Mysore State Railway
| Mysore State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Mysore State Railway Logo | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Mysore to Bangalore Bangalore to Harihar | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 296 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1887 | Leased to Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| 1919 | Mysore-Bangalore section reverted to State | |
| 1938 | Bangalore-Harihar section reverted to State | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Madras | |
| Stations | Bangalore, Birur, Harihar, Kadur, Maddur, Mysore, Seringapatam, Tumkur | |
| System agency | ||
| 1882 | Worked by Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| 1938 | Reverted to Mysore State Railway control | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Mysore State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1887 | Original Mysore State Lines leased to Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| 1912 | System re-formed by State of Mysore | |
| 1919 | Reversion of some lines | |
| 1938 | Lease terminated and lines reverted to full State of Mysore control | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1919 & 1938 | Mysore State Railway | |
| 1938 | Anandapuram-Sagara Railway | |
| 1919 | Birur-Shimoga Railway | |
| 1916 | Bowringpet-Chikballapur Railway | |
| 1921 | Chickjajur-Chitaldrug Railway | |
| 1918 | Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway | |
| 1918 | Mysore-Arsikere Railway | |
| 1919 | Mysore-Nanjangud Railway | |
| 1926 | Nanjangud-Chamrajnagar Railway | |
| 1934 | Shimoga-Anandapuram Railway | |
| 1921 | Tadasa-Hebbe Tramway | |
| 1917 | Tarikere-Narasimharajapura Tramway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Mysore | |
| Workshops | Bangalore | |
| Major Stations | Arsikere, Birur, Bowringpet, Chamrajnagar, Chikballapur, Chitaldrug, Harihar, Hassan, Hindupur, Kadur, Maddur, Nanjangud, Seringapatam, Shimoga, Tumkur | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1950 | Nationalised | |
| 1951 | Southern Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 600 miles (1940) | |
| 2' 6" NG | 102 miles (1940) | |
| 2' 0" | 36 miles (1940) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The name, Mysore State Railway (MSR), originally referred to the metre gauge(MG) line which connected the State capital, Mysore, to Bangalore and named the Mysore-Bangalore Railway. The MSR also developed a number of other railways which from 1887 were initially leased to the Southern Mahratta Railway (SMR).
Later, the MSR, or Mysore Railway as it was sometimes known in this context, was the name applied to a network of disjointed metre gauge(MG) branch lines owned by the Princely Mysore State Durbar.
Original Mysore State Railway History

- 1872-73: Proposals to develop railways in Mysore State were turned down in favour of irrigation projects “for the improvement and re-establishment of the ancient system of irrigation, before any outlay is applied to the construction of a railway” [1]
- 1876-77: following the disastrous famine the original sections of the MSR were planned and built by the State of Mysore,
- 1881-82 opening to traffic.
- 1887: in order to eradicate its "famine debt", the State of Mysore leased the MSR to the Southern Mahratta Railway (SMR) for a period of 45 years.[2].
- 1893: it was determined that the Mysore State Railway (MSR) would cede ownership and jurisdiction of “the mainline from Harihar to Bangalore and to Hindupur which will be taken over by the British Government” ...”The section from Bangalore to Mysore and Nanjangode is an isolated local line, jurisdiction over which should be retained by the Mysore State” [3]
- 1907: the SMR transformed itself into the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway (M&SMR), with the lease following. At this time, the Railway Department of the State of Mysore was defunct.
Original Mysore State Railway Lines
See separate pages for further information.
- ‘Mysore-Bangalore Railway’, 86 miles(138km) MG from Mysore to Bangalore via Chanapatna, constructed by Mysore State, opened 1881-82 [4]. Worked by Mysore State until 1887, then by SMR. In 1893 ownership transferred to the Government of India and worked by SMR until 1907, then M&SMR as part of the M&MSR ‘Mysore Section’ until 1919, when it reverted to MSR.
- ‘Bangalore Harihar Railway’, 210 miles(336km) MG from Bangalore to Harihar via Yesvantpur Junction, constructed by Mysore State, opened in stages from 1884-89 [4], with 33 stations [5] . Worked by Mysore State until 1887, SMR 1887-1907. In , then M&SMR as part of the M&MSR ‘Mysore Section’ until 1938 when it reverted to MSR.
