| The Families In British India Society (FIBIS) is a self-help organisation devoted to members researching their British India family history and the background against which their ancestors led their lives in India under British rule. Let FIBIS help you break down those brick walls in your research |
Satpura Railway: Difference between revisions
References format corrected |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Satpura Railway''' was a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) network developed by the [[Bengal Nagpur Railway]](BNR) from 1903 to 1913. | The '''Satpura Railway''' was a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) network developed by the [[Bengal Nagpur Railway]](BNR) from 1903 to 1913. The name ‘Satpura’ appears to have been adopted to describe the network after the ‘Satpura Range’ of hills in the [[Central Provinces]] <ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satpura_Range Wikipedia “Satpura Range” "]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref>. | ||
[[Nainpur]] was the focal point of the network which connected [[ | [[Nainpur]] was the focal point of the network which connected [[Jubbulpore]] with [[Gondia]], [[Mandla]] Fort, [[Chhindwara]] and [[Nagpur]] <ref name=wiki>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satpura_narrow_gauge_lines Wikipedia "Satpura Narrow Gauge Lines"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref>. | ||
<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satpura_narrow_gauge_lines Wikipedia "Satpura Narrow Gauge Lines"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> | |||
At [[Nagpur]] and [[Gondia]] there were connections with BNR's [[Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway |Nagpur Chhattisgarh section]] broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) mainline that crossed the Satpura network. | At [[Nagpur]] and [[Gondia]] there were connections with BNR's [[Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway |Nagpur Chhattisgarh section]] broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) mainline that crossed the Satpura network. | ||
== | ==History== | ||
Some ten years after the Bengal Nagpur Railway Company(BNR) was formed, engineering surveys were carried out in the then Central Provinces with a view to open a low-cost railway that would unite the region into a whole. The object of the railway was two-fold: first, to open up the agricultural and mineral resources of the region; and secondly, to safeguard the inhabitants of the area should a famine arise. The gauge selected for the purpose was 2 feet 6 inches | Some ten years after the [[Bengal Nagpur Railway]] Company(BNR) was formed in 1887, engineering surveys were carried out in the then Central Provinces with a view to open a low-cost railway that would unite the region into a whole. The object of the railway was two-fold: first, to open up the agricultural and mineral resources of the region; and secondly, to safeguard the inhabitants of the area should a famine arise. The gauge selected for the purpose was 2 feet 6 inches narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) | ||
<ref name=name>[http://railwaysofraj.blogspot.fr/2013/05/a-tribute-to-satpura-railway-part-i.html "A Tribute to the Satpura Railway (Part I)"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> | <ref name=name>[http://railwaysofraj.blogspot.fr/2013/05/a-tribute-to-satpura-railway-part-i.html "A Tribute to the Satpura Railway (Part I)"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> | ||
BNR signed a contract with Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) for the Narrow Gauge Satpura Railway on 23rd January 1902 for constructing the Gondia- | [[File:Satpura Railway 1909.png|thumb| Satpura Railway 1909]] | ||
[[File:Satpura Railway c.1930.png|thumb| Satpura Railway c.1930]] | |||
BNR signed a contract with Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) for the Narrow Gauge Satpura Railway on 23rd January 1902 for constructing the Gondia-Jubbulpore, Nainpur-Mandla Fort, Nainpur-Seoni-Chhindwara lines. | |||
<ref>[http://www.secr.indianrailways.gov.in/uploads/files/1312278598168-Tourist%20Places.pdf Indian Railways "History of Nagpur Division"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> | <ref>[http://www.secr.indianrailways.gov.in/uploads/files/1312278598168-Tourist%20Places.pdf Indian Railways "History of Nagpur Division"]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> | ||
The 1918 “Administration Report” (see references below) gave a total network length of 705miles(1134km) comprising:- | |||
* [[Jubbulpore-Gondia Railway]] - 391 miles(629km) | |||
*[[Nagpur-Chhindwara Railway]] - 97 miles(156km) | |||
*[[ Gondia-Chanda Extension Railway]] - 217 miles(349 km) | |||
