Bikaner State Railway: Difference between revisions
'1924 onwards' internal links added |
Date change 1930-31 and ref change; 'Classification' and 'Later Development' headings added |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{System_Railways_Infobox | {{System_Railways_Infobox | ||
|image= | |image= Bikaner State Railway Logo b.jpg | ||
|caption= | |caption= Bikaner State Railway Logo | ||
|timeline1date= 1924 | |timeline1date= 1924 | ||
|timeline1details= System formed | |timeline1details= System formed | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
For operational purposes the JBR was divided into two sections:- the 'Bikaner Section' and the 'Jodhpur Section' | For operational purposes the JBR was divided into two sections:- the 'Bikaner Section' and the 'Jodhpur Section' | ||
'''Bikaner Section of the JBR''' - 1918 grand total, | [[File: Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway Map 1909.png|right|400px|Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway Map 1909]] | ||
'''Bikaner Section of the JBR''' - 1918 grand total, 498 miles(1013km) open line <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n195/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 187 (pdf195)]]; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016</ref> as follows:- | |||
* | * ‘Main Line’, MG, 249 miles(401km) | ||
**Bhagu(Marwar Frontier)-Bikaner, opened 1891, 48 miles | ** Bhagu(Marwar Frontier)-Bikaner, opened 1891, 48 miles | ||
**Bikaner-Dumera, opened 1898, 42 miles | ** Bikaner-Dumera, opened 1898, 42 miles | ||
**Dulmera-Suratgarh, opened 1901,71 miles | ** Dulmera-Suratgarh, opened 1901,71 miles | ||
**Suratgarh-Bhatinda, opened 1902, 88 miles | ** Suratgarh-Bhatinda, opened 1902, 88 miles | ||
* ‘Hisar Extension Line’, MG, 136 miles(219km) | |||
* | ** Marwar Frontier to Ratangarh, opened 1909-10, 30 miles | ||
**Marwar Frontier to Ratangarh, opened 1909-10, 30 miles | ** Ratangarh-Churu, opened 1910, 26 miles | ||
**Ratangarh-Churu, opened 1910, 26 miles | ** Churu-Hisar, opened 1911, 80 miles | ||
**Churu-Hisar, opened 1911, 80 miles | * ‘Bikaner-Ratangarh Chord Line’, MG, 85 miles(137km) | ||
* | |||
**Bikaner-Ratangarh, opened 1912, 85 miles | **Bikaner-Ratangarh, opened 1912, 85 miles | ||
* ‘Sardarshahr Extension Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km) | |||
** Hudera(2 miles from Ratangarh)- Sardarshahr, opened 1916, 27 miles | |||
With 132 miles(212km) sanctioned for construction | |||
* ‘Hanumangarh-Sadupur Line’, MG, 105 miles(169km) | |||
** Hanumangarh to Sadupur, sanctioned for construction 1915, 105 miles | |||
* ‘Bikaner-Kolayat Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km) | |||
** Bikaner to Kolayat , sanctioned for construction 1915, 27 miles | |||
==Bikaner State Railway== | |||
In 1924, the JBR was divided into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the [[Jodhpur State Railway]](JSR) and '''Bikaner State Railway'''(BkSR) formed to take over responsibility for working the raiway. The JSR taking the “Jodhpur Section” of the [[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]], together with the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]](British Section). | |||
The '''Bikaner State Railway''' (BkSR) was created in 1924 from the “Bikaner Section” of the [[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]], the exact mileage comprising the “Bikaner Section” is not known but in 1918 it was 498 miles(801km) open line and approximately 568 miles(km) open line by 1924 | |||
[[File:Bikaner State Railway.png|right|400px|Bikaner State Railway ]] | |||
*Bikaner-Kolayat | In 1930-31 the open line route mileage for the BkSR had expanded to 796 miles(1281km) of metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) lines <ref name=Hist1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 223, pdf 266 ]; Retrieved 19 Aug 2020</ref> as follows:- | ||
** | * ‘Main Line’, MG, 249 miles(401km). Bhagu(Marwar Frontier) to Bhatinda - ''details as above'' | ||
* ‘Hisar Extension Line’, MG, 136 miles(219km). Marwar Frontier to Hisar - ''details as above'' | |||
* ‘Bikaner-Ratangarh Chord Line’, MG, 85 miles(137km). Bikaner to Ratangarh - ''details as above'' | |||
* ‘Sardarshahr Extension Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km). Hudera(2 miles from Ratangarh) to Sardarshahr- ''details as above'' | |||
* ‘Kolayat Extension Line’, MG, 29 miles(47km). Lalgarh to Kolayat, opened 1922 | |||
* ‘Canal Loop Line’, MG, 126 miles(203km) | |||
** Hanumangarh via Sadulshahr to Sri Ganga Nagar, opened 1923, 42 miles | |||
** Sri Ganga Nagar via Kesrisinghpur to Raisinghnagar, opened 1929-27, 49 miles | |||
** Raisinghnagar to Suratgarh, opened 1925, 35 miles | |||
* ‘Hanumangarh-Sadulpur Line’, MG, 107 miles(172km) | |||
** Hanumangarh via Nohar to Tabsil Bhadran, opened 1927-28, 71 miles | |||
** Tabsil Bhadran to Suratpura, opened 1930, 37 miles | |||
* ‘Anupgarh Branch’, MG, 35 miles(56km) | |||
