Difference between revisions of "Khyber Railway"
(→External links) |
(→External links) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khyber_Pass Wikipedia -" Khyber Pass Railway"]; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015</ref> | <ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khyber_Pass Wikipedia -" Khyber Pass Railway"]; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015</ref> | ||
| − | + | Described in some records as the '''Peshawar-Landi Kotal Railway''' | |
| − | + | [[File:Khyber Pass Railway 2.png|thumb|Khyber Pass Railway]] | |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The terminus was until 1932 at Landi Khana ''(as seen on 1931 map)''. This station, on the Afghan border near Torkham, opened in April 1926 and closed in Nov 1932 on Afghan Government request <ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Landi_Khana_railway_station Wikipedia ‘Landi Khana Railway Station’]; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019</ref>. |
| − | + | [[Landi Kotal]] was a station, 5 miles(8km) from the Afghan border, and after 1932 became the terminus of the Khyber Pass Railway | |
| + | <ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Landi_Kotal_railway_station Wikipedia ‘Landi Kotal Railway Station’]; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019</ref>. | ||
| − | Colonel [[Gordon Risley Hearn|Gordon Hearn]] was | + | ==History== |
| + | 1879: a reconnaissance survey was conducted with an aim to find the feasibility of laying railways through Khyber Pass. Many years passed without any action on the ground <ref name=ref1>[http://www.irfca.org/articles/khyber-pass-railway.html IRFCA "Khyber Pass Railway"]; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=ref2>[https://en-gb.facebook.com/permalink.php?story_fbid=315059328554077&id=285704338156243 Facebook "Railways in Indo-Pak"]; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1897-98: a survey was carried out for a narrow gauge ([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) fof 33 miles(53km) line from [[Peshawar]] to [[Landi Kotal]]. It was reported to meet “the heavy demands for transport during military operations on the frontier, the question of laying down light railways has been under consideration”.<ref>[https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.208633/page/n7 “Summary of the principal measures of the viceroyalty of the Earl of Elgin in the Public Works Department Jan 1894 to Dec 1898” ]; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019</ref>. | ||
| + | <br>The survey and report also examined an additional route from [[Nowshera]] to [[Durgai]]. | ||
| + | <br>''See page'' ‘[[Nowshera-Durgai Railway]]’ ''for more information.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1901: opening of the railway between [[Peshawar]] and [[Jamrud]] as broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) . Described as the ‘Pershawar-Jamrud Branch’ of the NWR ‘Frontier – Military Section’, a length of 11 miles, opened 1 Jan 1901 <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n117/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 108(pdf117)]; Retrieved 28 Apr 2019</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1905-07: finally the construction started from a place called Kacha Garhi between [[Peshawar]] and [[Jamrud]]. The [[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]] railway made progress westwards and 20 miles(32km) of track was laid by 1907 <ref name=ref1/><ref name=ref2/>. | ||
| + | <br>''See page'' ‘[[Jamrud-Dakka-Jalabad Portable Railway]]’ ''for more information.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1907: The terms of the Anglo-Russian Convention was that Russia accepted that Afghanistan was outside its sphere of influence <ref>[https://encyclopedia.1914-1918-online.net/article/afghanistan International Encyclopaedia of the First World War – Afghanistan, prior to 1918 by Hugh Beattie"]; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019</ref>. This made British consider Russia no longer a threat and the work on Khyber Pass Railway was stopped. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1909: several kilometers of permanent way and bridges were uprooted from Khyber Pass and sent to other areas of India to be used there<ref name=ref1/><ref name=ref2/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1919-25: A ropeway for carrying of military supplies, with a length of 19 miles(31km), was constructed from [[Landi Kotal]] | ||
