Barsi Light Railway
| Barsi Light Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1897 | Line opened to traffic | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Kurduvadi | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | Barsi Road, Barsi, Pandharpur, Tadwala | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1954 | purchased by Indian Railways | |
| System mileage | ||
| 2' 6" NG | 22 miles (1897, 1905) | |
| 202 miles (1927) | ||
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
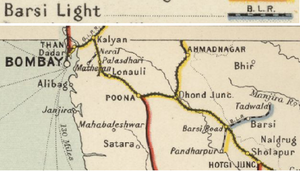
Barsi Light Railway (BLR)
The Barsi Light Railway Company owned and worked the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) railway that initially connected Barsi to the main Bombay-Madras trunk line of the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (GIPR) at Barsi Road, a distance of 22 miles(35km). [1]
Conceived by the ex-GIPR engineer, Everard Richard Calthrop, the Barsi Light Railway revolutionised the approach to narrow gauge feeder lines in India, and was immensely successful. By 1927, the line had been extended significantly over 202 route miles(323km).
The line remained in private ownership until 1954 when it was purchased by Indian Railways.
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [2] gives 33 references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/3 "Records of the Barsi Light Railway Company; 1895-1941”
- L/AG/46/22 “Records of the India Office relating to the Barsi Light Railway Company; 1895-1921”
- L/F/7/290-296 “Collection 30: Barsi Light Railway; 1926-1937”