Cutch State Railway: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
1937 Admin info, Statistics and Classification , ‘Later Development, Map’added |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The | [[File:Cutch State Railway.png|thumb| Cutch State Railway ]] | ||
The '''Cutch State Railway''' was a isolated 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) line built, financed and operated by the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Cutch State]]. The construction was sanctioned in 1903 and [[Tuna]] was connected to [[Anjar]] in the year 1905<ref name=name>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n231/mode/1up " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 223]; Retrieved 22 Feb 2016</ref> | |||
The railway, upon independence of India | The first section ran from Tuna, a port on the Gulf of Cutch, northwards to Anjar and was constructed at the cost of HH the Maharaja Maha Rao Sahib of Cutch . It was continued north-westwards to the state capital Bhuj in 1908, making a | ||
total of 36½ miles(59km). In 1910 99,075 passengers were carried together with 4457 tons of raw cotton, 3768 tons of grain and 2403 tons of sugar <ref name=Hughes>“Indian Narrow Gauge Locomotives 1863-1940” by Hugh Hughes, published by ‘The Continental Railway Circle’ Paragraph 12 Page 33</ref>. | |||
The ‘Tuna to Anjar Section’, 12 miles(19km) opened in 1905 and extended 1908 by the ’Anjar to Bhuj Section’ , 25 Miles(40km) | |||
<ref name=Hist1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 275 pdf 318]; Retrieved 30 Jul 2020</ref>. | |||
The eastern ‘Kandla Branch’ from Anjar via Warsamedi to Kandla, 15 miles(25km) fully opened in 1929, although the ‘Kandla to Warsamedi Section’ had opened in late 1927. The ‘Bhachau Branch’ from Warsamedi to Bhachau, 20 miles(32km) opened 1931<ref name=Hist1937/>. | |||
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the total system of 72 miles(116km) in 1937 and the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 <ref name=Hist1937/> | |||
== Classification == | |||
[[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class III railway system. | |||
==Later Development== | |||
The railway, upon independence of India in 1947 worked as a separate system till 1951 when it was merged into the Western Railway Division of Indian Railways. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Indian States Railways]] | [[Category:Indian States Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Narrow Gauge (NG) Railways]] | |||
Latest revision as of 09:49, 1 August 2020
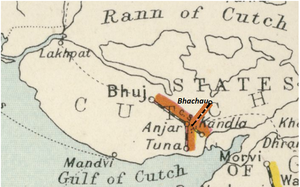
The Cutch State Railway was a isolated 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) line built, financed and operated by the Princely Cutch State. The construction was sanctioned in 1903 and Tuna was connected to Anjar in the year 1905[1]
The first section ran from Tuna, a port on the Gulf of Cutch, northwards to Anjar and was constructed at the cost of HH the Maharaja Maha Rao Sahib of Cutch . It was continued north-westwards to the state capital Bhuj in 1908, making a total of 36½ miles(59km). In 1910 99,075 passengers were carried together with 4457 tons of raw cotton, 3768 tons of grain and 2403 tons of sugar [2].
The ‘Tuna to Anjar Section’, 12 miles(19km) opened in 1905 and extended 1908 by the ’Anjar to Bhuj Section’ , 25 Miles(40km) [3].
The eastern ‘Kandla Branch’ from Anjar via Warsamedi to Kandla, 15 miles(25km) fully opened in 1929, although the ‘Kandla to Warsamedi Section’ had opened in late 1927. The ‘Bhachau Branch’ from Warsamedi to Bhachau, 20 miles(32km) opened 1931[3].
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the total system of 72 miles(116km) in 1937 and the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 [3]
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class III railway system.
Later Development
The railway, upon independence of India in 1947 worked as a separate system till 1951 when it was merged into the Western Railway Division of Indian Railways.
References
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 223; Retrieved 22 Feb 2016
- ↑ “Indian Narrow Gauge Locomotives 1863-1940” by Hugh Hughes, published by ‘The Continental Railway Circle’ Paragraph 12 Page 33
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 275 pdf 318; Retrieved 30 Jul 2020