Difference between revisions of "Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway"
(Major Revision based on 1937 History and separation of Broad and Metre Gauge) |
(‘Major Stations Infobox ‘ revised) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
|headquarters= [[Madras]] | |headquarters= [[Madras]] | ||
|workshop= [[Perambur ]]; [[Dharwar]]/[[Hubli]] <br>''See'' [[M&SMR Railway Workshops]] | |workshop= [[Perambur ]]; [[Dharwar]]/[[Hubli]] <br>''See'' [[M&SMR Railway Workshops]] | ||
| − | |stations= | + | |stations= '''[[Madras]] ''' |
| + | ''See also separate page'' [[Madras_Railways_%26_Stations#Madras_Stations| ''' Madras Stations''']] ''for details'' | ||
|system1date= | |system1date= | ||
|system1details= | |system1details= | ||
Latest revision as of 15:51, 14 March 2021
| Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Logo | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1908 | Formed from 2 existing systems | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1908 | Madras Railway(Broad Gauge) | |
| 1908 | Southern Mahratta Railway(Metre Gauge) | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Madras | |
| Workshops | Perambur ; Dharwar/Hubli See M&SMR Railway Workshops | |
| Major Stations | Madras
See also separate page Madras Stations for details | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1951 | Southern Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 1092 miles (1943) | |
| Metre gauge | 1712 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Rifles | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(M&SMR) was formed in 1908 mainly from the merger of [1]:-
- 'Madras Railway'(MR), broad gauge(BG) 1032 miles(1660km), see separate page for details'
- 'Southern Mahratta Railway'(SMR), metre gauge(MG) 1687 miles(2715km), see separate page for details'.
Contents
History
The former ‘Madras Guaranteed Railway Company’ contract expired on the 31 Dec 1907. The lines owned by that Company were purchased by the Secretary of State for India, and on 1 Jan 1908 the ‘Madras Railway’ (with the exception of the broad gauge ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Section’ which was made over to the ‘South Indian Railway’) and together with the metre gauge sections of the ‘South Indian Railway’ ‘Katpadi-Gudur’ and ‘Pakala-Dharmavaram’ Sections, was made over to the ‘South Mahratta Railway Company’ for working. The enlarged Company being styled the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Company[1]
In addition to the lines comprised in the system, the Company, worked the ‘Birur-Shimoga Section’, the ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Section’ and ‘Mysore-Bangalore Section’, all of which were made over to the Mysore Durbar on 1 Oct 1919 [2].
The GoI took over direct control of the M&SMR on 1 April 1944.
On 14 April 1951, the M&SMR, the South Indian Railway(SIR) and the Mysore State Railway(MSR) merged together to become Southern Railway, a zone of Indian Railways.
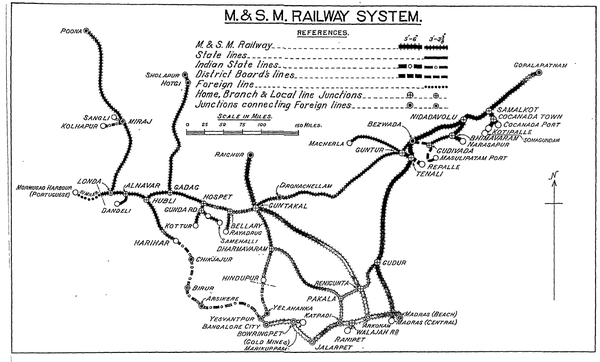
Madras and Southern Mahratta System Railway System
The ‘Madras and Southern Mahratta System Railway System’ can be defined as made up of the ‘M&SMR Broad Gauge Division ‘ and the M&SMR Metre Gauge Division ‘ .
