Bombay Port Trust Railway: Difference between revisions
1918 Admin Report details checked/added/corrected |
Revised layout with map |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Bombay]] Port | [[File:Bombay Port Trust Logo c.jpg|thumb|Bombay Port Trust Logo]] | ||
* | ==Bombay Port Land Reclaimation== | ||
*Victoria | The 'Elpinstone Land and Press Company' was formed in 1858 to reclaim two large parcels of land on the south-east side of the Bombay peninsular <ref name =darvill >“Industrial Railways and Locomotives of India and South Asia” compiled by Simon Darvill. Published by ‘The Industrial Railway Society’ 2013. ISBN 978 1 901556 82-7. Available at http://irsshop.co.uk/India. Reference: Entry MH34 page ....</ref>:- | ||
*'Appollo Bunder-Mazagoan', 250 acres(100ha), which was allocated to create the Port of Bombay | |||
*'Bori Bunder', 100 acres(40ha), to be given to the [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]](GIPR) for the building of the Victoria Terminus. | |||
The company went bankrupt in the 1865 crash, and their equipment, along with the reclaimed land was divided partly given to the [[GIPR]] and partly to the newly formed '''Bombay Port Trust'''. The equipment included broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) locomotives <ref name =darvill/>. | |||
Railway | ==Bombay Port Trust== | ||
[[File:Bombay Port Trust Railway.png|thumb| Bombay Port Trust Railway]] | |||
[[File:Bombay_Docks_Plan_1913.jpg|thumb|Bombay Docks Plan 1913]] | |||
'Bombay Port Trust' was created in 1873 and modelled on the Mersey Board in England to control all harbour activities. It undertook extensive land reclamation work, and the creation of docks | |||
<br>Half of all Indian exports passed through Bombay's docks. <ref name=Mumbai>[http://www.mumbaiport.gov.in/writereaddata/linkimages/3709970893.pdf Mumbai Port Commission, Chapter 1, Part 1 “Early History” pdf pages 8-9]; Retrieved 30 Apr 2017</ref> | |||
John Fleming was responsible for the establishment of the 'Bombay Port Trust' and involved in the land reclamatiion projects of the mid 1860's. In 1884 Fleming went on to form '[[John Fleming & Co]]' a company of Merchants and Agents <ref name =MH43>“Industrial Railways and Locomotives of India and South Asia” compiled by Simon Darvill. Published by ‘The Industrial Railway Society’ 2013. ISBN 978 1 901556 82-7. Available at http://irsshop.co.uk/India. Reference: Entry MH43 page ....</ref>. | |||
<ref>[https:// | |||
==Bombay Port Trust Railway== | |||
The railway system for the Port Trust was sanctioned in 1913, The first part to open in 1915 was the section between from the GIPR line at Wadlala Junction via the Victoria overbridge to the Docks, a length of nearly 14 miles(22km). In addition to the BG spur lines a dedicated line opened in 1915 ran from Ballard Pier to Wadala. Along this railway were built grain and fuel oil depots. The kerosene oil installations were developed at Sewri and for petrol at Wadala. | |||
<ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n49/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 40 (pdf49)]; Retrieved 30 Apr 2017</ref> <ref>ibid: Darvill Entry MH69 page ....</ref> | |||
Within the docks there were a further 104 miles(166km) of track, giving a total of 118 miles(189km). The system was primarily a goods operation but passenger trains were operated over Port Trust track, mainly troop trans and postal and passenger trains in connection with the mail steamers <ref>ibid: Darvill Entry MH69 page ....</ref>. The Raoli Junction to Ballard Pier section and from Manson Road to Alexandra Dock sections opened in 1915, <ref>ibid: Darvill Entry MH70 page ....</ref>. | |||
Railway sidings spurred off the broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]](GIPR) mainline to a collection of sidings to the docks in the east Bombay. | |||
<br>There were numerous spurs to:- | |||
*Princess Dock, that had been constructed by [[Glover & Co|'Glover & Co', Contractors]], 1880-85. Prior to 1914 the docks were not rail served <ref name=Mumbai/>. | |||
*Victoria Dock, that had been constructed 1883-88, ditto | |||
*Merewether Dry Dock, that had been constructed 1891-93, ditto | |||
*Alexandra Dock. In 1905 the contract was let to construct a new dock, a dry dock and dock head pier, the foundation stone was laid by the Prince of Wales on 13 Nov 1905. The dock was completed by 1914. Most of the stone came from Elephant Island and the records show that nearly 4000 tons of stone was being transported each day to the work sites by rail <ref>ibid: Entry MH70 page ....</ref>. | |||
*Carnac Basin, thought to have been served by the railway some time after 1915 | |||
*Malet Basin, ditto | |||
*Frere Basin, ditto | |||
*Clerk Basin, ditto | |||
=== RailwayClassification === | |||
[[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class III railway system <ref name=Hist1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 268 pdf 311]; Retrieved 27 Jul 2020</ref>. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 39: | ||
[[Category:Port Railways]] | [[Category:Port Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Industrial Railways]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 8 January 2021

Bombay Port Land Reclaimation
The 'Elpinstone Land and Press Company' was formed in 1858 to reclaim two large parcels of land on the south-east side of the Bombay peninsular [1]:-
- 'Appollo Bunder-Mazagoan', 250 acres(100ha), which was allocated to create the Port of Bombay
- 'Bori Bunder', 100 acres(40ha), to be given to the Great Indian Peninsula Railway(GIPR) for the building of the Victoria Terminus.
