Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway: Difference between revisions
Princley State link added |
Revised ‘Developments after 1918’ sub heading and ‘Further Informatio’ added |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Gaekwar’s Mehsana Railway''' was owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Baroda State]]. The metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railway first opened in 1887 with the line from [[Mehsana]] to [[Vadnagar]] a distance of 21 miles (34km). | {{Line Railways Infobox | ||
|image= | |||
|caption= | |||
|route= [[Viramgam]]-[[Mehsana]]-Taranga Hill<br>Kakosi extension<br>Harij branch<br>Bechraji extension | |||
|gauge1= Metre gauge | |||
|gauge1details= 162 miles (1918)<br> 193 miles (1921) | |||
|gauge2= | |||
|gauge2details= | |||
|gauge3= | |||
|gauge3details= | |||
|gauge4= | |||
|gauge4details= | |||
|timeline1date= 1887 Mar | |||
|timeline1details= [[Mehsana]]-[[Vadnagar]] section opened, extended to Kherain,1888; [[Viramgam]],1891 and Taranga Hill,1909 | |||
|timeline2date= 1891 Jul | |||
|timeline2details= [[Mehsana]]-Patan section opened; extended to Wagrod,1915 and Kakosi,1916 | |||
|timeline3date= 1908 Oct | |||
|timeline3details= Harji branch and Bechraji extension opened | |||
|timeline4date= after 1918 | |||
|timeline4details= further extensions | |||
|timeline5details= | |||
|presidency= [[Bombay (Presidency)|Bombay]] | |||
|stations= [[Viramgam]], [[Mehsana]], [[Vadnagar]] etc | |||
|system1date= 1897 | |||
|system1details= Worked by [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]] | |||
|system2date= 1921 | |||
|system2details= Worked by [[Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway]] | |||
|system3date= | |||
|system3details= | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway.png |thumb|Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway]] | |||
The '''Gaekwar’s Mehsana Railway''' (GMR) was owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Baroda State]]. The metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railway first opened in 1887 with the line from [[Mehsana]] to [[Vadnagar]] a distance of 21 miles (34km). | |||
The network was progressively expanded from 1888 through to 1921 to a total of 193 miles(309km). | The network was progressively expanded from 1888 through to 1921 to a total of 193 miles(309km). | ||
<ref>[https:// | <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n35/mode/2up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 27-28]; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019</ref> <ref>"Indian railways new chronology" by Keith Scholey</ref> | ||
<ref>"Indian railways new chronology" by Keith Scholey</ref> | |||
In 1904 the Vadnagar-Vijapur line was surveyed by the [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]](BB&CIR) as a MG line but did not proceed. Instead the Baroda Durbar resurveyed the route on a different alignment entirely within Baroda territory. The 1906 Report states that “the line from either Visnager or Vadnagar to Vijapur was to be constructed at the expense of the the Gaekwar of Baroda” <ref name=Hist1906>[https://archive.org/stream/RailwayProjects/Railway%20projects#page/n0/mode/2up Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906, page 18]; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019</ref> In the event neither route was selected, instead the ‘[[Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway]]’ was constructed. ''See below, marked 8 on 1931 map'' | |||
Up to 1921 the network was worked by [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]](BB&CIR). | Up to 1921 the network was worked by [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]](BB&CIR). | ||
From 1921 the network was worked by [[Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway]](GBSR) and in | From 1921 the network was worked by [[Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway]](GBSR) | ||
==GMR Network== | |||
'''Development as at 1918''' <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n64/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 55 (pdf64) ]; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019</ref> | |||
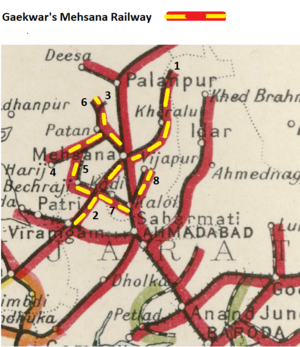
* ‘Mehsana-Taranga Hill Section’, from [[Mehsana]] to [[Vadnagar]] 21 miles opened 1887; extended to Kheralu 7 miles 1888; to Taranga Hill 8 miles 1909. Total 36 miles(58km). ''Marked 1 on map'' | |||
* ‘Mehsana-Viramgam Section’, from [[Mehsana]] to [[Viramgam]] 40 miles(64km) opened 1891. ''Marked 2 on map'' | |||
* ‘Mehsana-Kakoshi Section’ from [[Mehsana]] to Patan 25 miles(40km), opened 1891; extended to Vagrod 15 miles 1915; to Kakoshi 10 miles 1916. Total 50miles(80km). ''Marked 3 on map'' | |||
* ‘Harij Branch’ from Manund Road to Harij 21 miles(34km) opened 1908. ''Marked 4 on map'' | |||
* ‘Bechargi Extension’ from Chanama to Bechraji 17 miles(27km) opened 1908. ''Marked 5 on map'' | |||
* ‘Vagrod-Khareda Branch’ from Vagrod to Khareda 12 miles(19km), sanctioned 1913. ''Marked 6 on 1931 map, but opening date not found and not seen on modern maps'' | |||
* ‘Khalipur to Khakhal Proposal’ 7 miles(11km), sanctioned 1913. ''Line apparently not constructed . '' | |||
''''Developments after 1918''' <ref>"Indian railways new chronology" by Keith Scholey</ref> | |||