- ‘Bangalore Hindupur Railway’, 51 miles(82km) MG from Yesvantpur to the Mysore Frontier at Hindupur constructed by Mysore State. On opening in 1893 ownership transferred to the Government of India and worked by SMR until 1907, then M&SMR as part of the M&MSR ‘Mysore Section’ until 1938 when reverted to MSR.
- ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Railway’, 16 miles(26km) MG from Mysore to Nanjangud, a branch line, constructed by Mysore State , opened 1891 [4]. Worked by SMR until 1907; then M&SMR until 1919; then reverted to MSR.
- ‘Yesvantpur-Hindupur Railway, total 58½ miles(94km) MG. ‘Yesvantpur Junction to Mysore Frontier Section’, 51¼ miles opened 1893-94 [6]; ‘Mysore Frontier to Hindupur Section’, 7¼ miles opened 1893 [7]/>. Worked by SMR until 1907; then M&SMR until 1919; then reverted to MSR.
- ‘Birur-Shimoga Railway’, 38 miles(61km) MG from Birur to Shimoga, a branch line, constructed by Mysore State, opened 1899 [8]. Worked by SMR until 1907; then M&SMR until 1919; then reverted to MSR.
Second Mysore State Railway History
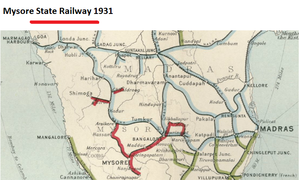
This development is clearly seen on the 1931 Map.
- 1912: the State of Mysore again became actively involved in the promotion and construction of railway lines within its boundaries and, between 1916 and 1918, opened 232 miles of railway to traffic.
- 1919, the Mysore State successfully sought the reversion from the M&SMR of the ‘Mysore -Bangalore Section’ and two branch lines, the ‘Birur-Shimoga Railway’ and the ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Railway’ became another part of the the MSR[9]
- Further construction, chiefly between 1921 and 1934, added 105 miles of new track.
- 1938. From 1 January 1938, the lines leased to M&SMR reverted to the control of the State of Mysore, creating a homogenous railway of just under 740 miles.
- 1950, MSR was nationalised and in 1951 became part of Southern Railway, one of the then newly formed zones of Indian Railways.
Second Mysore State Railway Lines
See separate pages for further information.
The following Metre Gauge(MG) Lines based on 1937 ‘History of Railways’, listed in chronological order
[10]:-
- ‘Mysore-Bangalore Railway’, 86 miles(138km) MG from Mysore to Bangalore via Chanapatna, constructed by the Original MSR, opened 1881-82
- ‘Mysore-Nanjangud Railway’, 16 miles(26km) MG from Mysore to Nanjangud, a branch line, constructed by the Original MSR , opened 1891
- ‘Birur-Shimoga Railway’, 38 miles(61km) MG from Birur to Shimoga, a branch line, constructed by the Original MSR, opened 1899
- ‘Mysore-Arsikere Railway’, 103 miles(166km) MG railway, from Mysore to Arsikere, opened 1918.
- ‘Chickjajur-Chitaldrug Railway’, 21 miles(34km) MG branch line from Chickjajur to Chitaldrug, opened 1921.
- ‘Najangud-Chamrajnagar Railway’, 22 miles(37km) MG extension of Mysore-Nanjangud Railway from Najangud to Chamrajnagar, opened 1926.
- ‘Shimoga-Anandapuram Railway’, 36 miles(58km) MG further extension of Birur-Shimoga Railway from Shimoga to Anandapuram, opened 1929-34.
- ‘Anandapuram-Sagara Railway’, 16 miles(26km) MG further extension of Birur-Shimoga Railway from Anandapuram to Sagara opened 1938. Sanctioned 1935 “to develop a tract of country rich in forest produce and minerals [11]
- ‘Sagara-Talaguppe Railway’, MG further extension to Talaguppe of the Birur-Shimoga Railway, opened 1940.
