903 [3]. The GDR ‘Masor Road-Jambusar Section’ was finally opened in 1917.
- ‘Nar-Petlad-Nadiad Line’, (“Blue Line K”),about 29 miles(46km) NG; from Nar Town to Petlad(see note ‡‡) and then via Sojitra, Dewa Deva, Vaso to Nadiad 29 miles. Part was first surveyed in 1905 as the ‘Nar-Nadiad Loop’ 20 miles(32km) [3] and not completed until much later:-
- ‘Petlad-Vaso Railway’, (“Purple Line S“) 16 miles(25km) NG, as a separate Railway Company. The line ran from Petlad‡‡ to Vaso and opened in 1914. This section was incorporated into the ‘Nar-Petlad-Nadiad Line’ given above, and was extended a further 3½ miles(6km) to Pihij in 1915. The line was operated by the BB&CIR and was absorbed into GBSR in 1921.
- ‘Nar-Petlad Section’ was completed by GBSR on date unknown
- ‘Vaso-Nadiad Section’ was completed by GBSR on date unknown
- ‘Choranda Junction-Moti Koral Line’, (“Blue Line L”) 12 miles(19km) NG, sanctioned in 1914 for the GDR [4]. Finally completed and opened by GBSR in Nov 1921 [5].
- ‘Petlad-Bhadran Line’, (“Blue Line M”) 14 miles(22km) NG, opened by GBSR Jun 1922 [5].The line connected Bhadran to the Petlad Juction(see note ‡‡)
- ‘Motipura-Taukhala Line’, (“Blue Line N”) 26 miles(42km) NG, sanctioned in 1914 for the GDR [4]. Finally completed and opened by GBSR in Mar 1923 [5]. Motipura given in the 1918 Admin Report but not identified - thought it refers to the ‘Chhuchhapura Junction to Taukala Line’ of about 24 miles(38km).
- ‘Jambusar-Kavi Line’, (“Blue Line P”) 16 miles(26km) NG, from Jambusar to Kavi, a village on the coast; opened by GBSR Aug 1929 [5].
- ‘Samni-Dahej Line’, (“Blue Line R”) 42 miles(67km) NG, from Samni to Dahej, a village on the coast on the Gulf of Cambey; opened by GBSR Mar 1930 [5].
Note ‡‡ Petlad was station between Anand and Cambay on the broad gauge(BG) Petlad-Cambay Railway worked by BB&CIR which linked to the 'BB&CIR BG Mainline'. At this station there were interchange with the narrow gauge ‘Petlad-Bhadran Line’ also the ‘Petlad-Vaso Railway'
.
Narrow Gauge Second Division – Headquarters Navsari GBSR set up a second ‘Narrow Gauge Division’ based in Navsari with two isolated lines initially operated by BB&CIR but from 1921 the working was transferred to GBSR [6].
- ‘Bilimora-Waghai Railway’, (“Green Line X”) 39 miles(62km) NG. From Bilimora (an interchange station on the ‘BB&CIR BG Mainline’) initially to Kalamba (now named Kalva Amba) ; extended to reach Waghai , 4 miles(7km) by Nov 1929 [5]. Worked by BB&CIR until 1921 then by GBSR [6]
- ‘Kosamba-Zankhvav-Umarpada Line’, (“Green Line Y”) 38 miles(61km) NG; developed as two sections:-.
- ‘Kosamba-Zankhvav Railway’, 26 miles(42km) NG. Surveyed in 1900 [3], opened in 1912 from Kosamba to Zankhvav [7] . Initially operated by BB&CIR but from 1921 GBSR took over the working.
- ‘Zankhvav-Umarpada Section’, 12 miles(19km) NG from Zankhvav to Umarpada , opened by GBSR Jul 1929 [5]
- ‘Zankhvav-Bardipadu Extension’, 22 ½ miles(36km) NG, sanction in 1914 [7] There is no indication that line was constructed
- ‘Navsari-Kamrej Light Railway, 20 miles(32km) NG, sanctioned as a steam tramway in 1914 for the Baroda Durbar1912 [8] . There is no indication that line was constructed
The 1936-37 “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways” gives the Route Mileage of the GBSR ‘Narrow Gauge Division’ as 333 Miles [9]. In addition it separately lists under GBSR Narrow Gauge ‘Bodeli-Dhhota-Udaipur Railway’, 23 miles
GBSR Metre Gauge System
In 1921 the working of the ‘Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway’(GMR) , a metre gauge (MG) system, was transferred to the GBSR, previously being worked by the ‘Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway’(BB&CIR).
- ‘Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway’(GMR) route mileage in 1921 was 193 miles(311km) . Marked lines 1 to 6 on map - see separate page,
- ‘Bechraji-Bhoyani Link Line’ from Bechraji to Katosan Road 15 miles, opened 1920; to Bhoyani 6 miles 1921. Total 21 miles(34km). Marked 7 on map
At the same time, 1921, the following metre gauge(MG) line being worked by the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) was transferred to the newly formed ‘Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway’(GBSR):-
- ‘Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway’, 41 miles(65km) MG; owned by the Princely Baroda State; opened 1902-3 from Vijapur to Kadi and extended by a further 5 miles(8km) in 1912 to‘Bhoyani Road- and extended a further 21 miles(34km) to reach Bechraji before 1921 where it connected to the GMR . Marked 7 and 8 on map. - see separate page
Adding the route mileages above gives a 1921 total route mileage of the GBSR of 260 miles(418km)
The following metre gauge(MG) line was worked by GBSR in 1921
- ‘Okhamandal State Railway’, 37 miles(59km) MG; owned by Princely Okhamandal State, opened 1921; in 1922 became the Kuranga-Okha Railway and in 1923 transferred to ‘Jamnagar and Dwarka Railway’
The 1936-37 “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways” gives the Route Mileage of the GBSR ‘Metre Gauge Division’ as 255 Miles(410km) [10]
Later Developments
In 1949, the GBSR was merged into the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR).
External Lnks
- "Preserving rich heritage of Gaekwar’s Baroda State Rlys“ by Vikas Singh, Editor of Indian Steam Railway Society Magazine", 2015
- “History of Vadora/Baroda - Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway”
References
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 36 and 37; Retrieved 16 Nov 2016
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page35 (pdf43); Retrieved 13 Feb 2018
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906 “Railways in India – GOI Administrative Report 1916-17 / Native States Lines” page 17 (pdf44; Retrieved 10 Feb 2018
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 36; Retrieved 10 Feb 2018
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 ”Indian Railways – A New Chronology” by permission of the author and researcher Keith Scholey
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "History of Vadora/Baroda” – “Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway" Para 3; Retrieved 12 Feb 2018
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 38; Retrieved 10 Feb 2018
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 39; Retrieved 10 Feb 2018
- ↑ “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” Download GIPE-017080.pdf page 120 (pdf 149); Retrieved 10 Feb 2018
- ↑ “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” Download GIPE-017080.pdf page 42 (pdf 57); Retrieved 10 Feb 2018