The 1936-37 “Report on Indian Railway” <ref>[http://hdl.handle.net/10973/18160 “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” page 117 Appendix A (pdf 149)]; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015</ref> gave the Satpura Section of the Bengal Nagpur Railway as having a route mileage of 626 miles (1007km). The network comprising this extended line length has not been determined. | |||
==Satpura Network== | ==Satpura Network== | ||
*Gondia-Nainpur Railway, opened | Information taken from the” Administration Report for Railways 1918” | ||
*Nainpur | |||
* | '''[[Jubbulpore-Gondia Railway]]''' | ||
*[[Chhindwara | <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n15/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 6 (pdf15)]; Retrieved 11 Dec 2016</ref> | ||
*[[ | * ‘Jubbulpore-Gondia Mainline’, the first section [[Nainpur]] to [[Gondia]] via Balaghat opened 1903; [[Jubbulpore]] to [[Nainpur]] via Howbagh, and Burgi opened 1904-05. Total length 142 miles(228 km) | ||
*[[Nagpur | ** [[Nainpur-Mandla Fort Railway]], (described as the ‘Mandla Branch Line’), opened from [[Nainpur]] to [[Mandla]] Fort (described as Garha Mandia) , 1909. Length 26 miles (42km) | ||
** ‘Barkuhi Branch Line’ opened from [[Nainpur]] via Seoni and Chaurai to [[Chhindwara]], 1904; to Khirsadoh 1906; to Barkuhi, 1907. Length 109 miles(175km) | |||
**‘Katangi Branch Line’ from Balaghat to Katangi, opened 1913, 29 miles(46km); | |||
*** ‘Ram Rama Branch Line’, opened 1913, 5.4 miles(8km), ''shown on 1931 map, not now existing,'' | |||
** ‘Khirsadoh-Sirgora Spur Line’ from Khirsadoh on the ‘Barkuhi Branch Line’, under construction 1918. Length 8.4 miles(13km) | |||
** ‘Itwari Bazar Scheme’, under construction 1918 in suburbs of [[Nagpur]] . Length 0.6 miles(1km) | |||
'''[[Nagpur-Chhindwara Railway]]''' | |||
<ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n15/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 8 (pdf17)]; Retrieved 11 Dec 2016</ref> | |||
* ‘Nagpur-Chhindwara Mainline’, opened from Itwari , in suburbs of [[Nagpur]] via Saoner, Lodhikhera and Sansar, 1911; to [[Chhindwara]]. Length 89 miles(143km) | |||
** ‘Saoner-Khapa Branch Line’, opened from Saoner to Khapa, 1911. Length 4.5 miles(7km) | |||
** ‘ Katchidhana Branch Line’, route not identified, 1912. Length 4 miles(6km) | |||
'''[[ Gondia-Chanda Extension Railway]]''' | |||
<ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n15/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 6 (pdf15)]; Retrieved 11 Dec 2016</ref> | |||
* ‘Gondia-Chanda Mainline’, opened from [[Gondia]] to [[Nagbhir]], 1908; to Rajoli, 1910; to Babupeth, 1913; reaching [[Chanda]] Fort in 1916. The Nagbhir-Chanda work was started in 1906 but due to the shortage of funds was not completed until 1st April 1913 .<ref>[http://www.secr.indianrailways.gov.in/uploads/files/1312278598168-Tourist%20Places.pdf Indian Railways “History of Nagpur Division” ]; Retrieved 11 Dec 2016</ref> as far as Babupeth with the last 2 miles to [[Chanda]] Fort opening in 1916. Length 149 miles(239 km) | |||
* '[[Nagbhir-Nagpur Branch Railway]]’, opened from [[Nagbhir]] to Itwari , in suburbs of [[Nagpur]], 1908 with later rearrangements at Itwari. Length 68 miles ( 109km) | |||
== Worked by BNR's Satpura Railway== | == Worked by BNR's Satpura Railway== | ||
'''[[Chhindwara-Pench Coal Fields Railway]]''' opened from the Pench and Kanhan coalfields to [[Chhindwara]]; where it connected to the Satpura Railway network, 1906-7. Length 22 miles(36km) | |||
'''[[Tumsar-Katangi Light Railway]]''', a a 2ft/610mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]])private line built to carry manganese ore deposits found in the region; this line ceased operation in 1929. The line interchanged with ‘Katangi Branch Line’ of the Satpura network at Katangi; it also interchanged at Tumsar Raoad with BNR's [[Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway |Nagpur Chhattisgarh section]] broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) mainline that crossed the Satpura network. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 29: | Line 56: | ||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:State Railways]] | [[Category:State Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Narrow Gauge (NG) Railways]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:47, 15 June 2020
The Satpura Railway was a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) network developed by the Bengal Nagpur Railway(BNR) from 1903 to 1913. The name ‘Satpura’ appears to have been adopted to describe the network after the ‘Satpura Range’ of hills in the Central Provinces [1].
Nainpur was the focal point of the network which connected Jubbulpore with Gondia, Mandla Fort, Chhindwara and Nagpur [2].
At Nagpur and Gondia there were connections with BNR's Nagpur Chhattisgarh section broad gauge(BG) mainline that crossed the Satpura network.
