Bengal-Nagpur Railway - Lines Owned and Worked
Bengal-Nagpur Railway - Lines Owned and Worked
- a sub-section of the Bengal-Nagpur Railway(BNR) page
The Bengal-Nagpur Railway (BNR) owned and operated an extensive network of railways of broad gauge (BG) and 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge (NG) railways.
By 1918 there was total of 2,795 miles(4,498km) of open lines in the BNR system - this comprised:-
- 1,888 miles(3,038km) of BG lines
- 907 miles(1,468km) of NG.
- A further 328 miles(528km) were under construction - 266 miles(428km) of BG and 62 miles(100km) of NG.
By 1937 this had increased to 3392 miles(5459km)
- 2466 miles(3969km) of BG lines
- 926 miles(1490km) of Ng lines
The BNR also managed, worked and maintained a number of lines on behalf of other parties.
The BNR System Network is clearly shown on this 1937 map [1]
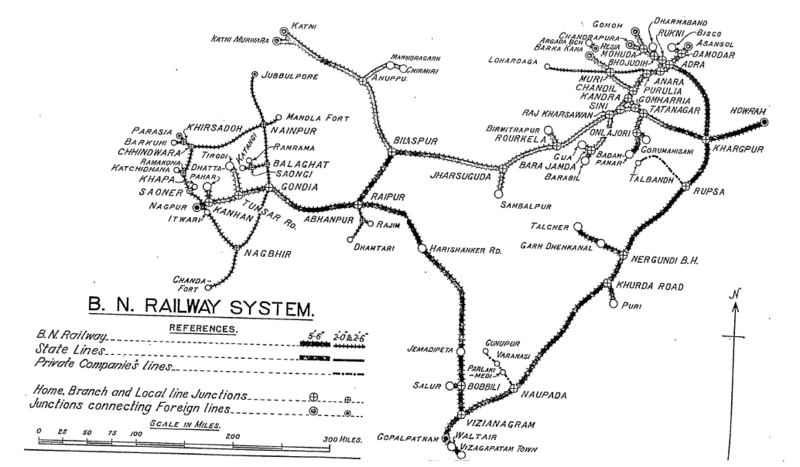
BNR Broad Gauge (BG) Network
1918 BG Network
The listing below is based on the “Administration Report on Railways 1918” [2]
- BNR Main Line Asansol to Nagpur; 630 miles (1,014km); fully opened as BG by 1891. The Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway in 1880-83 opened the 'Nagpur to Rajnandgaon Section', 144 miles(232km) as MG, converted to BG in 1888.
- Sanctoria Coal Branch Damodaodar to Sanctoria Collieries; opened 1889; 8 miles(13km)
- Chaurashi Branch Ramkanali to Nodila Colliery; opened 1903; 9 miles(14km)
- Sambalpur Branch Jharauguda to Sambalpar; opened 1893; 30 miles(48km)
- Katni Branch Bilaspur via Katni to the GIPR Marwara Junction; fully opened 1891; 197 miles(316km). This was the former Bilaspur-Etawa Provincial State Railway. The Katni-Umaria Provincial State Railway in 1886 had opened Katni to Umaria section, 36 miles(58km)
- Kanham - Dattapahar Spur; opened 1907; 17 miles(28km)
- Calcutta Extension Line Sini to Howrah; opened 1900; 171 miles(274km)
- Fort Gloster; Lawrence Mill; East Loop Narin Bank and Kidderpore Lines; opened 1900; 4 miles(6.4km)
- FulesVhwar Ring Mill Line; opened 1917; 0.4 mile(0.7km)
- Shalimar Branch Santragachi to Shalimar; opened 1901; 3.1 miles(5km)
- Cuttack Extension Khargpur to Cuttack; opened 1898-99; 182 miles(292km)
- Jharia Extension Khargpur to Midnapur, opened 1901; to Bhojudih, 1903; to Gomoh, 1907; to Bhowrah, 1914. Total 151 miles(243km) See separate page 'Jharia Coalfield Railways'
- Jhariah Coalfields Spurs ‘Bhojudih-Bhaga-Mounuda Loop’, opened 1903-04; ‘Bhowra Spur’, opened 1903; ‘Bhojudih-Pathardihi Link’, opened 1906 and extended 1915. Total 22 miles(35km); See separate page 'Jharia Coalfield Railways'
- Nonoodih BNR-EIR Connection, opened 1915, 1.4 miles(2.3km)
- Katras Connections Malkera to Katras, opened 1903; Khanoodih to Katras, opened 1907. Total 2.5 miles(4km)
- Murulidih Branch Mohuda to Murulidih Collieries, opened 1907, 2.7 miles(4.3km)
- Jamadoba Loop, opened 1903, 5.4 miles(8.7km)
- Aldih Branch, opened 1906, 2.5 miles(4km)
- Visianagram - Parvatipuram Extension Visianagram to Bobbili, opened 1908; Bobbili to Parvatipuram, opened 1900. Total 48 miles(77km)
- Bobbili - Salur Branch Bobbilli to Salur, opened 1913, 10 miles(16km)
- Kalimati - Gorumahisani Extension, Kalimati (later to become Tatanagar Junction) to Gorumahisani , opened 1911, 40 miles(64km). The ‘Badampahar Spur’ extended the line to the Badamphar Iron Mines in about 1922
- Bokharo Ramgarh Extension Mghuda via Jamuniatand to the BNR/EIR joint line, opened 1913-15. Total 22 miles(35km).
