Difference between revisions of "Howrah-Amta Light Railway"
HughWilding (talk | contribs) (Changed category) |
(→HALR System: km equivalents added) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|gauge4= | |gauge4= | ||
|gauge4details= | |gauge4details= | ||
| − | |timeline1date= | + | |timeline1date= 1898 |
| − | |timeline1details= | + | |timeline1details= Line opened to traffic |
|timeline2date= | |timeline2date= | ||
|timeline2details= | |timeline2details= | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | Also known as the '''Howrah-Amta Tramway''' in some records | |
| − | + | See also page '''[[Howrah Tramways (Light Railways)]]''' | |
| − | = | + | The '''Howrah-Amta Light Railway''' (HALR) was a short 2ft/610mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) railway which ran from [[Howrah]] westwards to [[Amta]]. |
| + | <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n251/mode/2up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 243]; Retrieved 31 Aug 2016</ref> | ||
| − | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Martin%27s_Light_Railways "Martin's Light Railways"] | + | [[File:Howrah-Amta Light Railway.png|thumb|'''Howrah-Amta Light Railway''']] |
| + | [[File: Howrah-Amta Light Railway Map 1909.png|thumb| Howrah-Amta Light Railway Map 1909]] | ||
| + | The HALR was one of several small narrow gauge concerns owned and worked by [[Martin's Light Railways]], a management company based in [[Calcutta]]. | ||
| + | <ref name=Wiki>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Martin%27s_Light_Railways Wikipedia"Martin's Light Railways"]; Retrieved 31 Aug 2016</ref> | ||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | On 12 June 1889 an agreement was signed between the District Board of Howrah and Messrs. Walsh, Lovett & Company on behalf of the Bengal District Road Tramways Company; this gave the Company the right to construct and work a tramway over a portion of roads <ref name=Admin/>. | ||
| + | This was subsequently renewed with [[Martin's Light Railways]] Co Ltd and sanctioned by Government notification in the Calcutta Gazette of 27 March 1895 <ref name=Wiki/>. On the 2 May 1895 the 'Howrah-Amta Light Railway Company’ was formed and worked by [[Martin's Light Railways]] (MLR). | ||
| + | |||
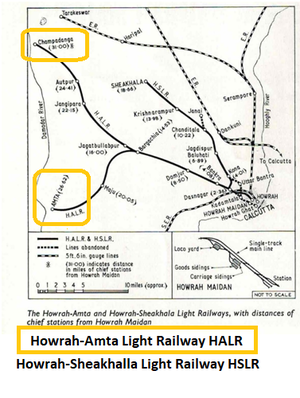
| + | The Howrah-Amta line was opened up to Domjur in 1897, and to [[Amta]] in 1898. An extension from Bargachhia (Bargechhe) junction to Autpur was opened in 1904, and a further extension to Champadanga in 1908, giving a total line length of 44 miles (70km) <ref name=Admin/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Howrah-Amta Light and the [[Howrah-Sheakhalla Light Railway|Howrah-Sheakhalla Light]] Railways start from Telkal Ghat on the Hooghly river, and skirting the Howrah Maidan pass through the crowded Panchanantala road to Kadamtala station. Here they separate, the Howrah-Sliiakhala line running north-west along the Benares road to the border of the district, and thence to Shiakhala in Hooghly district. The Howrah-Amta line runs west, chiefly along the side of the Jagatballabhpur road, and then goes south-west to [[Amta]] <ref name=Wiki/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A line from Autpur to Rajbalhat was sanctioned but never built <ref name=Maiden>”Two foot gauge at Howrah Maiden” by P J Bowcutt and H C Hughes. ‘Railway Magazine’ September 1965 Vol III No 773 pages 497-501</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Amta and Sheakhala companies both prospered and by 1904 the shareholders were already getting dividends of 7 and 5 per cent respectively. By 1914 over 2,500,000 passengers were being carried annually on the two lines, and by 1928 the number was nearly 4,000,000. Working frequent trains through the streets of Howrah, each preceded by a runner with a bell to warn pedestrians, became a major headache and from September 26, 1939, after the Municipality had refused to renew the existing agreement, Kadamtala became the terminus and the line to Howrah Ghat was abandoned <ref name=Maiden/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The lines continued to operate privately long after Independence in 1947, and finally converted to Broad Gauge and electrified from 1984 onwards <ref name=Wiki/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==HALR System== | ||
| + | The following is the progress in opening<ref name=Hist1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 282 pdf 324]; Retrieved 1 Aug 2020</ref>:- | ||
| + | * ‘Main Line’ | ||
| + | ** Telkul Ghat(Howrah) via Dumjur to Bargachia, 15 miles(24km), opened 1897, the first 2 miles(3.2km) to Kadamtala also worked by the ‘[[Howrah-Sheakhalla Light Railway]]’ | ||
| + | ** Bargachia via Maju to Amta, 12 miles(19km), opened 1898 | ||
| + | * ‘Champadanga Branch’ | ||
| + | ** Bargachia to Jagatbalabpur, 1½ miles(4km), opened 1897 | ||
| + | ** Jagatbalabpu to Autpur, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1904 | ||
| + | ** Autpur to Champadanga, 7 miles(11km), opened 1908 | ||
| + | Total line length 44 miles(71km) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 <ref name=Hist1937/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Classification == | ||
| + | [[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class III railway system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Stations== | ||
| + | Telkul Ghat, Howrah Maidan, Kadamtala, Dasnagar, Domjur, Bargachia, Maju, Amta | ||
| + | <br> Jagatbullabpur, Jangipara, Autpur, Champadanga. | ||
| + | <br>The section from Telkul Ghat via Howrah Maidan and Kadamtala to Dasnagar was abandoned and replaced with a line from Howrah to Dasnagar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further Information== | ||
| + | See page '''[[Howrah Tramways (Light Railways)]]''' | ||
| + | <br>and page '''[[Martin's Light Railways]] ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Private Railways]] | [[Category:Private Railways]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Narrow Gauge (NG) Railways]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Tramways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:29, 2 August 2020
| Howrah-Amta Light Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Howrah to Amta | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| 2' 0" NG | 37 miles (1905) 42 miles (1943) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1898 | Line opened to traffic | |
| 1971 | Closed | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Howrah, Amta | |
| System agency | ||
| Worked by Martin's Light Railways | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Also known as the Howrah-Amta Tramway in some records
See also page Howrah Tramways (Light Railways)
The Howrah-Amta Light Railway (HALR) was a short 2ft/610mm narrow gauge(NG) railway which ran from Howrah westwards to Amta.