History
Some ten years after the Bengal Nagpur Railway Company(BNR) was formed in 1887, engineering surveys were carried out in the then Central Provinces with a view to open a low-cost railway that would unite the region into a whole. The object of the railway was two-fold: first, to open up the agricultural and mineral resources of the region; and secondly, to safeguard the inhabitants of the area should a famine arise. The gauge selected for the purpose was 2 feet 6 inches narrow gauge(NG) [3]
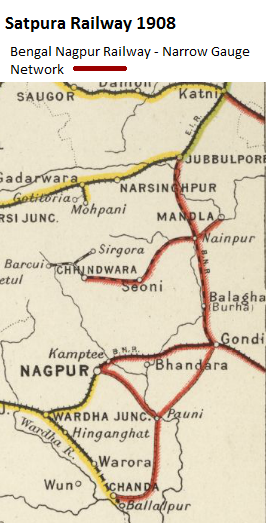

BNR signed a contract with Government of India(GoI) for the Narrow Gauge Satpura Railway on 23rd January 1902 for constructing the Gondia-Jubbulpore, Nainpur-Mandla Fort, Nainpur-Seoni-Chhindwara lines. [4]
The 1918 “Administration Report” (see references below) gave a total network length of 705miles(1134km) comprising:-
- Jubbulpore-Gondia Railway - 391 miles(629km)
- Nagpur-Chhindwara Railway - 97 miles(156km)
- Gondia-Chanda Extension Railway - 217 miles(349 km)
The 1936-37 “Report on Indian Railway” [5] gave the Satpura Section of the Bengal Nagpur Railway as having a route mileage of 626 miles (1007km). The network comprising this extended line length has not been determined.
Satpura Network
Information taken from the” Administration Report for Railways 1918”
- ‘Jubbulpore-Gondia Mainline’, the first section Nainpur to Gondia via Balaghat opened 1903; Jubbulpore to Nainpur via Howbagh, and Burgi opened 1904-05. Total length 142 miles(228 km)
- Nainpur-Mandla Fort Railway, (described as the ‘Mandla Branch Line’), opened from Nainpur to Mandla Fort (described as Garha Mandia) , 1909. Length 26 miles (42km)
- ‘Barkuhi Branch Line’ opened from Nainpur via Seoni and Chaurai to Chhindwara, 1904; to Khirsadoh 1906; to Barkuhi, 1907. Length 109 miles(175km)
- ‘Katangi Branch Line’ from Balaghat to Katangi, opened 1913, 29 miles(46km);
- ‘Ram Rama Branch Line’, opened 1913, 5.4 miles(8km), shown on 1931 map, not now existing,
- ‘Khirsadoh-Sirgora Spur Line’ from Khirsadoh on the ‘Barkuhi Branch Line’, under construction 1918. Length 8.4 miles(13km)
- ‘Itwari Bazar Scheme’, under construction 1918 in suburbs of Nagpur . Length 0.6 miles(1km)
- ‘Nagpur-Chhindwara Mainline’, opened from Itwari , in suburbs of Nagpur via Saoner, Lodhikhera and Sansar, 1911; to Chhindwara. Length 89 miles(143km)
- ‘Saoner-Khapa Branch Line’, opened from Saoner to Khapa, 1911. Length 4.5 miles(7km)
- ‘ Katchidhana Branch Line’, route not identified, 1912. Length 4 miles(6km)
Gondia-Chanda Extension Railway [8]
- ‘Gondia-Chanda Mainline’, opened from Gondia to Nagbhir, 1908; to Rajoli, 1910; to Babupeth, 1913; reaching Chanda Fort in 1916. The Nagbhir-Chanda work was started in 1906 but due to the shortage of funds was not completed until 1st April 1913 .[9] as far as Babupeth with the last 2 miles to Chanda Fort opening in 1916. Length 149 miles(239 km)
- 'Nagbhir-Nagpur Branch Railway’, opened from Nagbhir to Itwari , in suburbs of Nagpur, 1908 with later rearrangements at Itwari. Length 68 miles ( 109km)
Worked by BNR's Satpura Railway
Chhindwara-Pench Coal Fields Railway opened from the Pench and Kanhan coalfields to Chhindwara; where it connected to the Satpura Railway network, 1906-7. Length 22 miles(36km)
Tumsar-Katangi Light Railway, a a 2ft/610mm narrow gauge(NG)private line built to carry manganese ore deposits found in the region; this line ceased operation in 1929. The line interchanged with ‘Katangi Branch Line’ of the Satpura network at Katangi; it also interchanged at Tumsar Raoad with BNR's Nagpur Chhattisgarh section broad gauge(BG) mainline that crossed the Satpura network.
References
- ↑ Wikipedia “Satpura Range” "; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ Wikipedia "Satpura Narrow Gauge Lines"; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ "A Tribute to the Satpura Railway (Part I)"; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ Indian Railways "History of Nagpur Division"; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” page 117 Appendix A (pdf 149); Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 6 (pdf15); Retrieved 11 Dec 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 8 (pdf17); Retrieved 11 Dec 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 6 (pdf15); Retrieved 11 Dec 2016
- ↑ Indian Railways “History of Nagpur Division” ; Retrieved 11 Dec 2016