The 1937 Report [2] gives the total line length of 3229 miles(5196km) as follows:-
M&SMR Broad Gauge Division
In 1937 [2] the total line length of the broad gauge(BG)
‘M&SMR System’ BG including all worked lines was 1518 miles(2442km):-
- ‘South-West Main Line’, 133 miles(214km), opened 1856-60 by MR from Madras to Jalarpe, the final 2 miles(km) into Madras Terminal was completed in 1873
- ‘Rayapuram Branch’, 2.1 miles(3.4km) , opened 1856 by MR from Veyasapaudy to Rayapuram, extended to Basin Bridge by 1907 and from Korukkupettai to Veyasapaudy by M&SMR in 1931 giving a total of 5 miles(8km)
- ‘Ranipet Branch’ , 4.2 miles(6.8km), opened 1899 by MR from Walajah Road (Arcot ) to Ranipet
- ‘Bangalore Branch’, 87 miles(140km), opened 1864 by MR from Jalarpet Junction to Bangalore Cantonment, final 3 miles to Bangalore City in 1882
- ‘North-West Main Line’, 308 miles(496km), opened 1861-71 by MR from Arkonam to Raichur
- ‘North-East Main Line’, 480 miles(772km), opened in a series of dates from 1888 through to 1907 by MR from Basin Bridge (Madras) via Nellore and Bezwada to the Junction near Waltair. Also named the ‘[Bezwada-Madras Railway]]’
- ‘Samalkot Junction- Cocanada Port Branch’, 10 miles(16km), opened1893 by MR from Samalkot Junction to Cocanada Port
- ‘Guntur-Tenali Branch’, 16 miles(26km), opened 1916 by M&MSR from Guntur to Tenali
- ‘Nidadavolu-Narasapur Branch’, 47 miles(76km), opened 1929 by M&MSR from Nidadavolu to Narasapur
- ‘Cocanada-Kotipalle Branch’, 27 miles(43km), opened 1929 by M&MSR from Cocanada to Kotipalle
- ‘Kolar Gold Fields Railway’, 10 miles(16km), opened 1894, constructed by Mysore Durbar joining the Kolar Gold Fields to Bowringpet, where it connected with the ‘South-West Main Line’. Worked by MR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System
- ‘Tenali-Repalle Railway’, 21 miles(34km), opened 2016, constructed by M&MSR on behalf of Guntur District Board. Worked as part of the M&SMR System . Also described as the ‘Guntur-Repalle Railway’
M&SMR Metre Gauge Division
In 1937 [2] the total line length of the metre gauge(MG)-
‘M&SMR System’ MG including all worked lines was 2087 miles(3359km):-
- ‘Main Line’, 514 miles(827km), opened 1884-90 by ‘SMR’ from Frontier ,where it connected to the ‘West of India Portuguese Railway’, to Bezweda. The ‘’Cumbum-Tadepalli Section’, 122 miles(196km) first opened 1881 as a broad gauge(BG) line by the ‘MR’ , handed over to the ‘SMR’ and converted to metre gauge(MG) in 1887
- ‘Harihar Branch’, 81 miles(130km), opened 1886 by SMR from Hubli to Harihar
- ‘ Bijapur Branch’, 173 miles(278km), opened 1884 by SMR from Gadag to Hotgi, extended 1927 by M&SMR to Sholapur giving total 182 miles(293km)
- ‘Poona Branch’, 227 miles(365km), opened 1886-90 by SMR from Londra to Poona
- ‘Guntakal-Mysore Frontier Branch, 120 miles(193km), opened 1893-1902 by SMR from Guntakal via Hindapur to Mysore Frontier where it connected to the ‘Mysore State Railway’ worked by
- ‘Bellary-Rayadrug Branch’, 33 miles(53km), opened 1905 by SMR from Bellary to Rayadrug
- ‘Hospet-Kottur Branch’, 56 miles(90km), opened 1905-10 by SMR completed by M&SMR from Hospet via Kottur to Kanivihalli, extended 1928 by M&SMR to Swamihalli giving a total of 68 miles(109km)
- ‘Katpadi-Dharmavaram Branch’, 180 miles(290km), opened 1891-92 by SMR from Katpadi to Dharmavaram
- ‘Pakala-Gudar Branch’, 84 miles(135km), opened 1887-91 by SMR from Pakala to Gudar
- ‘Gudivada-Bhimavaram Branch’, 41 miles(68km), opened 1928 by M&SMR from Gudivada to Bhimavaram
- ‘Guntur-Macheria Branch, 80 miles(129km), opened 1930 by M&SMR from Guntur to Macheria
- ‘Alnavar-Dandeli Railway’, 19 miles(31km), opened 1919 by M&SMR on behalf of Government Forest Department, from Alnavar to Dandeli [3]
- ‘Bangalore Harihar Railway‘, 210 miles(338km), opened 1884-89 by SMR from Bangalore to Harihar. Originally part of the ‘M&SMR Mysore Section’ until 1919 when the Mysore to Bangalore section was ‘made over to the Mysore Durbar and named the ‘Mysore-Bangalore Railway’ [4]
- ‘Bezwada-Masulipatam Railway’, 52 miles(84km), opened 1908-09 from Bezwada to Masulipatam . Owned by Kistna District Board, a feeder line; worked as part of the M&SMR System[5]
