Difference between revisions of "1st Sikh War"
(→Historical books online) |
(→Historical books online) |
||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
====Historical books online==== | ====Historical books online==== | ||
| + | *[http://books.google.com.au/books?id=2L0IAAAAQAAJ&pg=PP7 ''The War in India: Despatches of Visct. Hardinge, Lord Gough, Sir Harry Smith, Bart., and other documents; comprising the engagements of Moodkee, Ferozeshah, Aliwal and Sobraon''] 1846 Google Books | ||
*[http://archive.org/stream/sikhsandsikhwar00innegoog#page/n10/mode/2up ''The Sikhs and the Sikh Wars: The Rise, Conquest, and Annexation of the Punjab State''] by Charles Gough , Arthur Donald Innes 1897 Archive.org | *[http://archive.org/stream/sikhsandsikhwar00innegoog#page/n10/mode/2up ''The Sikhs and the Sikh Wars: The Rise, Conquest, and Annexation of the Punjab State''] by Charles Gough , Arthur Donald Innes 1897 Archive.org | ||
*''The First and Second Sikh Wars'' Compiled for the General Staff, India by Lieutenant Colonel R G Burton 94th Russell’s Infantry 1911 may be read online on the [[Online books#Digital Library of India| Digital Library of India]] website. | *''The First and Second Sikh Wars'' Compiled for the General Staff, India by Lieutenant Colonel R G Burton 94th Russell’s Infantry 1911 may be read online on the [[Online books#Digital Library of India| Digital Library of India]] website. | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 16 April 2012
| 1st Sikh War | |
|---|---|
| 1845-46 | |
| Chronological list of Wars and Campaigns | |
| |
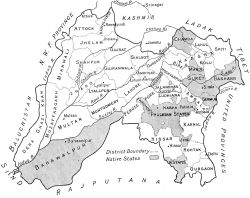
| Location: Punjab | |
| Combatants: | |
| East India Company | Sikh Empire |
| Result: British victory | |
| Medals: Sutlej Medal Clasps: Moodkee, Ferozeshuhur, Aliwal, Sobraon | |
| Links: | |
| Category: 1st Sikh War | |

|
See our interactive map of 1st Sikh War locations and routes on Google Maps | |
|---|---|---|
The 1st Sikh War, also called the First Anglo-Sikh War or the Sutlej Campaign.
Contents
Summary
After the death of Ranjit Singh in 1839, there was a period of internal strife as the succession to Sikh leadership was contested. Sikh forces were increased as were those of the British in the newly acquired territory adjoining the Punjab. Tension built up with demand and counter-demand until the British moved forces toward Firozpur and the Sikh Khalsa crossed the Sutlej. Four major actions were fought and all were won by the British. Large areas of territory were ceded to the British and a British Resident placed in Lahore effectively controlled the Sikh government.
Related articles
For details of events during this campaign see the following articles
| 16 December 1845 | Battle of Wadni Fort |
| 18 December 1845 | Battle of Moodkee |
| 21 December 1845 | Battle of Ferozeshah |
| 17 January 1846 | Surrender of Dharmkot Fort |
| 21 January 1846 | Occupation of Badhowal Fort |
| 28 January 1846 | Battle of Aliwal |
| 10 February 1846 | Battle of Sobraon |
| 17 February 1846 | Occupation of Phillour |
| 28 May 1846 | Battle of Kangrah |
Biographies
Entries in the Dictionary of Indian Biography 1906
Walter Gilbert (1785-1853)
Hugh Gough (1779-1869)
Henry Hardinge (1785-1856)
John McCaskill (17??-1845)
Robert Sale (1782-1845)
Dulip Singh (1837-1893)
Ranjit Singh (1780-1839)
Harry Smith (1787-1860)
Joseph Thackwell (1781-1859)
Hugh Wheeler (1789-1857)
Other biographies
Tej Singh Sikhiwiki
The Army of the Sutlej
Units at the first engagement at Moodkee. See other actions for forces on those occasions.
