| The Families In British India Society (FIBIS) is a self-help organisation devoted to members researching their British India family history and the background against which their ancestors led their lives in India under British rule. Let FIBIS help you break down those brick walls in your research |
Junagadh State Railway: Difference between revisions
m System Abrev. JunSR adopted replacing JSR which is Jodpur State Railway |
1937 Report info added, layout changes , Statisics added and Classification |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Line Railways Infobox | {{Line Railways Infobox | ||
|image= | |image= Junagadh State Railway Logo.png | ||
|caption= | |caption= Junagadh State Railway Logo. | ||
|route= [[Jetalsar]] to [[Veraval]] | |route= [[Jetalsar]] to [[Veraval]] | ||
|gauge1= | |gauge1= | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|timeline5details= | |timeline5details= | ||
|presidency= [[Bombay]] | |presidency= [[Bombay]] | ||
|stations= [[Jetalsar]], [[ | |stations= [[Jetalsar]], [[Junagadh]], [[Kutiyana]], [[Veraval]] | ||
|system1date= 1888 | |system1date= 1888 | ||
|system1details= [[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]] | |system1details= [[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
Also known as '''Junagad State Railway''' | |||
The '''Junagadh State Railway''' (JunSR) was a metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railway owned by the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Junagadh State]] and initially worked by the ‘[[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]]’ <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n201/mode/1up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193]; Retrieved 7 Feb 2016</ref> | |||
In 1869 a survey was undertaken and the [[Kathiawar_Peninsula_Railway_and_Tramway_Systems#Timeline_1863-1900 |’Junagadh-Veraval Railway Proposal ‘]] concluded that a Railway line from [[Junagadh]] to [[Veraval]] was feasible but the cost of 40 to 50 Lakhs of Rupees was too high for the Junagadh Durbar to go ahead. Proposals for a light railway system were to be looked at. <ref> British Library ‘India Office Records’ V/10/1384 “Indian States Administration Reports. Kathiawar” 1865-75, No 134 of 1869 </ref>. | |||
In 1872 another line was proposed and the [[Kathiawar_Peninsula_Railway_and_Tramway_Systems#Timeline_1863-1900|route from Veraval to Junagadh and Dhoraji]] was surveyed by Mr A W Forde C E, but the cost was beyond the means of Junagadh Durbar. This proposal came to nothing <ref name=Bombay8_247>[https://archive.org/stream/1884GazetteerByBombayPresidencyVol8Kathiawar349D/1884-gazetteerByBombayPresidency-vol8-kathiawar349-d_djvu.txtArchive.org “Gazetteer – Bombay Presidency” Vol.8; page 247-248 of 756]; Retrieved 1 Oct 2017</ref>. | |||
Construction finally commenced in 1886 from [[Jetalsar]] to [[Junagadh|Junagadh City]] in 1888 and onward To [[Veraval]] 1889, | |||
<br>Initially described as the '''Junadagh-Veraval Railway'''. | |||
==Administration== | |||
*1888-89: With the opening of the ‘Junagadh State Railway’(JunSR ) from [[Junagadh]] via [[Jetalsar]] to [[Veraval]] the railway joined the administrative coalition of the '[[Bhavnagar-Gondal State Railway]]’. <br>The coalition briefly became the '[[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Veraval Railway]]'(BGJPV) | |||
*1889: When the ‘[[Porbandar State Railway]]’ extension from [[Dhasa ]] reached [[Porbandar]] the coalition finally became the [[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway| '''Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway'''(BGJPR) ''- see separate page for further information'']]. | |||
*This BGJPR coalition was also described in some records as the '''Kathiawar Railway''', | |||
*also as the '''Kathiawar Union Railway''' | |||
*also as the '''Kathiawar State Railway'''. | |||
* 1911: The BGJPR coalition ceased to exist on 1 April 1911, from this date the line was worked independently as a separate and distinct railway <ref name=Admin/>. | |||
* 1911-1934: The operation of the ‘[[Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway]]’ caused serious financial and commercial disadvantages to the JunSr, resulting in acrimonious exchanges over many years [[Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway|''- see separate page for further information'']]. | |||
* 1935: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ put forward a proposal to take over the management of the ‘[[Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway]]’ which since 1911 had been operated by the ‘[[Gondal-Porbandar Railway]]’ <ref> British Library IOR/R/1/1/4784(1) and (2); "File 110-IB(C)/1935 Proposed taking over of management of the Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway by the Junagadh State Railway from the Gondal Railway"; 1935</ref>. There is no evidence that this proposal was accepted. | |||