- ‘Hindupur-Yesvantpur Railway’, 51 miles(82km), opened 1893 from Yesvantpur to Mysore Frontier. Also known as ‘Hindupur (Yesvantpur-Mysore Frontier) Railway’ and originally named the ‘Bangalore Hindupur Railway’ . Worked by SMR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System [6] and from 1938 reverte’d to the ‘Mysore State Railway’
- ‘Kolhapur State Railway’, 29 miles(47km), opened 1891 from Kolhapur to Miraj . Worked by SMR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System [7]
- ‘Sangli State Railway’, 5 miles(8km), opened 1907 from Miraj Junction to Sangli. Worked by SMR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System [8]
- ‘West of India Portuguese Railway’, 51 miles(82km) opened 1887-88 from Mormugao Harbour to the Portugese Frontier, where it connected to the ‘M&SMR Main Line’(see above) . Worked by SMR from 1902 then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System [9]
Railways previously worked by ‘Madras Railway’
- ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline’ metre gauge(MG), opened in 1860-62 by the ‘Madras Railway’ and extended 1901-04 as the ‘Calicut-Azikhal Railway’and reached Mangalore in 1907 as the ‘Azikhal-Mangalore Railway’. The total length of the line was 417 miles(617km) and with the following two branches 446 miles(717km) , all transferred to ‘South Indian Railway’ (SIR) on formation of the M&SMR in 1907:-
- ‘Palghat Branch Line’, opened 1868 from Palakkad Junction(Olavakode)
- ‘Mettupalaiyam Branch Line’, opened 1873 from Podanur
- ‘Morappur-Dharmapuri-Hosur Railway’, 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG), opened 1906 as a famine protection line , worked by MR then made over to the ‘South Indian Railway’ (SIR) on formation of the M&SMR in 1907
Railways worked by M&SMR then later reallocated
- ‘Mysore State Railway’ metre gauge(MG) , leased and worked by SMR; from 1908 by M&SMR. Then reverted to ‘Mysore State Railway’ in 1919 comprising:-
- ‘Mysore-Bangalore Railway’, constructed by Mysore State, opened 1881, leased and worked by SMR,; from 1908 by M&SMR until 1919
- ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Railway’, opened 1891, leased and worked by SMR, from 1908 by M&SMR until 1919
- ‘Birur-Shimoga Railway’, opened 1899. Worked by M&SMR until 1919
- ‘Hindupur-Yesvantpur Railway’, opened 1893,originally named the ‘Bangalore Hindupur Railway’ . Worked by SMR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System [10]. Ffrom 1938 reverted to ‘Mysore State Railway’
- ‘Bangalore Harihar Railway‘, opened 1884-89. Worked by SMR then from 1908 as part of the M&SMR System . From 1938 reverted to ‘Mysore State Railway’
M&SMR Collieries and Coal Supplies
See separate pages
- ‘Talcher Colliery’ was a M&SMR Colliery'
- ‘Jarangdih Colliery was a 'Joint M&SMR and Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway(BB&CIR) Colliery'
Railway Workshops
The former MR Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Workshops at Perambur became the M&SMR main workshops. In Madras there was a separate repair-shop for the locomotives and another for maintaining the carriages and wagons.[11]
For further information M&SMR Railway Workshops see seperate page
M&SMR Riles Regiment
See seperate page Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Rifles
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [12] gives many references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/33 “Records of the India Office relating to the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Company; 1882-1930"
- L/F/7/1513-1526 “Collection 266: Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway; date unspecified"
Personnel Records
Unfortunately there are no Staff agreements held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
The last Europeans were recruited in 1926. Percy Morris who worked on the M&SMR 1925-1955[13]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 81 - 97; Retrieved 9 Sept 2020
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 120 pdf 153; Retrieved 10 Sept 2020
- ↑ ibid page 131 pdf 166
- ↑ ibid page 132 pdf 167
- ↑ ibid page 134 pdf 169
- ↑ ibid page 135 pdf 170
- ↑ ibid page 136 pdf 171
- ↑ ibid page 138 pdf 173
- ↑ ibid page 139 pdf 174
- ↑ ibid page 135 pdf 170
- ↑ "Grandpa’s Story – Part V". The story (in 15 Parts) of Percy Morris who worked on the M&SMR 1925-1955
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved Jan 2016
- ↑ "Grandpa’s Story – Part IV". The story of Percy Morris.