Tirhoot State Railway: Difference between revisions
'Personnel' heading changed with text; 'Francis Langford O'Callaghan' name , link and text added. |
Infobox revisions, Maps added, Complete revion |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|image= | |image= | ||
|caption= | |caption= | ||
|route= | |route= See text | ||
|gauge1= Metre gauge | |gauge1= Metre gauge | ||
|gauge1details= 566 miles (1905) | |gauge1details= 209 miles (1886); 566 miles (1905); | ||
|gauge2= | |gauge2= | ||
|gauge2details= | |gauge2details= | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|gauge4details= | |gauge4details= | ||
|timeline1date= 1874 | |timeline1date= 1874 | ||
|timeline1details= Construction work begun | |timeline1details= Construction work begun - 'Tirhut Railway' | ||
|timeline2date= | |timeline2date= 1886 | ||
|timeline2details= | |timeline2details= renamed 'Tirhoot State Railway' | ||
|timeline3date= | |timeline3date= | ||
|timeline3details= | |timeline3details= | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tirhoot State Railway''' (TSR) was one of the first metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railways promoted by the Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]). | The '''Tirhoot State Railway''' (TSR) was one of the first metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railways promoted by the Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]). | ||
== | ==Tirhut Railway== | ||
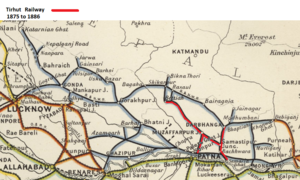
[[File:Tirhut Railway 1875 to 1886.png|thumb|’Tirhut Railway’ 1875 to 1886 ]] | |||
Originally named the ‘Tirhut Railway’ it was a temporary famine relief line between Dalsing Sarai (''midway between Samastra and Bachwara shown on map'') northwards to Samastipur to Darbhanga, 38 miles(61km), opened Nov 1875. | |||
The | The line was owned by the Provincial Government and some early records refer to the ‘[[Darbhanga State Railway]]’ and tlater as the ‘[[Nirmali Branch Railway]]’. | ||
The following is generally based on the 1918 ‘Administration Report for Railways’ <ref name=Adlmin1918>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n170/mode/1up " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 162-164]; Retrieved 22 Apr 2020</ref> and gives a total line length of opened lines of 209 miles(336km) in 1886. | |||
* Samastipur to Muzaffarpur Branch, 32 miles opened in 1877, extended to Bettiah in 1883, a further 68 miles. | |||
* Dalsing Sarai southwards to Bachwara and to Semaria Ghat , a southern extension opened 1883, 11 miles | |||
* Darbhanga to Jhanjharpur (nr Madhumbani), opened 1883, 24 miles , (part of ‘Darbhanga-Bhaptiahi Branch’ see below) | |||
== | * Muzaffapur southwards to Hajipur Junction and onward to Hajipur Ghat (facing Patna) opened in 1884, 36 miles. | ||
*[[ | ==Tirhoot Railway (TSR)== | ||
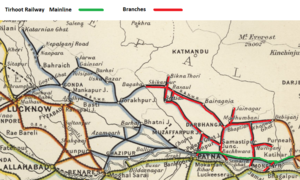
* | [[File:Tirhoot Railway from 1886.png|thumb|’Tirhoot Railway’ 1886 onwards]] | ||
* | Ownership is believed to have been later transferred to the Government of India(GoI)., '' date not determined''. The railway was worked by the GoI as part of the Indian State Railways from opening to late 1886. The records show the spelling changed to ‘Tirhoot Railway’ from then onwards. | ||
*Samastipur-Narkatiaganj | |||
* | The following is generally based on the 1918 ‘Administration Report for Railways’ <ref name=Adlmin1918/> | ||
* | ===Tirhoot Mainline=== | ||
* | 'The ‘Tirhoot Mainline’ metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]), total 169 miles(272km) consisting of following sections:- | ||
*Jaynagar | * Sonapore-Hajipur Junction, opened 1887, 3 mile extension from Hajipur Junction westwards to Sonapore('' Sonpur on map'') | ||
* | *Hahjipur Junction-Bachhwara, opened 1900,44 miles, | ||
* | *Bachhwara-Baranni Junction, opened 1888, 10 miles, | ||
* | *Baranni Junction-Katihar Junction, opened 1900-02, 112 miles | ||
===Tirhoot Railway Branches=== | |||
The ‘Tirhoot Railway Branches’ metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]), total 635 miles(1022m) consisting of following sections:- | |||
<br>§ indicates a portion of the original ‘Tirhut Railway’ | |||
