Havelock Bridge: Difference between revisions
m Minor changes only |
minor revisions and added info |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Havelock Bridge''' (Godavari Old Bridge) spanned the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh | The '''Havelock Bridge''' (Godavari Old Bridge) spanned the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh. The bridge formed a vital link in the broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) [[East Coast State Railway]] mainline between [[Howrah]] and [[Madras]](Chennai). | ||
The construction of the bridge commenced on November 11, 1897 and opened for traffic on August 30, 1900. | Some records describe this as the ‘Godavri Bridge’ which is identified as the ‘Godavri Old Bridge’ | ||
<ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Old_Godavari_Bridge Wikipedia "Old Godavari Bridge"]; Retrieved | |||
[[File:Havelock Bridge.png|thumb|Havelock Bridge]] | |||
The construction of the bridge commenced on November 11, 1897 and opened for traffic on August 30, 1900. | |||
<br> The bridge was constructed with stone masonry and steel girders. It had 56 spans each of 45.7 metres (150 ft)and is 3,480 metres (11,420 ft) long | |||
<ref name=Wiki>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Old_Godavari_Bridge Wikipedia "Old Godavari Bridge"]; Retrieved 25 Nov 2020</ref> | |||
==Personnel== | |||
The Consulting Engineer on the project was [[Francis Joseph Edward Spring]] as Consulting Engineer to the Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) <ref name=Wiki/> | |||
The Bridge was named after Sir Arthur Elibank Havelock, the then Governor of Madras. | |||
*[[Frederick Thomas Granville Walton]] served as the Engineer-in-chief assisted by executive engineers:- | |||
** R.A.Delanougerede | |||
** F.D.Couchman | |||
** J.E.Eaglesome | |||
==Later History== | |||
In 1901 the southern section of the [[East Coast State Railway]] - which included the ‘Havelock Bridge’ - was transferred to the [[Madras Railway]](MR) in 1901; subsequently renamed [[Madras (North-East) Railway]]; becoming the [[Madras-Waltair NE Mainline]] of the [[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway]](M&SMR) in 1908. | |||
In 1946 there was complete ‘re-flooring’ of the bridge by replacing the wooden longitudinal and wooden sleepers with a steel system <ref name=ICE1946>[https://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/ijoti.1946.13744 Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers, Volume 26 Issue 7, May 1946, pp. 403-405 “The re-flooring of the Kistna and Godavari Bridges on the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway “by D.H.McPherson]; Retrieved 26 Nov 2020</ref>. | |||
The bridge was decommissioned in 1997 replaced by the Godavari Arch Bridge <ref name=Wiki/>. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 27 November 2020
The Havelock Bridge (Godavari Old Bridge) spanned the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh. The bridge formed a vital link in the broad gauge(BG) East Coast State Railway mainline between Howrah and Madras(Chennai).
Some records describe this as the ‘Godavri Bridge’ which is identified as the ‘Godavri Old Bridge’
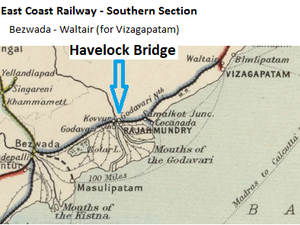
The construction of the bridge commenced on November 11, 1897 and opened for traffic on August 30, 1900.
The bridge was constructed with stone masonry and steel girders. It had 56 spans each of 45.7 metres (150 ft)and is 3,480 metres (11,420 ft) long
[1]
Personnel
The Consulting Engineer on the project was Francis Joseph Edward Spring as Consulting Engineer to the Government of India(GoI) [1]
The Bridge was named after Sir Arthur Elibank Havelock, the then Governor of Madras.
- Frederick Thomas Granville Walton served as the Engineer-in-chief assisted by executive engineers:-
- R.A.Delanougerede
- F.D.Couchman
- J.E.Eaglesome
Later History
In 1901 the southern section of the East Coast State Railway - which included the ‘Havelock Bridge’ - was transferred to the Madras Railway(MR) in 1901; subsequently renamed Madras (North-East) Railway; becoming the Madras-Waltair NE Mainline of the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(M&SMR) in 1908.
In 1946 there was complete ‘re-flooring’ of the bridge by replacing the wooden longitudinal and wooden sleepers with a steel system [2].
The bridge was decommissioned in 1997 replaced by the Godavari Arch Bridge [1].
References