| The Families In British India Society (FIBIS) is a self-help organisation devoted to members researching their British India family history and the background against which their ancestors led their lives in India under British rule. Let FIBIS help you break down those brick walls in your research |
Duar War: Difference between revisions
Symorsebrown (talk | contribs) m Temp save |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
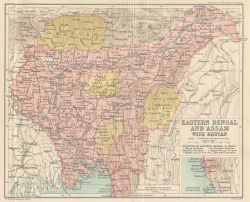
{{War|name=Duar War|dates=1864-65 |image=Assam.jpg |location=[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Bengal West Bengal] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Assam Assam]|combatant1=British |combatant2=[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhutan Bhutan] |result=British victory |medal=[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/India_General_Service_Medal_(1854) India General Service Medal 1854]<br>Clasp: Bhootan |category=[[:Category:Duar War|Duar War]] |link1=}} | |||
{{Battlemap|war=Duar War|link=http://maps.google.co.uk/maps/ms?t=p&ie=UTF8&hl=en&msa=0&msid=101241150585833319689.000478e60a5f91d598b68&ll=27.362011,90.230713&spn=3.912073,4.367065&z=8}} | |||
The '''Duar War''' was also known as the '''Bhutan War.''' | |||
==Spelling variants== | |||
*Duar, Doar, Dooar, Dhooar | |||
*Bhutan, Bhotan, Bhootan, Bootan | |||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
Following the [[1st Burma War]], [[Assam]] was ceded to Britain and the [[East India Company]] came into conflict with [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhutan Bhutan] over control of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dooars Duars] - the plains areas between the Brahmaputra and the foothills of Bhutan. A British mission under [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ashley_Eden Ashley Eden] was sent to Bhutan to try to establish political relations but was humiliated and ejected after being forced to sign a treaty ceding the Duars. | |||
Britain declared war on 12 November 1864 using four columns to secure the forts and passes in the foothills of southern Bhutan. After initial successes the Bhutanese regained some of the strongholds and it was seen that a stronger response would be required. Brigadier General Frazer Tytler took over command from General Dunsford and [[Henry Tombs|Major General Sir Henry Tombs]] took over from General Mulcaster. Following a series of victories and the threat of a major invasion of Bhutan, the war ended with the Treaty of Sinchula on 11 November 1865. Bhutan ceded territories in the Assam Duars and Bengal Duars, as well as the 83 square kilometre territory of Dewangiri, in return for an annual subsidy of 50,000 rupees. | |||
== British Forces == | |||
'''Duar Field Force''' commanded by Brigadier-General Dunsford | |||
'''Dewangiri Column''' | |||
:Three Mountain Guns of Eurasian Artillery Company | |||
:One Squadron [[5th Bengal Cavalry]] | |||
:[[43rd Gurkha Rifles|3rd Assam Light Infantry]] | |||
:One Coy [[Sebundy Sappers and Miners|Sibundy Sappers]] | |||
:One Coy [[Bengal Sappers and Miners|Bengal Sappers]] | |||
:''In support at Gauhati'' | |||
:Three Coys [[12th (Khelat-i-Ghilzie) Bengal Infantry|12th Native Infantry]] | |||
:Assam Local Artillery | |||
'''Sidli Column''' | |||
:Three Mountain Guns of Eurasian Artillery Company | |||
:One Squadron [[5th Bengal Cavalry]] | |||
:Two Squadrons [[14th Regiment of Bengal Lancers|14th Bengal Cavalry]] | |||
:One Coy [[Sebundy Sappers and Miners|Sibundy Sappers]] | |||
:Half Coy [[Bengal Sappers and Miners]] | |||
:One wing [[44th Gurkha Rifles|44th Assam Light Infantry]] | |||
:''In support at Goalpara'' | |||
:Two Coys [[12th (Khelat-i-Ghilzie) Bengal Infantry|12th Native Infantry]] | |||
'''Buxa Column''' | |||
:Half Armstrong Mountain Train Battery | |||
:Two 8-inch Mortars | |||
:[[2nd Gurkha Rifles|2nd Gurkhas]] | |||
:[[11th Regiment of Rajput Infantry|11th Native Infantry]] | |||
:One Squadron [[14th Regiment of Bengal Lancers|14th Bengal Cavalry]] | |||
'''Daling Column''' | |||
:Two Armstrong Mountain Guns | |||
:Two 8-inch Mortars | |||
:One Coy [[Sebundy Sappers and Miners|Sibundy Sappers]] | |||