** ‘Hajiipur-Muzaffapur Branch’ , 36 miles from Muzaffapur southwars to Hajiipur and onward to the ‘Hajipur Ghat Branch’, opened 1884 §. | |||
** ‘Semaria Ghat Extension’ from Barauni Junction, opened 1883 §, 5 miles.) | |||
** ‘Bachhwara-Bagaha Branch’ , total 178 miles from Bachwara to Dalsing Sarai, opened 1883 §; Dalsing Sarai to Samastipur, opened 1875 §; Samastipur to Muzaffapur, opened 1877 §; Muzaffapur to Bettiah opened 1883 §; Bettiah via Shikarpur to Bagaha opened 1906-07 and extended to the [[Gundak Bridge]] East Bank 1912. | |||
** ‘Raxaul Branch’, 2 miles from egauli to Raxaul, opened 1899 | |||
** ‘Samastipur-Darbhanga-Narkatiaganj Loop’, total 142 miles from Samastipur to Darbhanga, opened 1875 §; Darbhanga to Riga, opened 1990-91; Riga to Bairagnia, opened 1901-02; Bairagnia to Narkatiaganj Junction(Shikarpur on map), opened 1907. | |||
** ‘Bhika Throree Branch’, 22 miles, Narkatiaganj Junction(Shikarpur) to Bhikna Thoree('' Bikna Thori on map''), opened 1906. | |||
** ‘Darbhanga-Bhaptiahi Branch’, 54 miles from Darbhanga to Jhanjharpur (''near Madhumbani on map''), opened 1883 § and Jhanjharpur to Bhaptiahi, opened 1887. | |||
** ‘Bhaptiahi -Pertabganj Ghat’, 11 miles from Bhaptiahi to Pertabganj Ghat, (''Khanwa Ghat on map''), opened 1888 | |||
** ‘Jaynagar Branch’, also known as the ‘[[Sakri-Jainager Branch Railway]]’ 30 miles from Sakri to Jaynagar''(Jainagar on map) '', opened 1905 | |||
** ‘Bhaptiahi-Mansi Branch’, 60 miles from Bhaptiahi to Mans, opened 1907 | |||
** ‘Baijnathpur Branch’, 5 miles from Saharsa to Baijnathpur, opened 1908. Extended to Dauram Madhepuraj | |||
** ‘Monghyr Branch’, 6 miles from Sahobpur Kamal to Monghyr Ghat, opened 1900 | |||
** ‘Bhagalpur Branch’, from Thana Bibpur to Mahadeopur Ghat, opened 1901, 11 Miles; Mahadeopur Ghat to Barari Ghat by Steamer Service; Barari Ghat to Blagalpur Kachery, opened 1906; Blagalpur Kachery to Bhagalpur EIR Station, 1910 | |||
** ‘Samastipur-Rusera-Khagaria Extension’, 53 miles from Samastipur to Rusera Ghat, opened 1912; Rusera Ghat to-Khagaria, opened 1915 | |||
==Lines worked by TSR== | ==Lines worked by TSR== | ||
*[[Segowlie-Raxaul Railway]] – Privately owned; opened 1899 and worked by B&NWR; Absorbed by Tirhoot State Railway c.1920 | *[[Segowlie-Raxaul Railway]] – Privately owned; opened 1899 and worked by B&NWR; Absorbed by Tirhoot State Railway c.1920 | ||
==Railway Constructions== | |||
The [[Gunduck Bridge]] was constructed by the Tirhoot State Railway completing the connection with the Bengal and North- Western Railway. The bridge was opened in 1887 and consisted of 5 spans of 250 feet with a half mile viaduct on one bank of the river. [[Horace Bell]] was the Engineer-in-Chief and [[R.A.Way]] was the Executive Engineer in charge of construction. | |||
==Working Arrangements== | |||
‘Tirhoot State Railway’ (TSR) operated the line from late 1886 to 30th June 1890. | |||
<br>TSR was then worked in conjunction with '''[[Bengal and North-Western Railway]]''' (B&NWR) from 1st July 1890. | |||
<br>The 1908 Map <ref>[https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gaz_atlas_1909/fullscreen.html?object=30 ‘Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 26, Atlas 1909 edition, Railway Map--Sectional (2), p. 24.’ ]; Retrieved 20 Apr 2020</ref> shows on the TSR as a part of the B&NWR network. | |||
<br>The 1918 Administration Report for Railways | |||
<ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n172/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 164 (pdf172)]; Retrieved 120 Apr 2020</ref> shows that the TSR, although included under the B&NWR was submitting separate Statistics of Working’ . | |||
TSR was merged into the Oudh and Tirhut Railway on 1st January 1943 | |||
==Records== | ==Records== | ||
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the [http://www.fibis.org/store/fibis-books-and-publications/bff-0004-research-sources-for-indian-railways-1845-1947/ Fibis shop]. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the [[India Office Records]] (IOR) held at the [[British Library]] | Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the [http://www.fibis.org/store/fibis-books-and-publications/bff-0004-research-sources-for-indian-railways-1845-1947/ Fibis shop]. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the [[India Office Records]] (IOR) held at the [[British Library]] | ||
Revision as of 10:57, 22 April 2020
| Tirhoot State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| See text | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 209 miles (1886); 566 miles (1905); | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1874 | Construction work begun - 'Tirhut Railway' | |
| 1886 | renamed 'Tirhoot State Railway' | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | ||
| System agency | ||
| 1890 | Bengal and North-Western Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Tirhoot State Railway (TSR) was one of the first metre gauge(MG) railways promoted by the Government of India(GoI).