** Sarupsar to Anupgarh , opened 1929, 35 miles | |||
With a further 86 miles (138km) sanctioned for construction | |||
* ‘Sadulpur-Rewari Line’, sanctioned for construction in 1937, 86 miles (138km). “The line will traverse portions of the Bikaner, Loharu, Patiala and Nabha States and the Gurgaon District of the Punjab, and is intende to develop an area rather thinly populated and at present unirrigated” <ref>[http://hdl.handle.net/10973/18160 “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” Para 37, page 40 pdf 55]; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020</ref> | |||
The ‘Statistics of Working’, 1937 <ref name=Hist1937/> show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 and the BSR System rising from 470 miles(756km) reaching 796 miles (1281km) from 1930-31 onwards<ref name=Hist1937/> | |||
By 1943 the BkSR was operating a network of 883 miles(1421km) | |||
== Classification == | |||
[[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class II railway system. | |||
At Independence in 1947 | ==Later Development== | ||
At Independence in 1947 the western portions of the ‘[[Bikaner State Railway]]’, the ‘[[Jodhpur State Railway ]]’ and the British section of the ‘[[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]]’ were ceded to the government of Pakistan becoming part of ‘[[Pakistan Railways]]’<ref>[http://rajasthanhistory.com/gpage5.html “History of Rail in Rajasthan” by Dr Mohanlal Gupta, Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of Rajasthan, Jodhpur]; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016</ref>. | |||
The remaining portions | The remaining eastern portions of the ‘[[Bikaner State Railway]]’ and the ‘[[Jodhpur State Railway ]]’, excluding the ‘Marwar-Phulad Section’ became part of the of [[Northern Railway| ‘Indian Railways - Northern Railway Zone’ ]] in 1952 | ||
==Further Information== | ==Further Information== | ||
Latest revision as of 08:47, 19 August 2020
| Bikaner State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Bikaner State Railway Logo | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1924 | System formed | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1924 | Bikaner section of Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Bikaner | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | ||
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1952 | Northern Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 883 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Bikaner State Railway (BkSR) was created in 1924 and took over responsibility for working the Bikaner section of the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway.
Background
Originally named the Jodhpur Railway the first section opened as a metre gauge(MG) line in 1882, becoming the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) in 1889.
In 1908 the JBR operated 828 miles(1325km) in the territories of Sind (under British control) and in territories of the States of Jodhpur and Bikaner.
By 1918 the ‘JBR System’ had expanded to 1355 miles(2180km); which comprised 1106 miles(1179km) plus a further 249 miles(401km) which JBR was working and operating under agreements with other railways [1].
A further 210 miles(400km) were sanctioned or under construction by JBR in 1918 [1].
For operational purposes the JBR was divided into two sections:- the 'Bikaner Section' and the 'Jodhpur Section'
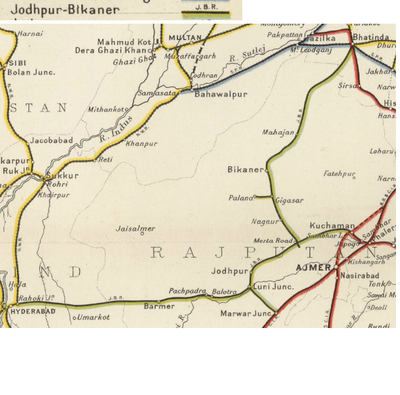
Bikaner Section of the JBR - 1918 grand total, 498 miles(1013km) open line [2] as follows:-
- ‘Main Line’, MG, 249 miles(401km)
- Bhagu(Marwar Frontier)-Bikaner, opened 1891, 48 miles
- Bikaner-Dumera, opened 1898, 42 miles
- Dulmera-Suratgarh, opened 1901,71 miles
- Suratgarh-Bhatinda, opened 1902, 88 miles
- ‘Hisar Extension Line’, MG, 136 miles(219km)
- Marwar Frontier to Ratangarh, opened 1909-10, 30 miles
- Ratangarh-Churu, opened 1910, 26 miles
- Churu-Hisar, opened 1911, 80 miles
- ‘Bikaner-Ratangarh Chord Line’, MG, 85 miles(137km)
- Bikaner-Ratangarh, opened 1912, 85 miles
- ‘Sardarshahr Extension Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km)
- Hudera(2 miles from Ratangarh)- Sardarshahr, opened 1916, 27 miles
With 132 miles(212km) sanctioned for construction
- ‘Hanumangarh-Sadupur Line’, MG, 105 miles(169km)
- Hanumangarh to Sadupur, sanctioned for construction 1915, 105 miles
- ‘Bikaner-Kolayat Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km)
- Bikaner to Kolayat , sanctioned for construction 1915, 27 miles
Bikaner State Railway
In 1924, the JBR was divided into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the Jodhpur State Railway(JSR) and Bikaner State Railway(BkSR) formed to take over responsibility for working the raiway. The JSR taking the “Jodhpur Section” of the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway, together with the Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway(British Section).