[1]
The HALR was one of several small narrow gauge concerns owned and worked by Martin's Light Railways, a management company based in Calcutta. [2]
History
On 12 June 1889 an agreement was signed between the District Board of Howrah and Messrs. Walsh, Lovett & Company on behalf of the Bengal District Road Tramways Company; this gave the Company the right to construct and work a tramway over a portion of roads [1]. This was subsequently renewed with Martin's Light Railways Co Ltd and sanctioned by Government notification in the Calcutta Gazette of 27 March 1895 [2]. On the 2 May 1895 the 'Howrah-Amta Light Railway Company’ was formed and worked by Martin's Light Railways (MLR).
The Howrah-Amta line was opened up to Domjur in 1897, and to Amta in 1898. An extension from Bargachhia (Bargechhe) junction to Autpur was opened in 1904, and a further extension to Champadanga in 1908, giving a total line length of 44 miles (70km) [1].
The Howrah-Amta Light and the Howrah-Sheakhalla Light Railways start from Telkal Ghat on the Hooghly river, and skirting the Howrah Maidan pass through the crowded Panchanantala road to Kadamtala station. Here they separate, the Howrah-Sliiakhala line running north-west along the Benares road to the border of the district, and thence to Shiakhala in Hooghly district. The Howrah-Amta line runs west, chiefly along the side of the Jagatballabhpur road, and then goes south-west to Amta [2].
A line from Autpur to Rajbalhat was sanctioned but never built [3]
The Amta and Sheakhala companies both prospered and by 1904 the shareholders were already getting dividends of 7 and 5 per cent respectively. By 1914 over 2,500,000 passengers were being carried annually on the two lines, and by 1928 the number was nearly 4,000,000. Working frequent trains through the streets of Howrah, each preceded by a runner with a bell to warn pedestrians, became a major headache and from September 26, 1939, after the Municipality had refused to renew the existing agreement, Kadamtala became the terminus and the line to Howrah Ghat was abandoned [3].
The lines continued to operate privately long after Independence in 1947, and finally converted to Broad Gauge and electrified from 1984 onwards [2].
HALR System
The following is the progress in opening[4]:-
- ‘Main Line’
- Telkul Ghat(Howrah) via Dumjur to Bargachia, 15 miles(24km), opened 1897, the first 2 miles(3.2km) to Kadamtala also worked by the ‘Howrah-Sheakhalla Light Railway’
- Bargachia via Maju to Amta, 12 miles(19km), opened 1898
- ‘Champadanga Branch’
- Bargachia to Jagatbalabpur, 1½ miles(4km), opened 1897
- Jagatbalabpu to Autpur, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1904
- Autpur to Champadanga, 7 miles(11km), opened 1908
Total line length 44 miles(71km)
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 [4]
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class III railway system.
Stations
Telkul Ghat, Howrah Maidan, Kadamtala, Dasnagar, Domjur, Bargachia, Maju, Amta
Jagatbullabpur, Jangipara, Autpur, Champadanga.
The section from Telkul Ghat via Howrah Maidan and Kadamtala to Dasnagar was abandoned and replaced with a line from Howrah to Dasnagar.
Further Information
See page Howrah Tramways (Light Railways)
and page Martin's Light Railways
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 243; Retrieved 31 Aug 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Wikipedia"Martin's Light Railways"; Retrieved 31 Aug 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 ”Two foot gauge at Howrah Maiden” by P J Bowcutt and H C Hughes. ‘Railway Magazine’ September 1965 Vol III No 773 pages 497-501
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 282 pdf 324; Retrieved 1 Aug 2020