- Kalamna - Itsari - Nagpur Section Kalamna via Itsari to Nagpur, opened 1911, 4 miles(6.4km)
- BNR East Coast Railway Northern Section Cuttack to Waltair formerly part of the East Coast State Railway, opened 1894-97, 321 miles(516km)
- Naupuda Salt Branch included in above
- Puri Branch included in above
BG Lines under construction as at 1918
- Raipur - Parvatipuram Line, sanctioned 1906, 261 miles(420km)
- Kandra - Gomharia Chord, sanctioned 1914, 5.5 miles(8.9km)
- Panposh-Ruipura Railway, sanctioned 1917, constructed and worked by BNR opened 1919-20, 14 miles(23km)
Later BG extensions after 1918
- Raipur - Vizianagram BNR Branch, opened in 1931. Originally surveyed in 1879-82 but not constructed, then known as the Vizagapatam-Raipur Railway
- Anuppur-Manendragarb-Chimiri Railway, opened 1939 by BNR; built primarily to convey coal from the Kotma area
1937 BG Lines
The following extensions to those given in the 1918 Report above are [3].
- Gua Branch, opened 1924-26, 69 miles(111km), from Raj Kharsawan Junction to Gua with a 4 miles branch to Barabil
- Birmitapur Branch,opened 1622-26, 18 miles(30km), from Rourkela to Birmitrepur
- Raipur-Vizianagram Railway, opened 290 miles(467km) incorporating the 'Visianagram - Parvatipuram Extension' of 44 miles (77km) which had opened in 1908-09
- Tumsar-Tirodi BG Conversion, opened 1929, 29 miles(47km)
- Tatanagar-Gorumahisani Branch, opened in 1922, 21 miles(34km) an further development from Onlajori to Badampahar, (including Salapet Branch), from the 'Kalimati - Gorumahisani Extension', 40 miles(64km) which had opened in 1911
- Nergundi to Talcher Branch, opened 1927, 62 miles(99km), from Nergundi to Talchar. This would have carried coal from the 'Talcher Colliery’, a 'Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway Colliery’ and the BNR's own ‘Deulberra Colliery’
- Bokharo-Ramgarh Extension, 1927, 72 miles(115km), Barakakhana to Chandil; an further section to the 'Mohuda to Chaudrapura Section' of 9 miles(15km) and the BNR and EIR lines at Nunudih 1.5 miles(2.5km) all opened 1913-15
BG Lines worked by BNR
See separate pages for details
- Bellary-Kistna State Railway , constructed before 1890; surveyed for Hindpur extension 1892-94; worked by BNR.
- Ganjam District Light Railway , surveyed 1899 but did not go ahead in entirety; Parlakimedi Light Railway opened 1 section, 1900 worked by BNR from 1902.
- Kamptee-Deolapar-Ramtek Railway , surveyed 1903 to construct light railway on public roads to convey Manganese; worked by BNR(qv); no further information
- Pench Valley Coalfield Railway , opened 1906-7; 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG)line, from the Pench and Kanhan coalfields to Chhindwara where it connected to the (BNR) Satpura Railway network; worked by BNR.
- Baripada-Talbond Railway , opened 1920, extension to Mayurbhanj Railway; worked by BNR.
- Visakhapatnam Port Trust Railway , inner harbour railway, built by BNR 1927-33 to export manganese ore.
- Central Indian Coalfields Railway , opened 1927, GoI owned; part worked by BNR; later amagamated with East Indian Railway(EIR)
BNR Narrow Gauge (NG) Network
The listing below is based on the “Administration Report on Railways 1918” [4]
BNR 2ft 6in/762mm Narrow Gauge Lines
See separate pages for details
- Raipur-Dhamtari Railway and Rajim Branch Railway. The first 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) branch of BNR, opened 1900 and extended to Rajim 1906. Total 57 miles(92km)
- Purulia Ranchi Light Railway. BNR NG line, opened 1907 and extended 1913. Total 115 miles(185km)
- Satpura Railway. NG network. Developed by the BNR from 1904 onward, eventually being described as the ‘Satpura Railway’; connected Jubbulpore with Gondia, Mandla Fort, Chhindwara and Nagpur; later extended. Comprising: -
- Jubbulpore-Gondia Railway. NG extension, opened 1903-13, owned by GoI, worked by BNR. Total 311 miles(501km)
- Gondia-Chanda Railway. NG extension, opened 1908-16. Total 217 miles(349km)
- Nagbhir-Nagpur Branch Railway, opened 1908. Total 66 miles(106km)
- Nagpur-Chhindwara Railway. NG extension, opened 1911, owned by GoI and worked by BNR. Total 97 miles(156km)
- Tumsar-Tirodi Light Railway. 2ft 0in/610mm narrow gauge(NG); opened 1910 as ‘Tumsar-Katangi Railway’ owned by Central India Mining Co ; Purchased in 1916-17 by GoI; worked by BNR; connecting to BNR's Satpura Railway.
NG Lines worked by BNR
See separate pages for details
- Parlakimedi Light Railway, 2ft 6in/762mm NG; owned by Raja of Parlakimedi, opened 1900, worked by BNR, 25 miles(39km).
- Mourbhanj State Railway, 2ft 6in/762mm NG; owned by Mourbhanj State, opened 1905, worked by BNR, 32 miles(km). Renamed Mayurbhanj Railway 1920 and transferred to private company.
References
- ↑ From US Archive.com ‘History Of Indian Railways - Railway Department,Government of India, 1937’ pdf #43 pdf page copied, cut and marked as necessary]; Retrieved 19 Apr 2020
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 1-3; Retrieved 22 Dec 2017
- ↑ US Archive.com ‘History Of Indian Railways - Railway Department,Government of India, 1937’ Pages 21-23, pdf pages 44-46; Retrieved 19 Apr 2020
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 6-11; Retrieved 22 Dec 2017