Carnatic Railway
| Carnatic Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Arakkonam-Conjeevaram Tramway | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| 3feet 6inch(1097mm) | Opened 1865 | |
| Broad Gauge(BG) | Converted to BG c.1870 | |
| Metre Gauge (MG) | Converted to MG 1878 | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1862 | Indian Tramway Co. formed | |
| 1870 | Carnatic Railway Co. formed with state assistance | |
| 1872 | Merged with the ‘Great Southern of India Railway | |
| 1874 | The two merged Companies became South Indian Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Madras | |
| Stations | ||
| System agency | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
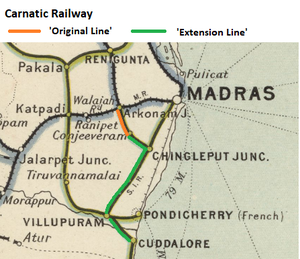
The Carnatic Railway(CAR) was formed in 1870 to acquire the operations and line and equipment of the Indian Tramway Co., a company which went into voluntary in liquidation
See separate page ‘Indian Tramway Company’ for further information
The CAR was able to secure a 5% Guarantee from the Government of India)[1].
Contract
The Contract [1] shows that the only line that had been constructed by the ‘Indian Tramway Co.’, was the ‘Arakkonam-Conjeevaram Tramway’, a 3 feet 6 inches(1067mm) Rail Gauge line of which "opened for traffic about 1 Aug 1865" and ran between the towns of Arkonam and Conjeeveram, a line length of 18.8miles (30.3km).
The Contract specified that the Company shall alter the gauge of the ‘Arakkonam-Conjeevaram Tramway’, described as the ‘Original Line’ in the Contract, to 5 feet 6 inches broad gauge(BG) throughout. It is known that the line from Arkonam Station to Conjeeveram was converted to BG (probably in late 1870 or early 1871 but exact date not known).
The Contract also specified that the Company shall undertake the construction of an BG ‘Extension Line’ from Conjeeveram to Cuddalore.
It is clear that this “Extension Line” was not constructed by the ‘Carnaic Railway Company’.
It was not until 1881 when the ‘South Indian Railway’ (SIR] opened the extension from Conjeeveram to Chingleput Junction (see ‘Later Developments - 1881’ below).
Later Developments
- 1872 the ‘Carnatic Railway’ merged with the ‘Great Southern of India Railway’. The background to this is fully explained in the record “Amalgamation of the Great Southern and Carnatic Railway Companies” [2], this record has been transcribed by FIBIS.
- 1874, the merged companies were renamed the ‘South Indian Railway’(SIR).
- 1878, the ‘ ‘Arkonam-Conjeeveram Line’ was converted in July 1878 to metre gauge(MG) as part of the SIR Metre Gauge systemwas adopted and the line was converted once again to MG [3].
- 1881, The SIR cextended the line as a metre gauge(MG) from Conjeeveram (now named Kanchipuram) in stages reaching Chingleput Junction in Jan 1881 forming the ‘SIR Arkonum MG Branch’. At Chingleput Junction the line joined the ‘SIR MG Mainline’ which had opened in 1876-77 [3], thus connecting throgh to Cuddalore.
Records
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [4] gives 7 references. The most important being:-
- L/F/8/11/874 “Carnatic Railway Company, Duplicate contract Secretary of State; 1870”
- L/PWD/5/3 “Public Works 'Old Series' (Collections), Coll 15, Amalgamation of Great Southern and Carnatic Railway Cos, 1869-1874”
Personnel
Unfortunately, there are no ‘Carnatic Railway’ staff records held in the India Office Records at the British Library.
In 1868 August, Frederick Lewis Dibblee was engaged as Chief Engineer of the ‘Carnatic Railway’, he had previously been Chief Engineer of the ‘Great Southern of India Railway’ also in the Madras Presidency.
Further Information
See Arakkonam-Conjeevaram Tramway
and Indian Tramway Co. for early history up to 1870.
See South Indian Railway for period after 1874
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 “Parliamentary Papers Accounts and Papers Volume 15 of 37” Session 9 February to 21 August 1871 Pages 231-244. ‘Contract between the Secretary of State and the Carnatic Railway Company’, dated 1 March 1870; Retrieved 30 Mar 2018
- ↑ IOR/L/PWD/5 “Amalgamation of the Great Southern and Carnatic Railway Companies”
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 138 (pdf146) ; Retrieved 30 Mar 2018
- ↑ British Library “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 20 Jan 2016