Tirhut Railway
Originally named the ‘Tirhut Railway’ it was a temporary famine relief line between Dalsing Sarai (midway between Samastra and Bachwara shown on map) northwards to Samastipur to Darbhanga, 38 miles(61km), opened Nov 1875.
The line was owned by the Provincial Government and some early records refer to the ‘Darbhanga State Railway’ and tlater as the ‘Nirmali Branch Railway’.
The following is generally based on the 1918 ‘Administration Report for Railways’ [1] and gives a total line length of opened lines of 209 miles(336km) in 1886.
- Samastipur to Muzaffarpur Branch, 32 miles opened in 1877, extended to Bettiah in 1883, a further 68 miles.
- Dalsing Sarai southwards to Bachwara and to Semaria Ghat , a southern extension opened 1883, 11 miles
- Darbhanga to Jhanjharpur (nr Madhumbani), opened 1883, 24 miles , (part of ‘Darbhanga-Bhaptiahi Branch’ see below)
- Muzaffapur southwards to Hajipur Junction and onward to Hajipur Ghat (facing Patna) opened in 1884, 36 miles.
Tirhoot Railway (TSR)
Ownership is believed to have been later transferred to the Government of India(GoI)., date not determined. The railway was worked by the GoI as part of the Indian State Railways from opening to late 1886. The records show the spelling changed to ‘Tirhoot Railway’ from then onwards.
The following is generally based on the 1918 ‘Administration Report for Railways’ [1]
Tirhoot Mainline
'The ‘Tirhoot Mainline’ metre gauge(MG), total 169 miles(272km) consisting of following sections:-
- Sonapore-Hajipur Junction, opened 1887, 3 mile extension from Hajipur Junction westwards to Sonapore( Sonpur on map)
- Hahjipur Junction-Bachhwara, opened 1900,44 miles,
- Bachhwara-Baranni Junction, opened 1888, 10 miles,
- Baranni Junction-Katihar Junction, opened 1900-02, 112 miles
Tirhoot Railway Branches
The ‘Tirhoot Railway Branches’ metre gauge(MG), total 635 miles(1022m) consisting of following sections:-
§ indicates a portion of the original ‘Tirhut Railway’
- ‘Hajiipur-Muzaffapur Branch’ , 36 miles from Muzaffapur southwars to Hajiipur and onward to the ‘Hajipur Ghat Branch’, opened 1884 §.
- ‘Semaria Ghat Extension’ from Barauni Junction, opened 1883 §, 5 miles.)
- ‘Bachhwara-Bagaha Branch’ , total 178 miles from Bachwara to Dalsing Sarai, opened 1883 §; Dalsing Sarai to Samastipur, opened 1875 §; Samastipur to Muzaffapur, opened 1877 §; Muzaffapur to Bettiah opened 1883 §; Bettiah via Shikarpur to Bagaha opened 1906-07 and extended to the Gundak Bridge East Bank 1912.
- ‘Raxaul Branch’, 2 miles from egauli to Raxaul, opened 1899
- ‘Samastipur-Darbhanga-Narkatiaganj Loop’, total 142 miles from Samastipur to Darbhanga, opened 1875 §; Darbhanga to Riga, opened 1990-91; Riga to Bairagnia, opened 1901-02; Bairagnia to Narkatiaganj Junction(Shikarpur on map), opened 1907.
- ‘Bhika Throree Branch’, 22 miles, Narkatiaganj Junction(Shikarpur) to Bhikna Thoree( Bikna Thori on map), opened 1906.
- ‘Darbhanga-Bhaptiahi Branch’, 54 miles from Darbhanga to Jhanjharpur (near Madhumbani on map), opened 1883 § and Jhanjharpur to Bhaptiahi, opened 1887.
