Barsi Light Railway: Difference between revisions
External Link format corrected |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|system3details= | |system3details= | ||
|gauge1= 2' 6" NG | |gauge1= 2' 6" NG | ||
|gauge1details= 22 miles (1897) | |gauge1details= 22 miles (1897, 1905) | ||
|gauge2= | |gauge2= | ||
|gauge2details= 202 miles (1927) | |gauge2details= 202 miles (1927) | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|auxillary forces= | |auxillary forces= | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File: Barsi Light Railway Map 1909.png|thumb| Barsi Light Railway Map 1909]] | |||
'''Barsi Light Railway''' (BLR) | '''Barsi Light Railway''' (BLR) | ||
The Barsi Light Railway Company owned and worked the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) railway that initially connected [[Barsi]] to the main Bombay-Madras trunk line of the [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]] (GIPR) at | The Barsi Light Railway Company owned and worked the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) railway that initially connected [[Barsi]] to the main Bombay-Madras trunk line of the [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]] (GIPR) at Barsi Road, a distance of 22 miles(35km). | ||
<ref>[https:// | <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n222/mode/1up " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 214]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref> | ||
Conceived by the ex-GIPR engineer, | Conceived by the ex-GIPR engineer, [[Everard Richard Calthrop]], the '''Barsi Light Railway''' revolutionised the approach to narrow gauge feeder lines in India, and was immensely successful. By 1927, the line had been extended significantly over 202 route miles(323km)<ref name=WikiBarsi>[ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barsi_Light_Railway Wikipedia “Barsi Light Railway” ]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref> | ||
the '''Barsi Light Railway''' revolutionised the approach to narrow gauge feeder lines in India, and was immensely successful. By 1927, the line had been extended significantly over 202 route miles(323km). | |||
The line remained in private ownership until 1954 when it was purchased by Indian Railways. | The line remained in private ownership until 1954 when it was purchased by Indian Railways. | ||
== | ==Background: The Barsee Tramway== | ||
[http:// | The [[Barsee Tramway]] was a project, proposed in 1862, to construct a bullock driven Tramway 'to connect Barsee with the Barsee railway station’. In the event the Tramway was not installed but the groundwork had been completed with the construction of the earth works, cuttings and bridges and was completed in 1870 <ref name=Engineering>“Barsi Light Rail - E.R.Calthrope & the Newly Exhibition” from ‘Engineering’ 20 Jan 1897, page 183. Reproduced by ‘Narrow Gauge and Industrial Railway Modeling Review’ No 69 Vol 9 January 2007, editor Roy C Link. ISSN 0958-0808</ref>. | ||
By the 1870’s [[Barsi]] had become the spelling of the town. Barsi Town was connected to Barsi Road Station , on the [[GIPR]], a distance of 22 miles (35km), utilising the completed groundworks providing a roadway of 24 foot width (7.3 metres) with 'hard shoulders' <ref>British Library IOR/V/23/232, No 71; "Papers relating to the project of connecting Barsee with the Barsee railway station by tramways.” Bombay: Education Society's Press, 1863" File held on Microfiche, page 25 </ref> and designed to be built with sufficient strength to carry locomotives and the gradients which did not exceed 1 in 100 <ref name=Engineering/>. The Seena (Sina) River bridge was a ten arch masonry constructed bridge. | |||
See '''[[Barsee Tramway]] ''' for further information. | |||
==History : The Barsi Light Railway (BLR)== | |||
[[Everard Richard Calthrop]] had, in 1887, registered in London the [[Indian Railways Feeder Lines Company]] to promote the construction of narrow gauge ([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) lines in India. He resigned from [[GIPR]] in 1889. | |||
Calthrop, in 1887, commenced negotiations with the Government of Bombay for a concession to build a Light Railway on the bed of the 'Road'. Negotiations were concluded and in 1895 the '''[[Barsi Light Railway|'Barsi Light Railway Company']]''' (BLR) was formed and incorporated in London on 11 July 1895 <ref>British Library IOR/L/F/5/117 “The Barsi Light Railway Company”, 1895 onwards. Document 1, page 1</ref> utilising engineering solutions based on many innovative designs. | |||
A request for tender was put out and on the 1 August 1895 an agreement was signed to build a 2ft 6inch narrow gauge [[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]] light railway between the Barsi Road Station on the [[GIPR]] Station (now Kurduvadi) and the Barsi (now Barshi) Town utilising the ‘The Road' as the trackbed. The line, of 21.59 miles (34.75km) opened to traffic on 1 March 1897 <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n222/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 214 (pdf222)]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref> becoming the first section of the BLR. | |||
