Southern Punjab Railway
| Southern Punjab Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Delhi to Samasata McLeod Ganj to Ludhiana Narwana to Kaithal (branch) | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 502 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1897 | Delhi to Samasata line opened to traffic | |
| 1930 | Line acquired by State and merged into NWR | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Bahawalpur, Bhatinda, Fazilka, Ferozepore, Ghaziabad, Jakhai, Rohtak
Ghaziabad was the connection to Delhi - see separate page Delhi Stations' for details | |
| System agency | ||
| Worked by North Western Railway | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Southern Punjab Railway(SPR) was a broad gauge(BG) line built to provide a more direct connection from Karachi to Delhi by linking to the original Indus Valley line at Samasata and avoiding the North Western Railway loop via Lahore. [1]
History
The Southern Punjab Railway(SPR) Company was formed in 1895 with Bradford Leslie as Chairman. Under contract with the Secretary of State for India, Leslie and his partners formed the company to build a BG Railway from Delhi to Samasata about 400 miles to the west.
Horace Bell was the Consulting Engineer for SPR in London for the construction.,
The Mainline ran north west from Delhi to Bhatinda then south west through Bahawalpur State to Samasata, a total distance of 402 miles(643km). Several extension lines (Jullunder, Sutlej Valley etc.) extended the length to 502 miles(803km) in 1905.
The SPR Mainline and the extensions were all worked by the ‘North Western Railway’(NWR) , each line reported financially individually until purchased by Government in 1929-30. From that time onwards the each line was absorbed into the ‘NWR System’.
SPR Network of Lines
The listings below are generally based on the “Administration Report on Railways 1918” [2] with page numbers (and pdf pages) noted at the end of each entry.
This 1918 Report [2] details the ‘SPR Network’ as part of the ‘NWR System’ but with the ‘Statistics of Working’ (route mileages, capital outlay, income etc) for each part of the SPR given as a separate entities..
Significant later information is shown in italics. The listings below includes information concerning the changes from 1929-30 when the SPR was fully integrated into the NWR System [3]
SPR Mainline and Branches
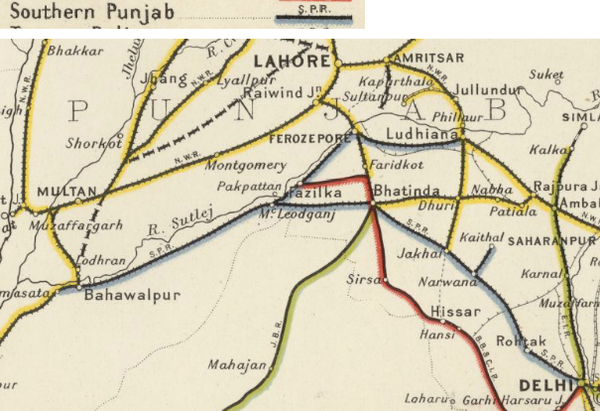
Total broad gauge BG line length 426 miles(685km). Page 121(pdf 130)
- ‘Delhi-Samasata Mainline’, from Delhi via Narwana, Jakhal, Bhatinda to Samasata, opened 1897, 399 miles(642km). From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Samastra-Bhatinda-Delhi Section’
- ‘Delhi Brewery Branch Line’, opened 1909, 0.8 mile(1.3km)
- ‘Narwana-Kaithal Branch Line’, opened 1899, from Narwana to Kaithal, 23 miles(37km). From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Narwana- Kurukshetra Section’, 53 miles(85km) by putting together the ’SPR Narwana-Kaithal Line’ with the ‘Thanesar-Kaithal Railway’ from Kaithal to Kurukshetra - see separate page
- ‘Jind City Branch Line’, from Jind Junction to Jind City, opened 1916, 2.5 miles(4km). From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Jind-Panipat Section’, 18 miles(29km) by putting together the ‘SPR Jind City Branch Line’ with the ‘Jind-Panipat Railway’ from Jind to Panipat - see separate page
Jullundur-Doab Extension Railway
Classified under the ‘SPR Network’ as part of the ‘NWR System’ . Total broad gauge BG line length 130 miles(209km). Page 123(pdf132)
- ‘Jullunder-Ferozepore Mainline', Jullunder via Karpurthala, Sultanpur Lodi, Lohian Khas, Gidarpind, Makhu to Ferozepore Cantonment, opened 1912-14, 73 miles(117km). From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Jullundur Doab Extension’
- ‘Phillaur Branch Line’, Lohian Khas to Phillaur, opened 1913, 39 miles(63km) . From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Phillaur-Lohian Khas Branch’
- ‘Jullundur-Nakodar Chord Railway' known as the ‘Nakodar Branch Line’, Jullunder to Nakodar, opened 1914, 19 miles(30km) . From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Jullundur City-Nakodar Branch’
Ludhiana Extension Railway
Classified under the ‘SPR Network’ as part of the ‘NWR System’ . Total broad gauge BG line length 152 miles(244km). Page 123(pdf132)'
- ‘Ludhiana-Ferozepore Line’, Ludhiana to Ferozepore, opened 1905, 77 miles(124km)
- ‘Ferozepore-MacLeod Ganj Line’, Ferozepore to McLeod Ganj (a suburb of Dharamsala), opened 1906, 75 miles(120km)
- From 1929-30 these two lines together became the ‘NWR Ludhiana Extension Railway’
Sutlej Valley Extension Railway
Classified under the ‘SPR Network’ as part of the ‘NWR System’ . Total broad gauge BG line length 208 miles(335km). Pages 124-5(pdf135-6)
- ‘Kasur-Lodhran Railway', Kasur to Lodhran, opened 1910, closed and dismantled 1917-18, 208 miles(335km). Reconstructed 1923-26 with line length 213 miles(343km). From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Sutlej Valley Extension Railway’
Ludhiana-Dhuri-Jakhal Railway
Classified under the ‘SPR Network’ as part of the ‘NWR System’ . Total broad gauge BG line length 79 miles(127km). Page 115(pdf124)
- Ludhiana via Dhuri to Jakhal, opened 1901. Managed, maintained and worked by North Western Railway (NWR) under an Agreement with the Princely Maler Kotla State Durbar and the Jhind State Durbars. The line was used by SPR linking the ’Delhi-Samasata Mainline’ at Jakhal with 'Ludhiana Extension Railway' at Ludhiana. From 1929-30 this became the ‘NWR Ludhiana-Dhuri-Jakhal Railway’
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [4] gives many references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/39 “Records of the India Office relating to the Southern Punjab Railway Company; 1895-1914".'
- L/F/7/2607-2615 “Collection 401: Southern Punjab Railway, date unspecified"
also concerning the working of the Southern Punjab Railway by NWR.
- L/AG/46/34 “ Records of the India Office relating to the North Western State Railway",
References
- ↑ Wikipedia "Fazilka railway station"; Retrieved 13 Dec 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” pages 120-126 (pdf 129-134; Retrieved 2 Nov 2020
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 151-156 pdf 190-195; Retrieved 2 Nov 2020
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved Jan 2016