:One Wing [[11th Regiment of Rajput Infantry|11th Native Infantry]] | |||
:Two Squadrons [[5th Bengal Cavalry]] | |||
:''In support at Jalpaiguri'' | |||
:Seven Coys [[80th Regiment of Foot|HM 80th Foot]] | |||
'''Bhutan Field Force''' commanded by Brigadier-General Mulcaster<br> | |||
:Three Coys [[48th Regiment of Foot|HM 48th Foot]] | |||
:Three Coys [[80th Regiment of Foot|HM 80th Foot]] | |||
:Two Coys [[17th (Loyal Purbeah) Regiment of Bengal Infantry|17th Native Infantr]]y | |||
== External links == | |||
*[http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=OIzreCGlHxIC&pg=PT73&dq=Henry+Tombs&hl=en&ei=aZqdTt1-xZeFB8u-2IoJ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=6&ved=0CEMQ6AEwBQ#v=onepage&q=Henry%20Tombs&f=false Bhutanese-British War of 1865] Google Books<br /> | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bhutan_War Bhutan War] Wikipedia<br> | |||
*[http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/bitstream/10603/20103/6/06_chapter%203.pdf "Chapter III Indo-Bhutanese Hostilities and Peace 1864-1866"] from [http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in/handle/10603/20103 ''India and Bhutan 1858-1910''] by Kapileshwar Labh 1969 thesis. Jawaharlal Nehru University. shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in | |||
== Historical books online == | |||
== | *[http://www.archive.org/stream/frontieroverseas04indi#page/130/mode/2up Expedition 1864] page 130, ''Frontier and Overseas Expeditions from India, Volume IV'' 1907 Archive.org | ||
[ | *[http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=uSUPAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover ''Political Missions to Bootan''] comprising the reports of The Hon'ble Ashley Eden 1864; Capt. R B Pemberton 1837, 1838 with Dr W Griffiths's Journal; and the account of Baboo Kishen Kant Bose. 1865 Google Books | ||
[ | *[https://books.google.com.au/books?id=AJdeAAAAcAAJ&pg=PR1 ''Papers Relating to Bootan''] Ordered, by the House of Commons, to be printed 15 February 1865. Google Books | ||
*[http://www.archive.org/stream/bhotanandstoryd00unkngoog ''Bhotan and the Story of the Dooar War''] by Surgeon Rennie, MD, 1866. He served with the [[80th Regiment of Foot|80th Regiment]] Archive.org [https://archive.org/details/b29352150 Additional Archive.org file], with different coloured images. | |||
*[https://archive.org/stream/memoriesofsevenc00thor#page/132/mode/2up "Chapter X"] page 132 ''Memories of Seven Campaigns: a record of thirty-five years' service in the Indian Medical Department in India, China, Egypt, and the Sudan'' by James Howard Thornton, Deputy Surgeon General, Indian Medical Service, late Principal Medical Officer Punjab Frontier Force. 1895 Archive.org. The author was in the Bengal Medical Service 1856-1891. | |||
*[https://archive.org/stream/cu31924028000101#page/n267/mode/2up "The War in Bootan"] page 230, ''Recollections of a Military Life'' by General Sir John Adye , RA 1895 Archive.org. | |||
*[https://books.google.com.au/books?id=KIdNAAAAcAAJ&pg=PA518 "Six Weeks in Bhotan"] page 518 ''Colburn's United Service Magazine and Naval and Military Journal'', 1871, Part III Google Books. | |||
*[https://books.google.com.au/books?id=ifjoarx7ImgC&pg=PA409 "The War in Bhootan: The Bala Pass"] pages 409-410 ''The Illustrated London News Vol XLVI Jan. to June 1865'' Google Books | |||
:[https://books.google.com.au/books?id=ifjoarx7ImgC&pg=PA440 "Sketches of the War in Bhootan"] pages 440-441, same volume, quoting Captain Warren, RA. | |||
[[Category:Wars and Campaigns|Duar War]] | [[Category:Wars and Campaigns|Duar War]] | ||
[[Category:Duar War| Duar War]] | [[Category:Duar War| Duar War]] | ||
[[Category:Campaigns with FIBIS Battle Maps|Duar War]] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:38, 1 June 2019
| Duar War | |
|---|---|
| 1864-65 | |
| Chronological list of Wars and Campaigns | |
| |
| Location: West Bengal and Assam | |
| Combatants: | |
| British | Bhutan |
| Result: British victory | |
| Medals: India General Service Medal 1854 Clasp: Bhootan | |
| Links: | |
| Category: Duar War | |

|
See our interactive map of Duar War locations and routes on Google Maps | |
|---|---|---|
The Duar War was also known as the Bhutan War.