- ‘Bhaptiahi -Pertabganj Ghat’, 11 miles from Bhaptiahi to Pertabganj Ghat, (Khanwa Ghat on map), opened 1888
- ‘Jaynagar Branch’, also known as the ‘Sakri-Jainager Branch Railway’ 30 miles from Sakri to Jaynagar(Jainagar on map) , opened 1905
- ‘Bhaptiahi-Mansi Branch’, 60 miles from Bhaptiahi to Mans, opened 1907
- ‘Baijnathpur Branch’, 5 miles from Saharsa to Baijnathpur, opened 1908. Extended to Dauram Madhepuraj
- ‘Monghyr Branch’, 6 miles from Sahobpur Kamal to Monghyr Ghat, opened 1900
- ‘Bhagalpur Branch’, from Thana Bibpur to Mahadeopur Ghat, opened 1901, 11 Miles; Mahadeopur Ghat to Barari Ghat by Steamer Service; Barari Ghat to Blagalpur Kachery, opened 1906; Blagalpur Kachery to Bhagalpur EIR Station, 1910
- ‘Samastipur-Rusera-Khagaria Extension’, 53 miles from Samastipur to Rusera Ghat, opened 1912; Rusera Ghat to-Khagaria, opened 1915
Lines worked by TSR
- Segowlie-Raxaul Railway – Privately owned; opened 1899 and worked by B&NWR; Absorbed by Tirhoot State Railway c.1920
Railway Constructions
The Gunduck Bridge was constructed by the Tirhoot State Railway completing the connection with the Bengal and North- Western Railway. The bridge was opened in 1887 and consisted of 5 spans of 250 feet with a half mile viaduct on one bank of the river. Horace Bell was the Engineer-in-Chief and R.A.Way was the Executive Engineer in charge of construction.
Working Arrangements
‘Tirhoot State Railway’ (TSR) operated the line from late 1886 to 30th June 1890.
TSR was then worked in conjunction with Bengal and North-Western Railway (B&NWR) from 1st July 1890.
The 1908 Map [2] shows on the TSR as a part of the B&NWR network.
The 1918 Administration Report for Railways
[3] shows that the TSR, although included under the B&NWR was submitting separate Statistics of Working’ .
TSR was merged into the Oudh and Tirhut Railway on 1st January 1943
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [4] gives the following: -
- L/F/8/20/1749 “Bengal and North-Western Railway Company Limited, Contract for construction and working of new extensions of the Bengal and North-Western and Tirhoot State Railway systems; 1928"
Personnel in Chronological order
There are no Staff Records for the TSR in the IOR.
The underlisted have been identifiede from varios other sources -
- Frederick Smith Stanton with the famine in Behar and Tirhoot of 1873-74 he was sent on emergency duty to construct a short line of 63 miles from the River Ganges to Durbhunga in Tirhoot, which he opened for traffic in fifty-three days. The construction of this temporary line, which was carried out at the rate of a mile a day, was, in the words of Sir Richard Temple, then Lieutenant-Governor of Bengal, "an extraordinary achievement in respect of speed. To carry the line over a country intersected by three considerable streams; to make it strong enough to carry 2,000 tons in a day; to open it within the prescribed time, demanded primarily an indefatigable energy, but also professional skill and administrative ability. All these qualities were displayed by Major F. S. Stanton, R.E., the Engineer-in-Chief. Having made this line, he worked its heavy traffic with the same efficiency." [5].
- Vans Righy was deployed from the Public Works Department from 1875 to 1880 as Executive Engineer on the Tirhoot State Railway. In 1880 he became Manager and Superintendent Way and Works. His resposibility jointly included Patna & Gaya State Railway. He retained this position until transferred in 1886 [6].
- Francis Langford O'Callaghan, was posted from State Railways to TSR as Chief Engineer, 1877-79 [7]
- Horace Bell was deployed from the Railway Branch of the Public Works Department, to the TSR early in 1884, first as Engineer-in-Chief, and then as both Manager and Engineer-in-Chief. With the exception of a short interval from July to October, 1881, when he officiated as Director of the North Western State Railway, was employed on the TSR and received the thanks of the Government of India for his services in connection with the consruction of the Gunduck Bridge on that line in 1887 [8].
- R.A.Way was the Executive Engineer in charge of the construction of the Gunduck Bridge completed in 1887 [9].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 162-164; Retrieved 22 Apr 2020
- ↑ ‘Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 26, Atlas 1909 edition, Railway Map--Sectional (2), p. 24.’ ; Retrieved 20 Apr 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 164 (pdf172); Retrieved 120 Apr 2020
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved Jan 2016
- ↑ "Grace's Guide - Frederick Smith Stanton”; Retrieved on 21 Apr 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 600 (pdf page 563) Retrieved on 27 May 2016
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "Biographical Dictionary of Civil Engineers in Great Britain and Ireland - O'Callaghan, Francis Langford "; Retrieved on 13 Jul 2016
- ↑ "Grace's Guide - Horace Bell”; Retrieved on 16 Apr 2016
- ↑ “ Indian Engineering” 19 March 1887, pages 146, 174”; Retrieved on 12 May 2016