Difference between revisions of "Jodhpur State Railway"
('Person link' to 'Walter Home' created and text added) |
m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{System_Railways_Infobox | {{System_Railways_Infobox | ||
| − | |image= | + | |image= Jodhpur Railway Logo.png |
| − | |caption= | + | |caption= Jodhpur (State) Railway Logo |
|timeline1date= 1924 | |timeline1date= 1924 | ||
|timeline1details= System formed | |timeline1details= System formed | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | The '''Jodhpur State Railway''' (JSR) was created in 1924 and took over responsibility for working the "[[Jodhpur]] Section" of the [[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]], including the British section of the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Background == | |
| + | Originally named the '''Jodhpur Railway''' the first section opened as a metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) line in 1882, becoming the '''[[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]] ''' (JBR) in 1889. | ||
| − | In | + | In 1908 the JBR operated 828 miles(1325km) in the territories of Sind (under British control) and in territories of the States of Jodhpur and Bikaner. |
| − | By | + | By 1918 the ‘JBR System’ had expanded to 1355 miles(2180km); which comprised 1106 miles(1179km) plus a further 249 miles(401km) which JBR was working and operating under agreements with other railways <ref name=Admin1918>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n194/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page185, pdf page 194]; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016</ref>. |
| − | In 1924, the '''Jodhpur State Railway''' (JSR) | + | A further 210 miles(400km) were sanctioned or under construction by JBR in 1918 <ref name=Admin1918/>. |
| + | |||
| + | In 1924, the JBR was divided into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the '''Jodhpur State Railway'''(JSR) and [[Bikhaner State Railway]](BSR) formed to take over responsibility for working the raiway. The JSR taking the “Jodhpur Section” of the [[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]], together with the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]](British Section). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==1924 onwards== | ||
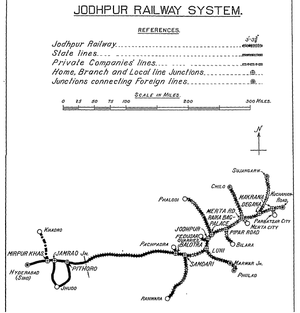
| + | [[File:Jodhpur Railway_System_1937_Map.png|thumb|Jodhpur Stae Railway System 1937 Map]] | ||
| + | '''Jodhpur State Railway''' (JSR) was created in 1924, the exact mileage comprising the “Jodhpur Section” is not known but in 1918 it was 687 miles(1105km) plus 124 miles(200km) of the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]](British Section). | ||
Writing critically in 1929 about third class travelling, Mahatma Ghandi condemned the latrines in JSR carriages as being "absolutely intolerable, insanitary and unfit for human use . . . The State railways should really be a model to the British system; whereas the actual state of things is the other way." | Writing critically in 1929 about third class travelling, Mahatma Ghandi condemned the latrines in JSR carriages as being "absolutely intolerable, insanitary and unfit for human use . . . The State railways should really be a model to the British system; whereas the actual state of things is the other way." | ||
<ref>[http://www.gandhiserve.org/cwmg/VOL045.PDF Mahatma Ghandi, "Third-Class Travelling, ''Letters of Mahatma Ghandi'', Vol 45, 14 Feb 1929 page 41]; Retrieved 14 Jan 2016</ref> | <ref>[http://www.gandhiserve.org/cwmg/VOL045.PDF Mahatma Ghandi, "Third-Class Travelling, ''Letters of Mahatma Ghandi'', Vol 45, 14 Feb 1929 page 41]; Retrieved 14 Jan 2016</ref> | ||
| − | At Independence in 1947, the British section of the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]] became part of [[ | + | In 1936-37 the route mileage for the JSR had expanded to 767 miles(1234km); they were also operating the British section of the [[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]](British Section), expanded to 239 miles(384km) and also the [[Mirpur Khas-Khadro Railway]], 49 miles(79km). All these being metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) lines <ref>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 116, pdf 147 ]; Retrieved 18 Apr 2020</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | At Independence in 1947 the western portions of the ‘[[Jodhpur State Railway ]]’,the ‘[[Bikaner State Railway]]’ and the British section of the ‘[[Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway]]’ were ceded to the government of Pakistan becoming part of ‘[[Pakistan Railways]]’<ref>[http://rajasthanhistory.com/gpage5.html “History of Rail in Rajasthan” by Dr Mohanlal Gupta, Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of Rajasthan, Jodhpur]; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The remaining eastern portions of the ‘[[Jodhpur State Railway ]]’, excluding the ‘Marwar-Phulad Section’ and the ‘[[Bikaner State Railway]]’ became part of the of [[Northern Railway| ‘Indian Railways - Northern Railway Zone’ ]] in 1952. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further Information== | ||