| + | <br>''See page'' ‘[[Khyber Ropeway Company]]’ ''for more information.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1920-25: Colonel [[Gordon Risley Hearn|Gordon Hearn]] was assigned to the work of surveying and recommending the best route through Khyber Pass. Previously all surveys recommended a metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) track. However the proposal to use broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) was adopted and construction restarted in 1920. [[Victor Bayley]] was the engineer who was assigned the construction of the line. The section from [[Jamrud]] to [[Landi Kotal]] was opened on November 3, 1925 by the wife of the engineer [[Victor Bayley]]. | ||
<ref>Bayley, Victor (1939). Permanent Way Through the Khyber. London: Jarrold</ref> | <ref>Bayley, Victor (1939). Permanent Way Through the Khyber. London: Jarrold</ref> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 41: | ||
*L/MIL/7/6643; “Collection 145/106 Construction of Khyber railway.”; 1919-1926 (Three maps) | *L/MIL/7/6643; “Collection 145/106 Construction of Khyber railway.”; 1919-1926 (Three maps) | ||
*L/PS/10/951/2: “File 8929/1920 Pt 3 NW Frontier: Afghanistan and Khyber Railway; HMG's Waziristan policy”; 1922-26 | *L/PS/10/951/2: “File 8929/1920 Pt 3 NW Frontier: Afghanistan and Khyber Railway; HMG's Waziristan policy”; 1922-26 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | * [[Jamrud-Dakka-Jalabad Portable Railway| Jamrud-Dakka-Jalabad Portable Railway, 1905-07]] | ||
| + | * [[Khyber Ropeway Company|Khyber Ropeway Company, 1919 to c 1925]] | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | *[http://www.maverickpakistanis.com/wp-content/themes/iGreatBlack/book/books/khyber/15.asp The Khyber Railway] by Qazi Bahader Ali, originally published in the monthly ''The Busy World International'', Peshawar, December 1994-January 1995. | + | *[https://web.archive.org/web/20180221113935/http://www.maverickpakistanis.com/wp-content/themes/iGreatBlack/book/books/khyber/15.asp The Khyber Railway] by Qazi Bahader Ali, originally published in the monthly ''The Busy World International'', Peshawar, December 1994-January 1995. Now archived. |
*[https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/politics/1980/03/14/khyber-pass-train-gives-nostalgic-glimpse-of-british-empire/0846dbef-9d67-4a96-bfd8-1b48102b4729/ "Khyber Pass Train Gives Nostalgic Glimpse of British Empire"] by Liz Thurgood and Manchester Guardian March 14, 1980 ''The Washington Post''. | *[https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/politics/1980/03/14/khyber-pass-train-gives-nostalgic-glimpse-of-british-empire/0846dbef-9d67-4a96-bfd8-1b48102b4729/ "Khyber Pass Train Gives Nostalgic Glimpse of British Empire"] by Liz Thurgood and Manchester Guardian March 14, 1980 ''The Washington Post''. | ||
| + | *[https://www.christianwolmar.co.uk/2018/06/was-this-the-craziest-railway-ever-built/ Was this the craziest railway ever built?] Christian Wolmar | ||
| + | ===Historical books online=== | ||
| + | *[http://pahar.in/wpfb-file/1939-permanent-way-through-the-khyber-by-bayley-s-pdf/ ''Permanent Way Through the Khyber''] by Victor Bayley 1939, first published 1934. Link to a pdf download PAHAR Mountains of Central Asia Digital Dataset. [https://archive.org/details/dli.pahar.2743 Archive.org mirror version]. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 22:59, 30 May 2021
The Khyber Pass Railway was a line from India to Afghanistan via Khyber Pass; built as a strategic line to thwart any Afghan or Russian invasion of India and opened in 1925. [1]
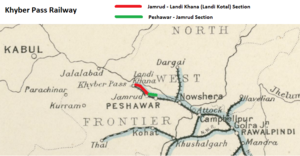
Described in some records as the Peshawar-Landi Kotal Railway
The terminus was until 1932 at Landi Khana (as seen on 1931 map). This station, on the Afghan border near Torkham, opened in April 1926 and closed in Nov 1932 on Afghan Government request [2].
Landi Kotal was a station, 5 miles(8km) from the Afghan border, and after 1932 became the terminus of the Khyber Pass Railway [3].