The line followed what is now designated Route 77 and crossed the Seena River on the bridge of 10 masonry arches, into the Nizam of Hyrdabad territory and then passing out again into Government territory and terminating in [[Barsi]] <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 1</ref> The road rails were to be grooved or double rails and be maintained flush with the metalled road where it either crossed or ran along it. Only one set of rails were to be allowed on the metalled surface. <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 2</ref> The Locomotives were to be oil/petrol fired steam engines. <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 5</ref> | |||
The BLR was a commercial success and in 1905 yielded a return on capital of 4.96% <ref>[http://www.new.dli.ernet.in/handle/2015/94040 Digital Library of India “1907 Administration Report On The Railways In India” pdf format. “Appendix 38 History of open lines at 31 Dec 1906”, page 203 (pdf 214) )]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref>. | |||
The [[Railway Board]] had authorised further extensions (see below) and the initial 22 miles(35km) had expanded to 117 miles(183km) by 1918 with yield rising to 7.54% in 1916-17<ref name=Admin/>. By 1927 the line length had become 202 route miles(323km)<ref name=WikiBarsi/> | |||
The BSR continued to operate as a narrow-gauge railway until conversion to broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) began in the late 1990s but this was also on a different alignment as now the railway now runs around Barsi to the east and south of the old line. The narrow gauge line is now closed but the remnants are visible all along the route. The new line was completed on 19 October 2008 <ref name=WikiBarsi/> | |||
==BLR System and Extensions== | |||
Information generally based on “Administration Report on Railways 1918” <ref name=Admin/> | |||
* ‘Main Line’ | |||
** ‘Kurduvai To Barsi Town’, 22 miles(35km), opened 1897 | |||
* ‘Barsi Town-Latur Extension' | |||
** ‘Barsi Town-Kuslamb’, 6.miles(10km), opened 1905 | |||
** ‘Kuslamb-Tadwala’, 20 miles(32km), opened 1906 | |||
* ‘Kurduvadi-Pandharpur Extension' | |||
** ‘Kurduvadi to near Pandharpur, 31 miles(50km), opened 1905 | |||
** ‘Extension to Pandharpur Town, 2 miles(3km), opened 1906 | |||
<blockquote>From Kurduvadi (originally named Barsi Road) to Pandharpur, 20.56 miles, opened 2 Dec 1906, extended further 1.78 miles , 16 July 1915. The variation order had been approved on 20 August 1895 signed by the Principality of Pandharpur stated they were building a bridge over the Bhima river to take the railway into the town the route to follow route 161 a distance 34 miles(54km) <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 2</ref>. Pandharpur was a significant pilgrimage town and the line was an extension of the BLR from Kurduvadi (Barsi Road) where there was a connection with the GIPR mainline.</blockquote> | |||
* ‘Tadwale to Latur Extension’ | |||
** ‘Tadwale to Hyderabad Frontier, 1 mile(1.6km), opened 1911 | |||
** ‘Hyderabad Frontier to Latur, 36 miles(58km), opened 1911 | |||
*‘Pandharpur-Miraj Extension’ | |||
** ‘Pandharpur to Miraj, 84. miles(135km), opened 1927<ref name=Hist1937>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 214, pdf 257 ]; Retrieved 5 Aug 2020</ref>. | |||
<blockquote>From Pandharpur via Lonard to Miraj, 'approximate length 77 miles, to connect to the [[Southern Mahratta Railway]](SMR Poona Branch) at Miraj. This line involved bridges over the Phima river at Pandharpur and the Man, south of Sangola, and was first proposed in 1906 <ref name=Proj1906>[https://archive.org/stream/RailwayProjects/Railway%20projects#page/n0/mode/1up “1906 Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906” page 6 (pdf 29) )]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref>. The finalised route was approved in August 1916 for an extension from Pandaharpur to Lonard and Miraj, a distance of 79 ½ miles (Km 126) <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 4</ref></blockquote> | |||
*‘Pandharpur-Bijapur Extension’ (via Athani) - ''proposed but not constructed'' | |||
<blockquote> From Pandharpur to Bijapur, ‘a length of about 77 miles, which would form a chord between Poona and Bijapur branches of the South Mahratta Railway’ <ref name=Proj1906/>.</blockquote> | |||
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 and the BLR System rising from 116 miles(186km) reaching 203 miles (326km) from 1928-29 onwards<ref name=Hist1937/> | |||
== Classification == | |||
[[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class II railway system. | |||
==Technical Innovations== | |||