<br>The following MG railway, also owned by the Baroda Durbar, was connected to the GMR by 1921, and worked by the [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]](BB&CIR). <br>This line together with the GMR was transferred to the newly formed ‘[[Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway]]’(GBSR) in 1921:- | |||
* ‘[[Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway]]’, 41 miles(65km) MG; owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]] [[Baroda State]]; opened 1902-3 from [[Vijapur]] to [[Kadi ]] and extended by a further 5 miles(8km) in 1912 to‘ Bhoyani Road- and extended a further 21 miles(34km) to reach [[Bechraji ]] before 1921 where it connected to the GMR. ''Marked 7 and 8 on map.'' [[Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway|''- see separate page'']] | |||
=Further Information== | |||
See '''[[Bombay, Baroda & Central India Railway Network - Lines owned and worked|BB&CIR Network - Lines owned and worked]]''' for period up to 1921 | |||
<br>and '''[[Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway# GBSR Metre Gauge System]] from 1921 onwards | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:19, 15 June 2019
| Gaekwar's Mehsana Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Viramgam-Mehsana-Taranga Hill Kakosi extension Harij branch Bechraji extension | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 162 miles (1918) 193 miles (1921) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1887 Mar | Mehsana-Vadnagar section opened, extended to Kherain,1888; Viramgam,1891 and Taranga Hill,1909 | |
| 1891 Jul | Mehsana-Patan section opened; extended to Wagrod,1915 and Kakosi,1916 | |
| 1908 Oct | Harji branch and Bechraji extension opened | |
| after 1918 | further extensions | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Viramgam, Mehsana, Vadnagar etc | |
| System agency | ||
| 1897 | Worked by Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway | |
| 1921 | Worked by Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Gaekwar’s Mehsana Railway (GMR) was owned by the Princely Baroda State. The metre gauge(MG) railway first opened in 1887 with the line from Mehsana to Vadnagar a distance of 21 miles (34km).
The network was progressively expanded from 1888 through to 1921 to a total of 193 miles(309km). [1] [2]
In 1904 the Vadnagar-Vijapur line was surveyed by the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) as a MG line but did not proceed. Instead the Baroda Durbar resurveyed the route on a different alignment entirely within Baroda territory. The 1906 Report states that “the line from either Visnager or Vadnagar to Vijapur was to be constructed at the expense of the the Gaekwar of Baroda” [3] In the event neither route was selected, instead the ‘Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway’ was constructed. See below, marked 8 on 1931 map
Up to 1921 the network was worked by Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR).
From 1921 the network was worked by Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway(GBSR)
GMR Network
Development as at 1918 [4]
- ‘Mehsana-Taranga Hill Section’, from Mehsana to Vadnagar 21 miles opened 1887; extended to Kheralu 7 miles 1888; to Taranga Hill 8 miles 1909. Total 36 miles(58km). Marked 1 on map
- ‘Mehsana-Viramgam Section’, from Mehsana to Viramgam 40 miles(64km) opened 1891. Marked 2 on map
- ‘Mehsana-Kakoshi Section’ from Mehsana to Patan 25 miles(40km), opened 1891; extended to Vagrod 15 miles 1915; to Kakoshi 10 miles 1916. Total 50miles(80km). Marked 3 on map
- ‘Harij Branch’ from Manund Road to Harij 21 miles(34km) opened 1908. Marked 4 on map
- ‘Bechargi Extension’ from Chanama to Bechraji 17 miles(27km) opened 1908. Marked 5 on map
- ‘Vagrod-Khareda Branch’ from Vagrod to Khareda 12 miles(19km), sanctioned 1913. Marked 6 on 1931 map, but opening date not found and not seen on modern maps
- ‘Khalipur to Khakhal Proposal’ 7 miles(11km), sanctioned 1913. Line apparently not constructed .
'Developments after 1918 [5]
The following MG railway, also owned by the Baroda Durbar, was connected to the GMR by 1921, and worked by the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR).
This line together with the GMR was transferred to the newly formed ‘Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway’(GBSR) in 1921:-
- ‘Vijapur-Kalol-Kadi Railway’, 41 miles(65km) MG; owned by the Princely Baroda State; opened 1902-3 from Vijapur to Kadi and extended by a further 5 miles(8km) in 1912 to‘ Bhoyani Road- and extended a further 21 miles(34km) to reach Bechraji before 1921 where it connected to the GMR. Marked 7 and 8 on map. - see separate page
Further Information=
See BB&CIR Network - Lines owned and worked for period up to 1921
and Gaekwar's Baroda State Railway# GBSR Metre Gauge System from 1921 onwards
References
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 27-28; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019
- ↑ "Indian railways new chronology" by Keith Scholey
- ↑ Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906, page 18; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 55 (pdf64) ; Retrieved 8 Jun 2019
- ↑ "Indian railways new chronology" by Keith Scholey