Difference between revisions of "Dhrangadhra Railway"
('Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems' page link added under 'Further Information') |
(Total revision with map) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''Dhrangadhra Railway''' (DR) was a short metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) line owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Dhrangadhra State]]. | + | The '''Dhrangadhra Railway''' (DR) was a short metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) line constructed for and owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]] [[Dhrangadhra|Dhrangadhra State]]. |
| − | Initially, the DR was worked by the [[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]] | + | [[File: Dhrangadhra Railway.png|thumb|Dhrangadhra Railway]] |
| − | <ref>[https://archive.org/ | + | ==History== |
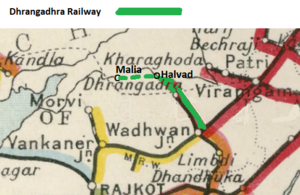
| + | '''1898'''. The first section of the ‘Dhrangadhra Railway’(DR) from [[Wadhwan]] to [[Dhrangadhra]], 20½ miles(33km) opened <ref name=Admin1918>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n178/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 170 (pdf178) ]; Retrieved 16 May 2020</ref>. | ||
| + | <br>''There was an interchange at [[Wadhwan]] to the broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) [[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]](BB&CIR) ‘[[Viramgam-Wadhwan Branch Line]]’ which had opened in 1873. <br>In 1902 this branch line was converted to [[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]] connected at [[Wadhwan|Wadhwan Junction]] the DR directly with the [[BB&CIR]].'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1898'''. Initially, the DR was worked by the '''[[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]]'''(BGJPR)<ref name=Admin1918/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1911'''. Upon the collapse of the BGJPR the working of the DR was undertaken by the '''[[Bhavnagar State Railway]]'''(BSR)<ref name=Admin1918/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1915'''. The line was extended from [[Dhrangadhra]] to [[Halvad]] , 20 miles(32km) opened , and the ‘Dhrangadra Quarry Branch’ 2½ mile(4km)<ref name=Admin1918/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1915'''. An application was made for a further extension of the line from [[Halvad]] to [[Malia]]. <br>''This caused an appeal by [[Morvi State]] that the line would be prejudicial to their [[Morvi Railway#Morvi Tramway|'Morvi Tramway']] that had been constructed from [[Morvi ]] to [[Malia]] and served the north-east part of Morvi territory. This tramway to [[Malia]] had been completed by 1910<ref>British Library IOR/V/10/1610 1909-10 TO 1927-28 ‘Report for 1909-10’ </ref>.'' | ||
| + | <br>''However this line that had at one time reached [[Malia]] had been removed at Malia’s expense back as far as the State line, and finished at Khakhrechi Road <ref name= Page4Para1>British Library IOR/R/2/746 306 Extension of Dhrangadra Railway to Malia Page 4 Paragraph 1 </ref>. The Bombay Government initially decided that the '[[Morvi Tramway]]' to [[Malia]] should be reinstated, but the requested Dhangadhra link to Malia would be preferred. This was intened to stop a disagreement between Morvi and Dhangadhra but only caused Dhangadhra and Malia to refuse to assist the Government and Morvi Engineers. | ||
| + | <br>Eventually in 1925 [[Dhrangadhra State]] was given approval for the extension to be built by 'Dhangadhra Railway'<ref name= Page4Para1/>'' '' see 1925 below'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1919'''. The working of the DR transferred to the '''[[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]]'''(BB&CIR) | ||
| + | <ref name =Admin1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 50-51, 73-74 pdf ]; Retrieved 16 May 2020</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1925'''. The further extension from [[Halvad]] to [[Malia]] was approved for construction after 10 years delay from application <ref name= Page4Para1/>. | ||
| + | <br>''The date of opening of this ‘Halvad-Malia Extension’ of approximately 25 miles(48km) has not been found, but it does appear on modern maps.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1926'''. The record shows the ‘Dhrangadra Quarry Branch’ had been closed but the ‘New entrance to Quarry siding at Kuda’ 0.13 mile(0.2km) had opened <ref name =Admin1937/>. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Records== | ==Records== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 69: | ||
==Further Information== | ==Further Information== | ||
| − | '''[[Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems]]''' gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula. | + | See '''[[Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems]]''' gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula. |
| + | <br>and '''[[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]]''' from 1898 to 1911 | ||
| + | <br>also '''[[Bhavnagar State Railway]]''' from 1911 to 1919 | ||
| + | <br>then '''[[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]]''' from 1919 onward | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:19, 17 May 2020
| Dhrangadhra Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Dhrangadhra to Wadhwan | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 21 miles (1905) 40 miles (1942) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1898 | Opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Dhrangadhra, Wadhwan | |
| System agency | ||
| 1898 | Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway | |
| 1911 | Bhavnagar State Railways | |
| 1943 | Morvi Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Dhrangadhra Railway (DR) was a short metre gauge(MG) line constructed for and owned by the Princely Dhrangadhra State.