The Barsi Light Railway is regarded as having revolutionised the narrow-gauge railway system of the Indian subcontinent. The engineer [[Everard Richard Calthrop]] applied a systematic and logical approach to narrow gauge design with an insistence on a rigidly imposed axle weight limit of five tons allowing lightweight construction of track work and engineering features while simultaneously building the rolling stock to the largest possible size to ensure maximum capacity. The introduction of rail inclination (now universal but then a new idea on railways of any gauge) which reduces wear on wheels and rails by tilting the rail a few degrees to make its surface more nearly parallel with that of the tyre <ref>[http://www.narrow-gauge-pleasure.co.uk/railways/rlyleekandmanifold.aspx Narrow Gauge Pleasure “ The Leek and Manifold Light Railway – Construction” by Nick Lewis]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017</ref>. Five 0-8-4T locomotives were constructed to Calthrop's specification by Kitson and Company. The goods rolling stock was constructed on common 25ft by 7 ft. (7.62 by 2.13 m) pressed-steel underframes, maximising wagon loads <ref name=WikiBarsi/>. | |||
The specification had 2 ft 6 inches overhang on each side of the track making a total width of 7 feet 6 inches <ref> IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 6</ref>. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:42, 19 August 2020
| Barsi Light Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1897 | Line opened to traffic | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Kurduvadi | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | Barsi Road, Barsi, Pandharpur, Tadwala | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1954 | purchased by Indian Railways | |
| System mileage | ||
| 2' 6" NG | 22 miles (1897, 1905) | |
| 202 miles (1927) | ||
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
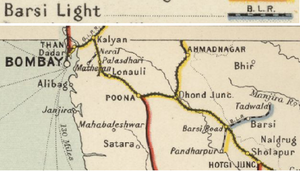
Barsi Light Railway (BLR)
The Barsi Light Railway Company owned and worked the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) railway that initially connected Barsi to the main Bombay-Madras trunk line of the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (GIPR) at Barsi Road, a distance of 22 miles(35km). [1]
Conceived by the ex-GIPR engineer, Everard Richard Calthrop, the Barsi Light Railway revolutionised the approach to narrow gauge feeder lines in India, and was immensely successful. By 1927, the line had been extended significantly over 202 route miles(323km)[2]
The line remained in private ownership until 1954 when it was purchased by Indian Railways.
Background: The Barsee Tramway
The Barsee Tramway was a project, proposed in 1862, to construct a bullock driven Tramway 'to connect Barsee with the Barsee railway station’. In the event the Tramway was not installed but the groundwork had been completed with the construction of the earth works, cuttings and bridges and was completed in 1870 [3].
By the 1870’s Barsi had become the spelling of the town. Barsi Town was connected to Barsi Road Station , on the GIPR, a distance of 22 miles (35km), utilising the completed groundworks providing a roadway of 24 foot width (7.3 metres) with 'hard shoulders' [4] and designed to be built with sufficient strength to carry locomotives and the gradients which did not exceed 1 in 100 [3]. The Seena (Sina) River bridge was a ten arch masonry constructed bridge.
See Barsee Tramway for further information.
History : The Barsi Light Railway (BLR)
Everard Richard Calthrop had, in 1887, registered in London the Indian Railways Feeder Lines Company to promote the construction of narrow gauge (NG) lines in India. He resigned from GIPR in 1889.
Calthrop, in 1887, commenced negotiations with the Government of Bombay for a concession to build a Light Railway on the bed of the 'Road'. Negotiations were concluded and in 1895 the 'Barsi Light Railway Company' (BLR) was formed and incorporated in London on 11 July 1895 [5] utilising engineering solutions based on many innovative designs.
A request for tender was put out and on the 1 August 1895 an agreement was signed to build a 2ft 6inch narrow gauge NG light railway between the Barsi Road Station on the GIPR Station (now Kurduvadi) and the Barsi (now Barshi) Town utilising the ‘The Road' as the trackbed. The line, of 21.59 miles (34.75km) opened to traffic on 1 March 1897 [6] becoming the first section of the BLR.
The line followed what is now designated Route 77 and crossed the Seena River on the bridge of 10 masonry arches, into the Nizam of Hyrdabad territory and then passing out again into Government territory and terminating in Barsi [7] The road rails were to be grooved or double rails and be maintained flush with the metalled road where it either crossed or ran along it. Only one set of rails were to be allowed on the metalled surface. [8] The Locomotives were to be oil/petrol fired steam engines. [9]
The BLR was a commercial success and in 1905 yielded a return on capital of 4.96% [10].
