Junagadh State Railway
| Junagadh State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Junagadh State Railway Logo. | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Jetalsar to Veraval | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 140 miles (1922) 229 miles (1944) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1888 | First section opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Jetalsar, Junagadh, Kutiyana, Veraval | |
| System agency | ||
| 1888 | Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway | |
| 1911 | Own agency | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Also known as Junagad State Railway
The Junagadh State Railway (JunSR) was a metre gauge(MG) railway owned by the Princely Junagadh State and initially worked by the ‘Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway’ [1]
In 1869 a survey was undertaken and the ’Junagadh-Veraval Railway Proposal ‘ concluded that a Railway line from Junagadh to Veraval was feasible but the cost of 40 to 50 Lakhs of Rupees was too high for the Junagadh Durbar to go ahead. Proposals for a light railway system were to be looked at. [2].
In 1872 another line was proposed and the route from Veraval to Junagadh and Dhoraji was surveyed by Mr A W Forde C E, but the cost was beyond the means of Junagadh Durbar. This proposal came to nothing [3].
Construction finally commenced in 1886 from Jetalsar to Junagadh City in 1888 and onward To Veraval 1889,
Initially described as the Junadagh-Veraval Railway.
Administration
- 1888-89: With the opening of the ‘Junagadh State Railway’(JunSR ) from Junagadh via Jetalsar to Veraval the railway joined the administrative coalition of the 'Bhavnagar-Gondal State Railway’.
The coalition briefly became the 'Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Veraval Railway'(BGJPV) - 1889: When the ‘Porbandar State Railway’ extension from Dhasa reached Porbandar the coalition finally became the Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway(BGJPR) - see separate page for further information.
- This BGJPR coalition was also described in some records as the Kathiawar Railway,
- also as the Kathiawar Union Railway
- also as the Kathiawar State Railway.
- 1911: The BGJPR coalition ceased to exist on 1 April 1911, from this date the line was worked independently as a separate and distinct railway [4].
- 1911-1934: The operation of the ‘Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway’ caused serious financial and commercial disadvantages to the JunSr, resulting in acrimonious exchanges over many years - see separate page for further information.
- 1935: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ put forward a proposal to take over the management of the ‘Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway’ which since 1911 had been operated by the ‘Gondal-Porbandar Railway’ [5]. There is no evidence that this proposal was accepted.
- 1948: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ became part of the ‘Saurashtra Railway’.
Development of the Junagadh State Railway
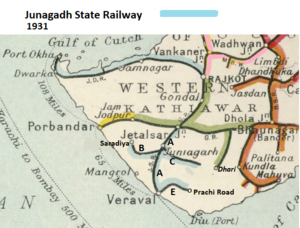
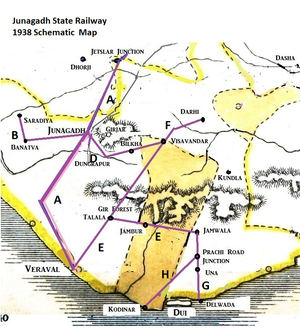
- The first section from Jetalsar to Junagadh opened in 1888 and extended to Veraval Docks in 1889, a total of 67 miles(108km) [4]. At Jetalasar Junction there was a connection to the ‘Gondal Railway - Mainline’ Dhasa to Jamjodhpur.
- Initially described as the Junadagh-Veraval Railway and became the ‘Main Line’
- Line ‘A’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1910-15: ‘Saradiya Branch Line’, 26 miles(42km); from Shapur , 5 miles(8km) south-west of Junagadh, to Saradiya [4] (shown as Juniagarh to Kutiyana on 1931 Railways Map )
- Line ‘B’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1912: ‘Visavadar Branch’, 26 miles(km); from Junagadh to Visavadar [4] .
- Line ‘C’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1912: ‘Dungarpur Quarry Line’, ¾ mile(1.2km); a short spur from the ‘Visavadar Branch’, 2 miles (3.2km) south-east of Junagarh [4] .
- Line ‘D’ on 1938 map
- 1918-23: ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’, 28 miles(45km); from Veraval, proposed as far as Una, delayed start, opened in stages from 1918, reached Prachi Road 1923 [6].
- Line ‘E’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1932: ‘Visavader-Dhari Branch’ 20 miles(32km); from Visavader to Dhari [6]
- Line ‘F’ on 1938 map
- 1934-35: ‘Prachi Road-Jamwala-Delvada Branch’ 31 miles(50km) [6]. This was an extension to the ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’ (Line ‘E’ above) and on reaching Delvada in 1935 became renamed ‘Una Branch’, with a total length from Veraval to Delvada of 25 miles(95km) [7].
- Line ‘G’ on 1938 map
- 1936-37: ‘Talala-Visavadar Railway’' via Sasan Gir, 29½ miles(47km) MG, constructed by the JunSR.See separate page
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 with a total route length of 229 miles(369km) <ref name=Hist>
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class III railway system.
Further Information
See Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway for period from 1899 to 1911.
and Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula.
References
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193; Retrieved 7 Feb 2016
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records’ V/10/1384 “Indian States Administration Reports. Kathiawar” 1865-75, No 134 of 1869
- ↑ “Gazetteer – Bombay Presidency” Vol.8; page 247-248 of 756; Retrieved 1 Oct 2017
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193; Retrieved 23 Jun 2019
- ↑ British Library IOR/R/1/1/4784(1) and (2); "File 110-IB(C)/1935 Proposed taking over of management of the Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway by the Junagadh State Railway from the Gondal Railway"; 1935
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 1943 ‘Kathiawar Economics’ by A B Trivedi, 1943 Digital Library of India Archive.org, Appendix B ‘Railways in Kathiawar with opening dates, pages 193(pdf217)
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 245 pdf 288; Retrieved 23 Aug 2020