Spelling variants
- Duar, Doar, Dooar, Dhooar
- Bhutan, Bhotan, Bhootan, Bootan
Summary
Following the 1st Burma War, Assam was ceded to Britain and the East India Company came into conflict with Bhutan over control of the Duars - the plains areas between the Brahmaputra and the foothills of Bhutan. A British mission under Ashley Eden was sent to Bhutan to try to establish political relations but was humiliated and ejected after being forced to sign a treaty ceding the Duars.
Britain declared war on 12 November 1864 using four columns to secure the forts and passes in the foothills of southern Bhutan. After initial successes the Bhutanese regained some of the strongholds and it was seen that a stronger response would be required. Brigadier General Frazer Tytler took over command from General Dunsford and Major General Sir Henry Tombs took over from General Mulcaster. Following a series of victories and the threat of a major invasion of Bhutan, the war ended with the Treaty of Sinchula on 11 November 1865. Bhutan ceded territories in the Assam Duars and Bengal Duars, as well as the 83 square kilometre territory of Dewangiri, in return for an annual subsidy of 50,000 rupees.
British Forces
Duar Field Force commanded by Brigadier-General Dunsford
Dewangiri Column
- Three Mountain Guns of Eurasian Artillery Company
- One Squadron 5th Bengal Cavalry
- 3rd Assam Light Infantry
- One Coy Sibundy Sappers
- One Coy Bengal Sappers
- In support at Gauhati
- Three Coys 12th Native Infantry
- Assam Local Artillery
Sidli Column
- Three Mountain Guns of Eurasian Artillery Company
- One Squadron 5th Bengal Cavalry
- Two Squadrons 14th Bengal Cavalry
- One Coy Sibundy Sappers
- Half Coy Bengal Sappers and Miners
- One wing 44th Assam Light Infantry
- In support at Goalpara
- Two Coys 12th Native Infantry
Buxa Column
- Half Armstrong Mountain Train Battery
- Two 8-inch Mortars
- 2nd Gurkhas
- 11th Native Infantry
- One Squadron 14th Bengal Cavalry
Daling Column
- Two Armstrong Mountain Guns
- Two 8-inch Mortars
- One Coy Sibundy Sappers
- One Wing 11th Native Infantry
- Two Squadrons 5th Bengal Cavalry
- In support at Jalpaiguri
- Seven Coys HM 80th Foot
Bhutan Field Force commanded by Brigadier-General Mulcaster
- Three Coys HM 48th Foot
- Three Coys HM 80th Foot
- Two Coys 17th Native Infantry
External links
- Bhutanese-British War of 1865 Google Books
- Bhutan War Wikipedia
- "Chapter III Indo-Bhutanese Hostilities and Peace 1864-1866" from India and Bhutan 1858-1910 by Kapileshwar Labh 1969 thesis. Jawaharlal Nehru University. shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in
Historical books online
- Expedition 1864 page 130, Frontier and Overseas Expeditions from India, Volume IV 1907 Archive.org
- Political Missions to Bootan comprising the reports of The Hon'ble Ashley Eden 1864; Capt. R B Pemberton 1837, 1838 with Dr W Griffiths's Journal; and the account of Baboo Kishen Kant Bose. 1865 Google Books
- Papers Relating to Bootan Ordered, by the House of Commons, to be printed 15 February 1865. Google Books
- Bhotan and the Story of the Dooar War by Surgeon Rennie, MD, 1866. He served with the 80th Regiment Archive.org Additional Archive.org file, with different coloured images.
- "Chapter X" page 132 Memories of Seven Campaigns: a record of thirty-five years' service in the Indian Medical Department in India, China, Egypt, and the Sudan by James Howard Thornton, Deputy Surgeon General, Indian Medical Service, late Principal Medical Officer Punjab Frontier Force. 1895 Archive.org. The author was in the Bengal Medical Service 1856-1891.
- "The War in Bootan" page 230, Recollections of a Military Life by General Sir John Adye , RA 1895 Archive.org.
- "Six Weeks in Bhotan" page 518 Colburn's United Service Magazine and Naval and Military Journal, 1871, Part III Google Books.
- "The War in Bhootan: The Bala Pass" pages 409-410 The Illustrated London News Vol XLVI Jan. to June 1865 Google Books
- "Sketches of the War in Bhootan" pages 440-441, same volume, quoting Captain Warren, RA.