The Bikaner State Railway (BkSR) was created in 1924 from the “Bikaner Section” of the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway, the exact mileage comprising the “Bikaner Section” is not known but in 1918 it was 498 miles(801km) open line and approximately 568 miles(km) open line by 1924
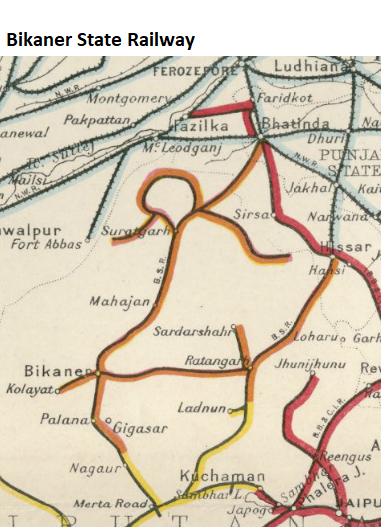
In 1930-31 the open line route mileage for the BkSR had expanded to 796 miles(1281km) of metre gauge(MG) lines [3] as follows:-
- ‘Main Line’, MG, 249 miles(401km). Bhagu(Marwar Frontier) to Bhatinda - details as above
- ‘Hisar Extension Line’, MG, 136 miles(219km). Marwar Frontier to Hisar - details as above
- ‘Bikaner-Ratangarh Chord Line’, MG, 85 miles(137km). Bikaner to Ratangarh - details as above
- ‘Sardarshahr Extension Line’, MG, 27 miles(43km). Hudera(2 miles from Ratangarh) to Sardarshahr- details as above
- ‘Kolayat Extension Line’, MG, 29 miles(47km). Lalgarh to Kolayat, opened 1922
- ‘Canal Loop Line’, MG, 126 miles(203km)
- Hanumangarh via Sadulshahr to Sri Ganga Nagar, opened 1923, 42 miles
- Sri Ganga Nagar via Kesrisinghpur to Raisinghnagar, opened 1929-27, 49 miles
- Raisinghnagar to Suratgarh, opened 1925, 35 miles
- ‘Hanumangarh-Sadulpur Line’, MG, 107 miles(172km)
- Hanumangarh via Nohar to Tabsil Bhadran, opened 1927-28, 71 miles
- Tabsil Bhadran to Suratpura, opened 1930, 37 miles
- ‘Anupgarh Branch’, MG, 35 miles(56km)
- Sarupsar to Anupgarh , opened 1929, 35 miles
With a further 86 miles (138km) sanctioned for construction
- ‘Sadulpur-Rewari Line’, sanctioned for construction in 1937, 86 miles (138km). “The line will traverse portions of the Bikaner, Loharu, Patiala and Nabha States and the Gurgaon District of the Punjab, and is intende to develop an area rather thinly populated and at present unirrigated” [4]
The ‘Statistics of Working’, 1937 [3] show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 and the BSR System rising from 470 miles(756km) reaching 796 miles (1281km) from 1930-31 onwards[3]
By 1943 the BkSR was operating a network of 883 miles(1421km)
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class II railway system.
Later Development
At Independence in 1947 the western portions of the ‘Bikaner State Railway’, the ‘Jodhpur State Railway ’ and the British section of the ‘Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway’ were ceded to the government of Pakistan becoming part of ‘Pakistan Railways’[5].
The remaining eastern portions of the ‘Bikaner State Railway’ and the ‘Jodhpur State Railway ’, excluding the ‘Marwar-Phulad Section’ became part of the of ‘Indian Railways - Northern Railway Zone’ in 1952
Further Information
See Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway for period up to 1924
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page185 (pdf194); Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 187 (pdf195)]; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 223, pdf 266 ; Retrieved 19 Aug 2020
- ↑ “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” Para 37, page 40 pdf 55; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ “History of Rail in Rajasthan” by Dr Mohanlal Gupta, Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of Rajasthan, Jodhpur; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016