The company went bankrupt in the 1865 crash, and their equipment, along with the reclaimed land was divided partly given to the GIPR and partly to the newly formed Bombay Port Trust. The equipment included broad gauge(BG) locomotives [1].
Bombay Port Trust
'Bombay Port Trust' was created in 1873 and modelled on the Mersey Board in England to control all harbour activities. It undertook extensive land reclamation work, and the creation of docks
Half of all Indian exports passed through Bombay's docks. [2]
John Fleming was responsible for the establishment of the 'Bombay Port Trust' and involved in the land reclamatiion projects of the mid 1860's. In 1884 Fleming went on to form 'John Fleming & Co' a company of Merchants and Agents [3].
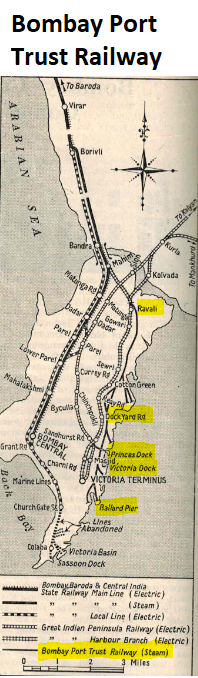
Bombay Port Trust Railway
The railway system for the Port Trust was sanctioned in 1913, The first part to open in 1915 was the section between from the GIPR line at Wadlala Junction via the Victoria overbridge to the Docks, a length of nearly 14 miles(22km). In addition to the BG spur lines a dedicated line opened in 1915 ran from Ballard Pier to Wadala. Along this railway were built grain and fuel oil depots. The kerosene oil installations were developed at Sewri and for petrol at Wadala. [4] [5]
Within the docks there were a further 104 miles(166km) of track, giving a total of 118 miles(189km). The system was primarily a goods operation but passenger trains were operated over Port Trust track, mainly troop trans and postal and passenger trains in connection with the mail steamers [6]. The Raoli Junction to Ballard Pier section and from Manson Road to Alexandra Dock sections opened in 1915, [7].
Railway sidings spurred off the broad gauge(BG) Great Indian Peninsula Railway(GIPR) mainline to a collection of sidings to the docks in the east Bombay.
There were numerous spurs to:-
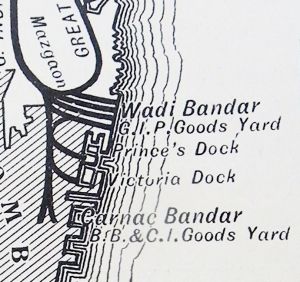
- Princess Dock, that had been constructed by 'Glover & Co', Contractors, 1880-85. Prior to 1914 the docks were not rail served [2].
- Victoria Dock, that had been constructed 1883-88, ditto
- Merewether Dry Dock, that had been constructed 1891-93, ditto
- Alexandra Dock. In 1905 the contract was let to construct a new dock, a dry dock and dock head pier, the foundation stone was laid by the Prince of Wales on 13 Nov 1905. The dock was completed by 1914. Most of the stone came from Elephant Island and the records show that nearly 4000 tons of stone was being transported each day to the work sites by rail [8].
- Carnac Basin, thought to have been served by the railway some time after 1915
- Malet Basin, ditto
- Frere Basin, ditto
- Clerk Basin, ditto
RailwayClassification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class III railway system [9].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 “Industrial Railways and Locomotives of India and South Asia” compiled by Simon Darvill. Published by ‘The Industrial Railway Society’ 2013. ISBN 978 1 901556 82-7. Available at http://irsshop.co.uk/India. Reference: Entry MH34 page ....
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mumbai Port Commission, Chapter 1, Part 1 “Early History” pdf pages 8-9; Retrieved 30 Apr 2017
- ↑ “Industrial Railways and Locomotives of India and South Asia” compiled by Simon Darvill. Published by ‘The Industrial Railway Society’ 2013. ISBN 978 1 901556 82-7. Available at http://irsshop.co.uk/India. Reference: Entry MH43 page ....
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 40 (pdf49); Retrieved 30 Apr 2017
- ↑ ibid: Darvill Entry MH69 page ....
- ↑ ibid: Darvill Entry MH69 page ....
- ↑ ibid: Darvill Entry MH70 page ....
- ↑ ibid: Entry MH70 page ....
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 268 pdf 311; Retrieved 27 Jul 2020