Bengal-Nagpur Railway
| Bengal-Nagpur Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Bengal-Nagpur Railway device | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Calcutta to Nagpur (Bombay) Calcutta to Waltair (Madras) Bilaspur to Katni | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 1696 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1887 | Company formed | |
| 1888 | Existing metre gauge converted to broad | |
| 1944 | Line acquired by state | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | ||
| System agency | ||
| Worked by Bengal-Nagpur Railway | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Bengal-Nagpur Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Bengal-Nagpur Railway device | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1944 | Management of line taken over by state | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Bengal-Nagpur Railway | ||
| Jubbulpore-Gondia Railway | ||
| Mayurbhanj Railway | ||
| Parlakimedi Light Railway | ||
| Raipur-Dhamtari Railway | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Calcutta | |
| Workshops | Motibagh Workshop, Nagpur,Kharagpur | |
| Major Stations | Asansol, Balasore, Bilaspur, Chanda, Chhindwara, Cuttack, Jubbulpore, Mandla, Nagpur, Raipur, Sambalpur, Vizagapattam | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1952 | Eastern Railway (IR zone) | |
| 1955 | South Eastern Railway (IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 1696 miles (1905) 2498 miles (1943) | |
| Narrow (2' 6") gauge | 343 miles (1905) 798 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Bengal Nagpur Railway Battalion | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Bengal-Nagpur Railway (BNR) was formed in 1887 with the following three objectives [1] :-
- To take over the metre gauge(MG) Nagpur-Chhattisgarh Railway, 149 miles (240km) from the Government and to convert the existing metre gauge track to broad gauge(BG)
- To extend the system eastwards by 480 miles(772km) to join the East Indian Railway at Asansol, 132 miles(212km) from Calcutta
- To construct the Branch Line from Bilaspur to Umaria for through connection with the Great Indian Peninsula Railway(GIPR) system at Katni
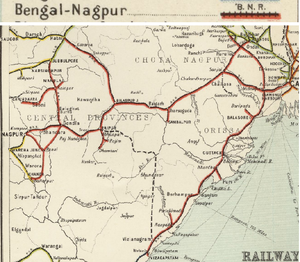

History
The BNR was the last major railway formed to benefit from a Government guarantee, with the system from the outset owned by the Government of India (GoI) who contracted the BNR Company to manage matters, initially for 25 years and thereafter determinable every 10 years.
The Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway had opened in 1880; previously named the ‘Chhattisgarh State Railway’, owned by the Provincial Government; worked as part of the Indian State Railways; merged into BNR, 1887. This included the Umaria Coalfield Railway which had opened 1883, and connected to BNR main line in 1886-87.
The BNR Company took over the Bilaspur-Etawa Provincial State Railway which in 1891 connected Bilaspur to Katni with a short onward link to the GIPR Marwara Junction
By 1891 both routes were completed which had created a shorter route between Calcutta and Bombay.
From 1898 the BNR established the 'Kharagpur Railway Workshops' - see separate page
The Cuttack-Midnapore-Calcutta Railway Survey was undertaken in 1899 by the Government and used for the expansion of BNR, the scope of the Survey was increased by BNR in 1901.
In 1901 the Cuttack to Waltair section of the East Coast State Railway was absorbed into the BNR and gave an important route to Madras
The BNR was the last company to be nationalised, on 1 October 1944. In 1952, the BNR was merged with the East Indian Railway to form the Indian Railway ‘Eastern Railway’ but in 1955, BNR re-emerged to form the ‘South Eastern Railway’.
BNR Workshops
The BNR had workhops at several locations
BNR Collieries and Coal Supplies
See separate pages
- ‘Umaria Colliery’, a BNR Colliery from 1888
- ‘Sanctoria Colliery’, from 1889
- ‘Nodila Colliery’, from 1903
- ‘Murulidih Colliery’, from 1907
- ‘ Argada Colliery’, a BNR Colliery
- ‘Deulberra Colliery’ (was ‘Talchar Colliery’), a BNR Colliery
- ‘Bokaro Joint Coalfield’, the BNR worked jointly with the ‘East Indian Railway’(EIR)
- ‘ Sawang Joint Coalfield’, the BNR worked jointly with EIR
BNR Railway Network
See Bengal-Nagpur Railway - Lines Owned and Worked for details
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [2] gives 47 references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/5 “Records of the Bengal Nagpur Railway Company; 1856-1947
- L/F/7/249-255 "Finance Department Records; 1890-1947
A series of articles on the BNR, then celebrating its (highly significant) 25th year, was published during 1911 in The Indian Railway Gazette. The December 1911 issue carried biographical entries on the top 12 staff complete with individual photographic portraits. Microfilm of the Gazette can be consulted at the British Library's Newsroom.
There are some reports, letters and notes on the railway's history covering 1890-1930 held at
- 'Hertfordshire Archives and Local Studies', including copies of the Bengal-Nagpur Railway Magazine for July 1929, August 1929, November 1930 and December 1930.
Personnel
There are no BNR Staff Agreements in the India Office Records.IOR but as a State Railway a search of the following may yield a result -
- L/F/8/1-20 "Appointments to State Railways made in the UK 1855-1946"
- Z/L/F/8/1-2 Index to Appointments to State Railways made in the UK 1855-1946"
Bengal-Nagpur Railway Personnel gives details of BNR staff from several sources:-
- “India Civil List 1890” [3] and the " India List and India Office List, 1905" [4] for Public Works Department Railway Branch or State Railways personnel deployed to BNR gives a number of entries. The most notable of these have been listed.
- "Grace's Guide ” for notable personnel [5]
External Links
- Evolution of SER over the years A history of the South Eastern Railway, including the BNR and its constituents. This archived link from South Eastern Railway is most likely chapters (or content) from the book South Eastern Railway: March to New Millennium 1878-2001 by R. R. Bhandari 2001. Unfortunately, not all the chapters are accessible.
- Kharagpur’s Diaspora Reunited Memories and photos of a BNR family, the Cramptons, from the 1930s to 1950s.
- A map on which the Bengal-Nagpur Railway is shown may be found in Correspondence Part 7 (scroll down a considerable way)
- "Indian Railway Notes" by Hugh Scholey
References
- ↑ Indian Railways “Nagpur Division Railway History”; Retrieved 22 Dec 2017
- ↑ British Library Archives & Manuscripts Catalogue; Retrieved 18 Jan 2016
- ↑ Fibis Records, scans of original ”
- ↑ " India List and India Office List, 1905" Retrieved on 1 Jun 2016
- ↑ “Grace’s Guide”; Retrieved 1 Jun 2016