History
1898. The first section of the ‘Dhrangadhra Railway’(DR) from Wadhwan to Dhrangadhra, 20½ miles(33km) opened [1].
There was an interchange at Wadhwan to the broad gauge(BG) Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) ‘Viramgam-Wadhwan Branch Line’ which had opened in 1873.
In 1902 this branch line was converted to MG connected at Wadhwan Junction the DR directly with the BB&CIR.
1898. Initially, the DR was worked by the Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway(BGJPR)[1].
1911. Upon the collapse of the BGJPR the working of the DR was undertaken by the Bhavnagar State Railway(BSR)[1].
1915. The line was extended from Dhrangadhra to Halvad , 20 miles(32km) opened , and the ‘Dhrangadra Quarry Branch’ 2½ mile(4km)[1].
1915. An application was made for a further extension of the line from Halvad to Malia.
This caused an appeal by Morvi State that the line would be prejudicial to their 'Morvi Tramway' that had been constructed from Morvi to Malia and served the north-east part of Morvi territory. This tramway to Malia had been completed by 1910[2].
However this line that had at one time reached Malia had been removed at Malia’s expense back as far as the State line, and finished at Khakhrechi Road [3]. The Bombay Government initially decided that the 'Morvi Tramway' to Malia should be reinstated, but the requested Dhangadhra link to Malia would be preferred. This was intened to stop a disagreement between Morvi and Dhangadhra but only caused Dhangadhra and Malia to refuse to assist the Government and Morvi Engineers.
Eventually in 1925 Dhrangadhra State was given approval for the extension to be built by 'Dhangadhra Railway'[3] see 1925 below
1919. The working of the DR transferred to the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) [4].
1925. The further extension from Halvad to Malia was approved for construction after 10 years delay from application [3].
The date of opening of this ‘Halvad-Malia Extension’ of approximately 25 miles(48km) has not been found, but it does appear on modern maps.
1926. The record shows the ‘Dhrangadra Quarry Branch’ had been closed but the ‘New entrance to Quarry siding at Kuda’ 0.13 mile(0.2km) had opened [4].
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [5] gives the following: -
- R/2/746/306; "File R/C 540:1916-1918:25 Railways - Extension of Dhrangadhra-Morvi Railway to Malia"; 1916-1918
- L/F/7/299; “Collection 31/3: Bombay Baroda and Central India Railway: Contract as to the costs of Railway Board's control of the Dhrangadhra Railway; 1930”
- L/F/8/20/1760; “Bombay Baroda and Central India Railway Company, Contract as to the costs of the Railway Board's control of the Dhrangadhra Railway; 1930”
Further Information
See Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula.
and Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway from 1898 to 1911
also Bhavnagar State Railway from 1911 to 1919
then Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway from 1919 onward
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 170 (pdf178) ; Retrieved 16 May 2020
- ↑ British Library IOR/V/10/1610 1909-10 TO 1927-28 ‘Report for 1909-10’
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 British Library IOR/R/2/746 306 Extension of Dhrangadra Railway to Malia Page 4 Paragraph 1
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 50-51, 73-74 pdf ; Retrieved 16 May 2020
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 22 Jan 2016