Narrow Gauge (NG) Lines worked by the Second MSR
See separate pages for further information. The following are listed as part of the ‘Mysore Railway System’
- ‘Tarikere-Narasimharajapura Tramway’, 2ft (610km) NG Tramway, 27 miles(43km), opened 1915. Worked by MSR [12].
- ‘Kolar District Railway’ original section known as the ‘Bowringpet-Chikballapur Railway’, 2ft 6in/762mm NG railway, 63 miles(101km), owned by Kolar and Mysore District Board, opened 1913-166. Worked by MSR [13].
- ‘Bangalore-Chik Ballapur Light Railway’, also known as the ‘Chikballapur-Bangalore City Railway’, 2ft 6in/762mm NG railway, 39 miles(62km), opened 1916-18. Worked by MSR[14].
- ‘Yelahaka-Bangarpet Railway’, 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) line owned by Kolar and Mysore District Board, opened 1913, and incorporated into the above, worked by MSR
- ‘Tadasa-Hebbe Tramway’, 2ft (610km) NG Tramway, 9.6 miles(15km), opened 1921. Worked by MSR [15].
Records
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [16] gives the following: -
- IOR/R/2/Box4/34; “Files 479A 1-3 1888 Cession to the British Govt. of jurisdiction over the Mysore State Railways”; 1886-93
- IOR/L/F/8/13/939; “Southern Mahratta Railway Company Limited, Contract for an extension of the Mysore State Railway and maintenance and working and extension as separate undertaking Secretary of State”; 31 Aug 1887
- IOR/L/F/8/20/1704; “Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Company Limited, Contract as to transfer of Mysore-Nanjangud, Birur-Shimoga and Mysore-Bangalore sections of the Mysore Railway to the Mysore Durbar Secretary" 24 Oct 1924
Personnel
Unfortunately, there are no MSR Staff agreements held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
The following have been found from other sources:-
- Augustus Le Messurier Col. R.E. Bombay Engineers, was appointed Engineer-in-Chief of Mysore State Railway in 1879 and became Manager in 1880 [17].
- Henry Wilkins Clift, Executive Engineer from State Railways was posted to the Mysore State Railway from c.1879 [18]
Further Information
See separate pages as detailed above for further information
- See also Southern Mahratta Railway for period 1887-1907.
- See also Madras and_Southern Mahratta Railway for period 1907-1912
- See also Tramways in Mysore State for details and map for railway and tramways in the north of Mysore State
References
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records L/PARL/2/100 “Railways in India for the year 1872-73” by Juland Danvers , Government Director of the Indian Railways’-– presented to both Houses of Parliament’ by HM Command. Extract from Annual Report 1872-73; Para 92
- ↑ "The Ex-Mysore State Metre Gauge Lines" by Ian Manning 2007. IRFCA Indian Railways Fan Club Retrieved on 9 Feb 2016
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records’ R/2/Box 4/35 Dispatch No 872-I, Fort William, 9 Mar 1893 from- Sir Mortimer Durand, K.C.I.E., C.S.I. Secretary to the Government of India, Foreign Department to The Resident in Mysore, Para 2.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 92 (pdf100) ; Retrieved 13 Feb 2018
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records’ IOR/R/2/Box 4/35
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 90 (pdf98) ; Retrieved 13 Feb 2018
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 86 (pdf94); Retrieved 13 Feb 2018
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 88 (pdf96) ; Retrieved 13 Feb 2018
- ↑ British Library IOR L/F/8/20/1704 ‘Contract with the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Co.Ltd as to the transfer of Mysore-Nanjangud , Birur-Shimoga and Mysore-Bangalore Railways sections of the Mysore Railway to the Mysore Durbar. Dated 24 Oct 1924 effective 1 Oct 1919
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 248, pdf 291; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ “Report by the Railway Board on Indian Railways for 1936-37. Vol. I; Railway Department, Government of India” Page 41 pdf 56 Para 40 (i) ; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 254, pdf 297; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ ibid , 31 March 1937 ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 252, pdf 295; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ ibid , 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 250, pdf 293; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ ibid , 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 255, pdf 298; Retrieved 8 Jul 2020
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 26 Jan 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 546 (pdf page 509 Retrieved on 23 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 456 (pdf page 419) Retrieved on 23 May 2016