| + | See '''[[Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway]] ''' for period up to 1924 | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 11 August 2020
| Jodhpur State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Jodhpur (State) Railway Logo | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1924 | System formed | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1924 | Jodhpur section of Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | |
| 1924 | Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Jodhpur | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | ||
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1947 | Pakistan Railways (British section, Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway) | |
| 1952 | Northern Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 807 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Jodhpur State Railway (JSR) was created in 1924 and took over responsibility for working the "Jodhpur Section" of the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway, including the British section of the Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway.
Background
Originally named the Jodhpur Railway the first section opened as a metre gauge(MG) line in 1882, becoming the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) in 1889.
In 1908 the JBR operated 828 miles(1325km) in the territories of Sind (under British control) and in territories of the States of Jodhpur and Bikaner.
By 1918 the ‘JBR System’ had expanded to 1355 miles(2180km); which comprised 1106 miles(1179km) plus a further 249 miles(401km) which JBR was working and operating under agreements with other railways [1].
A further 210 miles(400km) were sanctioned or under construction by JBR in 1918 [1].
In 1924, the JBR was divided into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the Jodhpur State Railway(JSR) and Bikhaner State Railway(BSR) formed to take over responsibility for working the raiway. The JSR taking the “Jodhpur Section” of the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway, together with the Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway(British Section).
1924 onwards
Jodhpur State Railway (JSR) was created in 1924, the exact mileage comprising the “Jodhpur Section” is not known but in 1918 it was 687 miles(1105km) plus 124 miles(200km) of the Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway(British Section).
Writing critically in 1929 about third class travelling, Mahatma Ghandi condemned the latrines in JSR carriages as being "absolutely intolerable, insanitary and unfit for human use . . . The State railways should really be a model to the British system; whereas the actual state of things is the other way." [2]
In 1936-37 the route mileage for the JSR had expanded to 767 miles(1234km); they were also operating the British section of the Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway(British Section), expanded to 239 miles(384km) and also the Mirpur Khas-Khadro Railway, 49 miles(79km). All these being metre gauge(MG) lines [3].
At Independence in 1947 the western portions of the ‘Jodhpur State Railway ’,the ‘Bikaner State Railway’ and the British section of the ‘Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway’ were ceded to the government of Pakistan becoming part of ‘Pakistan Railways’[4].
The remaining eastern portions of the ‘Jodhpur State Railway ’, excluding the ‘Marwar-Phulad Section’ and the ‘Bikaner State Railway’ became part of the of ‘Indian Railways - Northern Railway Zone’ in 1952.
Further Information
See Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway for period up to 1924
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page185, pdf page 194; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ Mahatma Ghandi, "Third-Class Travelling, Letters of Mahatma Ghandi, Vol 45, 14 Feb 1929 page 41; Retrieved 14 Jan 2016
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 116, pdf 147 ; Retrieved 18 Apr 2020
- ↑ “History of Rail in Rajasthan” by Dr Mohanlal Gupta, Department of Information and Public Relations, Government of Rajasthan, Jodhpur; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016