* 1948: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ became part of the ‘[[Saurashtra Railway]]’. | |||
==Development of the Junagadh State Railway== | |||
[[File:Junagadh State Railway 1931 Map.png|thumb|Junagadh State Railway 1931 Map]] | |||
[[File:Junagadh State Railway 1938 Schematic Map.png|thumb|Junagadh State Railway 1938 Scematic Map]] | |||
*The first section from [[Jetalsar]] to [[Junagadh]] opened in 1888 and extended to [[Veraval|Veraval Docks]] in 1889, a total of 67 miles(108km) <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n201/mode/1up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193]; Retrieved 23 Jun 2019</ref>. At [[Jetalsar |Jetalasar Junction]] there was a connection to the ‘[[Gondal Railway]] - Mainline’ [[Dhasa]] to [[Jamjodhpur]]. | |||
* Initially described as the '''Junadagh-Veraval Railway''' and became the ‘Main Line’ | |||
**''Line ‘A’ on 1931 and 1938 maps '' | |||
*1910-15: ‘Saradiya Branch Line’, 26 miles(42km); from Shapur , 5 miles(8km) south-west of Junagadh, to Saradiya <ref name=Admin/> (shown as Juniagarh to Kutiyana on 1931 Railways Map ) | |||
**''Line ‘B’ on 1931 and 1938 maps '' | |||
* 1912: ‘Visavadar Branch’, 26 miles(km); from Junagadh to Visavadar <ref name=Admin/> . | |||
**''Line ‘C’ on 1931 and 1938 maps '' | |||
*1912: ‘Dungarpur Quarry Line’, ¾ mile(1.2km); a short spur from the ‘Visavadar Branch’, 2 miles (3.2km) south-east of Junagarh <ref name=Admin/> . | |||
**''Line ‘D’ on 1938 map '' | |||
* 1918-23: ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’, 28 miles(45km); from [[Veraval]], proposed as far as [[Una]], delayed start, opened in stages from 1918, reached Prachi Road 1923 <ref name=page193>[https://ia801602.us.archive.org/6/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.96301/2015.96301.Kathiawar-Economics.pdf 1943 ‘Kathiawar Economics’ by A B Trivedi, 1943 Digital Library of India Archive.org, Appendix B ‘Railways in Kathiawar with opening dates, pages 193(pdf217)]</ref>. | |||
**''Line ‘E’ on 1931 and 1938 maps '' | |||
* 1932: ‘Visavader-Dhari Branch’ 20 miles(32km); from Visavader to Dhari <ref name=page193/> | |||
**''Line ‘F’ on 1938 map '' | |||
* 1934-35: ‘Prachi Road-Jamwala-Delvada Branch’ 31 miles(50km) <ref name=page193/>. This was an extension to the ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’ (Line ‘E’ above) and on reaching Delvada in 1935 became renamed ‘Una Branch’, with a total length from Veraval to Delvada of 25 miles(95km) <ref name=Hist>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 245 pdf 288]; Retrieved 23 Aug 2020</ref>. | |||
**''Line ‘G’ on 1938 map '' | |||
*1936-37: ‘[[Talala-Visavadar Railway]]’' via Sasan Gir, 29½ miles(47km) MG, constructed by the JunSR.[[Talala-Visavadar Railway|''See separate page'']] | |||
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 with a total route length of 229 miles(369km) | |||
<ref name=Hist> | |||
== Classification == | |||
[[Indian Railway Classification]] of 1926 - Class III railway system. | |||
==Further Information== | |||
See '''[[Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway]]''' for period from 1899 to 1911. | |||
<br>and '''[[Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems]]''' gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula. | |||
== References == | |||
<references /> | |||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
[[Category:Indian States Railways]] | [[Category:Indian States Railways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:50, 24 August 2020
| Junagadh State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Junagadh State Railway Logo. | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Jetalsar to Veraval | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 140 miles (1922) 229 miles (1944) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1888 | First section opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Jetalsar, Junagadh, Kutiyana, Veraval | |
| System agency | ||
| 1888 | Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway | |
| 1911 | Own agency | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Also known as Junagad State Railway
The Junagadh State Railway (JunSR) was a metre gauge(MG) railway owned by the Princely Junagadh State and initially worked by the ‘Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway’ [1]
In 1869 a survey was undertaken and the ’Junagadh-Veraval Railway Proposal ‘ concluded that a Railway line from Junagadh to Veraval was feasible but the cost of 40 to 50 Lakhs of Rupees was too high for the Junagadh Durbar to go ahead. Proposals for a light railway system were to be looked at. [2].
In 1872 another line was proposed and the route from Veraval to Junagadh and Dhoraji was surveyed by Mr A W Forde C E, but the cost was beyond the means of Junagadh Durbar. This proposal came to nothing [3].
Construction finally commenced in 1886 from Jetalsar to Junagadh City in 1888 and onward To Veraval 1889,
Initially described as the Junadagh-Veraval Railway.