The Railway Board had authorised further extensions (see below) and the initial 22 miles(35km) had expanded to 117 miles(183km) by 1918 with yield rising to 7.54% in 1916-17[6]. By 1927 the line length had become 202 route miles(323km)[2]
The BSR continued to operate as a narrow-gauge railway until conversion to broad gauge(BG) began in the late 1990s but this was also on a different alignment as now the railway now runs around Barsi to the east and south of the old line. The narrow gauge line is now closed but the remnants are visible all along the route. The new line was completed on 19 October 2008 [2]
BLR System and Extensions
Information generally based on “Administration Report on Railways 1918” [6]
- ‘Main Line’
- ‘Kurduvai To Barsi Town’, 22 miles(35km), opened 1897
- ‘Barsi Town-Latur Extension'
- ‘Barsi Town-Kuslamb’, 6.miles(10km), opened 1905
- ‘Kuslamb-Tadwala’, 20 miles(32km), opened 1906
- ‘Kurduvadi-Pandharpur Extension'
- ‘Kurduvadi to near Pandharpur, 31 miles(50km), opened 1905
- ‘Extension to Pandharpur Town, 2 miles(3km), opened 1906
From Kurduvadi (originally named Barsi Road) to Pandharpur, 20.56 miles, opened 2 Dec 1906, extended further 1.78 miles , 16 July 1915. The variation order had been approved on 20 August 1895 signed by the Principality of Pandharpur stated they were building a bridge over the Bhima river to take the railway into the town the route to follow route 161 a distance 34 miles(54km) [11]. Pandharpur was a significant pilgrimage town and the line was an extension of the BLR from Kurduvadi (Barsi Road) where there was a connection with the GIPR mainline.
- ‘Tadwale to Latur Extension’
- ‘Tadwale to Hyderabad Frontier, 1 mile(1.6km), opened 1911
- ‘Hyderabad Frontier to Latur, 36 miles(58km), opened 1911
- ‘Pandharpur-Miraj Extension’
- ‘Pandharpur to Miraj, 84. miles(135km), opened 1927[12].
From Pandharpur via Lonard to Miraj, 'approximate length 77 miles, to connect to the Southern Mahratta Railway(SMR Poona Branch) at Miraj. This line involved bridges over the Phima river at Pandharpur and the Man, south of Sangola, and was first proposed in 1906 [13]. The finalised route was approved in August 1916 for an extension from Pandaharpur to Lonard and Miraj, a distance of 79 ½ miles (Km 126) [14]
- ‘Pandharpur-Bijapur Extension’ (via Athani) - proposed but not constructed
From Pandharpur to Bijapur, ‘a length of about 77 miles, which would form a chord between Poona and Bijapur branches of the South Mahratta Railway’ [13].
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 and the BLR System rising from 116 miles(186km) reaching 203 miles (326km) from 1928-29 onwards[12]
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class II railway system.
Technical Innovations
The Barsi Light Railway is regarded as having revolutionised the narrow-gauge railway system of the Indian subcontinent. The engineer Everard Richard Calthrop applied a systematic and logical approach to narrow gauge design with an insistence on a rigidly imposed axle weight limit of five tons allowing lightweight construction of track work and engineering features while simultaneously building the rolling stock to the largest possible size to ensure maximum capacity. The introduction of rail inclination (now universal but then a new idea on railways of any gauge) which reduces wear on wheels and rails by tilting the rail a few degrees to make its surface more nearly parallel with that of the tyre [15]. Five 0-8-4T locomotives were constructed to Calthrop's specification by Kitson and Company. The goods rolling stock was constructed on common 25ft by 7 ft. (7.62 by 2.13 m) pressed-steel underframes, maximising wagon loads [2].
The specification had 2 ft 6 inches overhang on each side of the track making a total width of 7 feet 6 inches [16].
References
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 214; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 [ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barsi_Light_Railway Wikipedia “Barsi Light Railway” ]; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 “Barsi Light Rail - E.R.Calthrope & the Newly Exhibition” from ‘Engineering’ 20 Jan 1897, page 183. Reproduced by ‘Narrow Gauge and Industrial Railway Modeling Review’ No 69 Vol 9 January 2007, editor Roy C Link. ISSN 0958-0808
- ↑ British Library IOR/V/23/232, No 71; "Papers relating to the project of connecting Barsee with the Barsee railway station by tramways.” Bombay: Education Society's Press, 1863" File held on Microfiche, page 25
- ↑ British Library IOR/L/F/5/117 “The Barsi Light Railway Company”, 1895 onwards. Document 1, page 1
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 214 (pdf222); Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 1
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 2
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 5
- ↑ Digital Library of India “1907 Administration Report On The Railways In India” pdf format. “Appendix 38 History of open lines at 31 Dec 1906”, page 203 (pdf 214) ); Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 2
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 214, pdf 257 ; Retrieved 5 Aug 2020
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 “1906 Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906” page 6 (pdf 29) ); Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 4
- ↑ Narrow Gauge Pleasure “ The Leek and Manifold Light Railway – Construction” by Nick Lewis; Retrieved 11 Jan 2017
- ↑ IOR/L/F/5/117. Document 1, page 6