History
1879: a reconnaissance survey was conducted with an aim to find the feasibility of laying railways through Khyber Pass. Many years passed without any action on the ground [4] [5].
1897-98: a survey was carried out for a narrow gauge (NG) fof 33 miles(53km) line from Peshawar to Landi Kotal. It was reported to meet “the heavy demands for transport during military operations on the frontier, the question of laying down light railways has been under consideration”.[6].
The survey and report also examined an additional route from Nowshera to Durgai.
See page ‘Nowshera-Durgai Railway’ for more information.
1901: opening of the railway between Peshawar and Jamrud as broad gauge(BG) . Described as the ‘Pershawar-Jamrud Branch’ of the NWR ‘Frontier – Military Section’, a length of 11 miles, opened 1 Jan 1901 [7].
1905-07: finally the construction started from a place called Kacha Garhi between Peshawar and Jamrud. The NG railway made progress westwards and 20 miles(32km) of track was laid by 1907 [4][5].
See page ‘Jamrud-Dakka-Jalabad Portable Railway’ for more information.
1907: The terms of the Anglo-Russian Convention was that Russia accepted that Afghanistan was outside its sphere of influence [8]. This made British consider Russia no longer a threat and the work on Khyber Pass Railway was stopped.
1909: several kilometers of permanent way and bridges were uprooted from Khyber Pass and sent to other areas of India to be used there[4][5].
1919-25: A ropeway for carrying of military supplies, with a length of 19 miles(31km), was constructed from Landi Kotal
See page ‘Khyber Ropeway Company’ for more information.
1920-25: Colonel Gordon Hearn was assigned to the work of surveying and recommending the best route through Khyber Pass. Previously all surveys recommended a metre gauge(MG) track. However the proposal to use broad gauge(BG) was adopted and construction restarted in 1920. Victor Bayley was the engineer who was assigned the construction of the line. The section from Jamrud to Landi Kotal was opened on November 3, 1925 by the wife of the engineer Victor Bayley. [9]
The railway was worked by North Western Railway(NWR) until partition in 1947. Then by Pakistan Railways until closure. [10]
Records
An on-line search of the India Office Records (IOR) records held at the British Library relating to this railway [11] gives several entries, the most relevant as follows: -
- L/MIL/7/6643; “Collection 145/106 Construction of Khyber railway.”; 1919-1926 (Three maps)
- L/PS/10/951/2: “File 8929/1920 Pt 3 NW Frontier: Afghanistan and Khyber Railway; HMG's Waziristan policy”; 1922-26
See Also
External links
- The Khyber Railway by Qazi Bahader Ali, originally published in the monthly The Busy World International, Peshawar, December 1994-January 1995. Now archived.
- "Khyber Pass Train Gives Nostalgic Glimpse of British Empire" by Liz Thurgood and Manchester Guardian March 14, 1980 The Washington Post.
- Was this the craziest railway ever built? Christian Wolmar
Historical books online
- Permanent Way Through the Khyber by Victor Bayley 1939, first published 1934. Link to a pdf download PAHAR Mountains of Central Asia Digital Dataset. Archive.org mirror version.
References
- ↑ Wikipedia -" Khyber Pass Railway"; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015
- ↑ Wikipedia ‘Landi Khana Railway Station’; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019
- ↑ Wikipedia ‘Landi Kotal Railway Station’; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 IRFCA "Khyber Pass Railway"; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Facebook "Railways in Indo-Pak"; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015
- ↑ “Summary of the principal measures of the viceroyalty of the Earl of Elgin in the Public Works Department Jan 1894 to Dec 1898” ; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 108(pdf117); Retrieved 28 Apr 2019
- ↑ International Encyclopaedia of the First World War – Afghanistan, prior to 1918 by Hugh Beattie"; Retrieved 29 Apr 2019
- ↑ Bayley, Victor (1939). Permanent Way Through the Khyber. London: Jarrold
- ↑ Wikipedia "Khyber Train Safari"; Retrieved 12 Dec 2015
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 11 Apr 2016