Administration
- 1888-89: With the opening of the ‘Junagadh State Railway’(JunSR ) from Junagadh via Jetalsar to Veraval the railway joined the administrative coalition of the 'Bhavnagar-Gondal State Railway’.
The coalition briefly became the 'Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Veraval Railway'(BGJPV) - 1889: When the ‘Porbandar State Railway’ extension from Dhasa reached Porbandar the coalition finally became the Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway(BGJPR) - see separate page for further information.
- This BGJPR coalition was also described in some records as the Kathiawar Railway,
- also as the Kathiawar Union Railway
- also as the Kathiawar State Railway.
- 1911: The BGJPR coalition ceased to exist on 1 April 1911, from this date the line was worked independently as a separate and distinct railway [4].
- 1911-1934: The operation of the ‘Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway’ caused serious financial and commercial disadvantages to the JunSr, resulting in acrimonious exchanges over many years - see separate page for further information.
- 1935: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ put forward a proposal to take over the management of the ‘Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway’ which since 1911 had been operated by the ‘Gondal-Porbandar Railway’ [5]. There is no evidence that this proposal was accepted.
- 1948: The ‘Junagadh State Railway’ became part of the ‘Saurashtra Railway’.
Development of the Junagadh State Railway
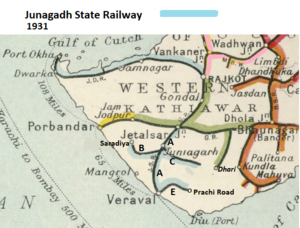
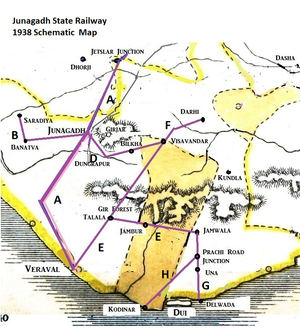
- The first section from Jetalsar to Junagadh opened in 1888 and extended to Veraval Docks in 1889, a total of 67 miles(108km) [4]. At Jetalasar Junction there was a connection to the ‘Gondal Railway - Mainline’ Dhasa to Jamjodhpur.
- Initially described as the Junadagh-Veraval Railway and became the ‘Main Line’
- Line ‘A’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1910-15: ‘Saradiya Branch Line’, 26 miles(42km); from Shapur , 5 miles(8km) south-west of Junagadh, to Saradiya [4] (shown as Juniagarh to Kutiyana on 1931 Railways Map )
- Line ‘B’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1912: ‘Visavadar Branch’, 26 miles(km); from Junagadh to Visavadar [4] .
- Line ‘C’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1912: ‘Dungarpur Quarry Line’, ¾ mile(1.2km); a short spur from the ‘Visavadar Branch’, 2 miles (3.2km) south-east of Junagarh [4] .
- Line ‘D’ on 1938 map
- 1918-23: ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’, 28 miles(45km); from Veraval, proposed as far as Una, delayed start, opened in stages from 1918, reached Prachi Road 1923 [6].
- Line ‘E’ on 1931 and 1938 maps
- 1932: ‘Visavader-Dhari Branch’ 20 miles(32km); from Visavader to Dhari [6]
- Line ‘F’ on 1938 map
- 1934-35: ‘Prachi Road-Jamwala-Delvada Branch’ 31 miles(50km) [6]. This was an extension to the ‘Veraval-Prachi Road Branch’ (Line ‘E’ above) and on reaching Delvada in 1935 became renamed ‘Una Branch’, with a total length from Veraval to Delvada of 25 miles(95km) [7].
- Line ‘G’ on 1938 map
- 1936-37: ‘Talala-Visavadar Railway’' via Sasan Gir, 29½ miles(47km) MG, constructed by the JunSR.See separate page
The ‘Statistics of Working’ show the year-by-year financial results from 1913-14 through to 1936-37 with a total route length of 229 miles(369km) <ref name=Hist>
Classification
Indian Railway Classification of 1926 - Class III railway system.
Further Information
See Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway for period from 1899 to 1911.
and Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula.
References
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193; Retrieved 7 Feb 2016
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records’ V/10/1384 “Indian States Administration Reports. Kathiawar” 1865-75, No 134 of 1869
- ↑ “Gazetteer – Bombay Presidency” Vol.8; page 247-248 of 756; Retrieved 1 Oct 2017
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 193; Retrieved 23 Jun 2019
- ↑ British Library IOR/R/1/1/4784(1) and (2); "File 110-IB(C)/1935 Proposed taking over of management of the Jetalsar-Rajkot Railway by the Junagadh State Railway from the Gondal Railway"; 1935
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 6.2 1943 ‘Kathiawar Economics’ by A B Trivedi, 1943 Digital Library of India Archive.org, Appendix B ‘Railways in Kathiawar with opening dates, pages 193(pdf217)
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 245 pdf 288; Retrieved 23 Aug 2020