Commanding in Chief: Maj-Gen Sir Hugh Gough
Second in Command: Maj-Gen Sir Henry Hardinge, Governor General of Bengal
Cavalry Division
Major General Sir Joseph Thackwell
- Brigadier Mactier’s Brigade
- 9th Bengal Irregular Horse
- One wing of 4th Bengal Light Cavalry
- Brigadier Gough’s Brigade
- Brigadier White’s Brigade
1st Infantry Division
Maj-Gen Sir Harry Smith
- 1st Brigade: Brigadier Bolton
- 2nd Brigade: Colonel Hugh Wheeler
2nd Infantry Division
Major General Walter Gilbert
- 1st Brigade
- 2nd Brigade
3rd Infantry Division
Major General Sir John McCaskill
- 1st Brigade
Artillery
- 5 troops of Horse Artillery
- 2 batteries of light Field Artillery
Sikh Khalsa Army
The Sikh army created by Ranjit Singh was a formidable fighting force trained by European instructors to fight and drill in the Western manner. They were thought (especially the artillery) to be the equal of the Company's troops. At the outbreak of the 1st Sikh War the army's strength was 45,000 infantry, 26,000 cavalry and 376 guns.
Medals
Also see Medals and Medal Rolls
- The Sutlej Campaign Medal northeastmedals.co.uk
- Army of the Sutlej 1845-6 Casualty Roll is available to buy through Amazon.co.uk from the FIBIS Shop
External Links

|
The FIBIS Google Books Library has books tagged: 1st Sikh War Sikhs | |
|---|---|---|
1st Sikh War 1845-46 Wikipedia
1st Anglo-Sikh War Sikhiwiki
Journal of the Sutlej Campaign Google Books
Despatches of the Generals Google Books
Sikh Khalsa Army Wikipedia
31st Regiment in the 1st Sikh War queensroyalsurreys.org.uk
Map of the Punjab Wikipedia
Historical books online
- The War in India: Despatches of Visct. Hardinge, Lord Gough, Sir Harry Smith, Bart., and other documents; comprising the engagements of Moodkee, Ferozeshah, Aliwal and Sobraon 1846 Google Books
- The Sikhs and the Sikh Wars: The Rise, Conquest, and Annexation of the Punjab State by Charles Gough , Arthur Donald Innes 1897 Archive.org
- The First and Second Sikh Wars Compiled for the General Staff, India by Lieutenant Colonel R G Burton 94th Russell’s Infantry 1911 may be read online on the Digital Library of India website.
- Contents, computer page 6-8 .Unfortunately the book is not complete. Missing text pages 129-130 and all the appendices, pages 131-148.
- The history of the Sikhs: containing the lives of the Gooroos; the history of the independent Sirdars, or Missuls, and the life of the great founder of the Sikh monarchy, Maharajah Runjeet Singh The history of the Sikhs Volume 2 Containing an Account of the War between the Sikhs and the British in 1845-46 contains details of the war from page 42 By William Lewis M’Gregor MD Surgeon 1st European Light Infantry 1846 Google Books
- The history of the Bengal European regiment : now the Royal Munster Fusiliers, and how it helped to win India, page 362 by Percival Robert Innes 1885, details the role of this regiment in the 1st Sikh War. (archive.org)
- Journal of a cavalry officer: including the memorable Sikh campaign of 1845-46 by William Wellington Waterloo Humbley, Captain 9th Queen’s Royal Lancers 1854 Google Books
- Military service and adventures in the Far East: including sketches of the campaigns against the Afghans in 1839 and the Sikhs in 1845-6, Volume 2 by Capt. Daniel Henry Mackinnon, late of the 16th Lancers, 2nd edition 1849 (Volume 1) Google Books
- Ten years in India, in the 16th Queen's Lancers by WJD Gould (1880) [Archive.org]
- "The First Sikh War 1845-1846", page 46, Reynell Taylor, C. B., C. S. I. a Biography by E. Gambier Parry 1888 Archive.org. The subject was in the Governor General's Bodyguard and was wounded at the Battle of Moodkee