Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway: Difference between revisions
Data added, links checked |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File: Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway Map.png| thumb|Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway]] | |||
The '''Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway''', also described as the '''Bangalore-Chik Ballapur Light Railway''', was a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) railway, operated by the ‘[[Mysore State Railway]]’(MSR). | |||
This railway was an enterprise by an Indian Company floated for the purpose under a guarantee from the Mysore Durbar . Construction was sanctioned in 1909 but the Company was unable to raise the entire capital and Mysore Durbar became joint owners <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n218/mode/1up " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 210]; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020</ref> | |||
The NG railway, 39 miles(62km) from [[Bangalore]] City via Yelanka to [[Chik-Ballapur]] opened in stages from 1915 from [[Chik-Ballapur]] where it connected to the NG ‘[[Kolar District Railway]]’ , to Yellanka in 1917 and finally reached Bangalore in 1918<ref name=Admin/>. | |||
Together these two railways were operated by the ‘[[Mysore State Railway]]’ as part of the ‘MSR System’ and provided a NG connection between [[Bangalore]] and [[Bowringpet]]. | |||
==Later Development== | |||
The section near Bangalore to Yelanka , 10 miles(16km), was subsequently dismantled<ref name=name>[http://www.irfca.org/articles/isrs/isrs082004-steam-history.html "Steam in History (India)"/ Yelahaka-Bangarpet Line by R R Bhandari. Reproduced by IRFCA ''Indian Railways Fan Club'']; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020</ref> leaving the line with the description '''Yelahaka-Bangarpet Railway''', worked as part of the ‘[[Mysore State Railway]]’(MSR). | |||
The date of this part closure has not been determined, it was certainly after 1937 <ref name=Hist>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 250, pdf 293 ]; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020</ref> where is was noted that this section had been converted to mixed gauge 2ft 6 in [[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]] and metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) with running rights given to the ‘[[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway]]’(M&SMR). It can be assumed this section, once closed was operating on [[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]] by the M&SMR. | |||
==External links== | |||
*[http://www.thehindu.com/features/magazine/siddharth-raja-on-the-100yearold-nandi-halt-station-that-time-forgot/article8537161.ece "The station that time forgot"] by Siddharth Raja April 30, 2016 ''The Hindu''. Nandi Halt station, at the foot of the Nandi Hills, was on part of the line which opened August 1, 1915. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Narrow Gauge (NG) Railways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:08, 17 October 2020
| Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Chikballapur to Bangalore | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| 2' 6" NG | 38 miles (1918) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1918 | Opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Madras | |
| Stations | Chikballapur, Bangalore | |
| System agency | ||
| 1918 | Worked by Mysore State Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
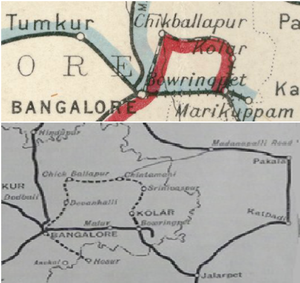
The Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway, also described as the Bangalore-Chik Ballapur Light Railway, was a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) railway, operated by the ‘Mysore State Railway’(MSR). This railway was an enterprise by an Indian Company floated for the purpose under a guarantee from the Mysore Durbar . Construction was sanctioned in 1909 but the Company was unable to raise the entire capital and Mysore Durbar became joint owners [1]
The NG railway, 39 miles(62km) from Bangalore City via Yelanka to Chik-Ballapur opened in stages from 1915 from Chik-Ballapur where it connected to the NG ‘Kolar District Railway’ , to Yellanka in 1917 and finally reached Bangalore in 1918[1].
Together these two railways were operated by the ‘Mysore State Railway’ as part of the ‘MSR System’ and provided a NG connection between Bangalore and Bowringpet.
Later Development
The section near Bangalore to Yelanka , 10 miles(16km), was subsequently dismantled[2] leaving the line with the description Yelahaka-Bangarpet Railway, worked as part of the ‘Mysore State Railway’(MSR).
The date of this part closure has not been determined, it was certainly after 1937 [3] where is was noted that this section had been converted to mixed gauge 2ft 6 in NG and metre gauge(MG) with running rights given to the ‘Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway’(M&SMR). It can be assumed this section, once closed was operating on MG by the M&SMR.
External links
- "The station that time forgot" by Siddharth Raja April 30, 2016 The Hindu. Nandi Halt station, at the foot of the Nandi Hills, was on part of the line which opened August 1, 1915.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 210; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020
- ↑ "Steam in History (India)"/ Yelahaka-Bangarpet Line by R R Bhandari. Reproduced by IRFCA Indian Railways Fan Club; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 250, pdf 293 ; Retrieved 14 Oct 2020