Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway
| Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway Logo | ||
| System timeline | ||
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway | ||
| Powayan Light Railway | ||
| from 1891 | Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway | |
| before 1891 | Lucknow-Sitapur-Sihramau Railway | |
| before 1891 | Bareilly-Pilibheet Provincial State Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Izatnagar | |
| Workshops | Bareilly | |
| Major Stations | Bareilly, Lucknow, Mailani, Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur
See also separate page Lucknow Junction Station for details | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1943 | Oudh and Tirhut Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 331 miles (1905) 687 miles (1943) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Bareilly to Kathgodam | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 54 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1882 | Company registered | |
| 1884 | Open to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Bhojeepura, Laikua, Haldwani | |
| System agency | ||
| Worked by Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway (R&KR) was a metre gauge(MG) railway whose northern terminus at Kathgodam served the submontane belt of the United Provinces between Lucknow and Moradabad, as well as a number of hill stations, such as Naini Tal.

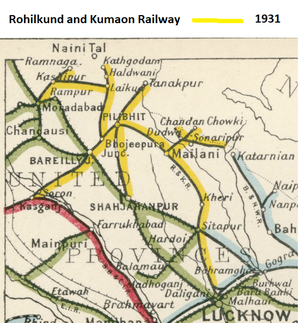
The ‘Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway Company’ started construction and working of a railway line from Bhojeepura (near Bareilly) to Kathgodam under a contract dated 12 Oct 1882. This was the original main line and opened on 12 Oct 1884 and ran 54 miles(84km) in a north-westerly direction to Kathgodam.
The R&KR also had working agreements with both the MG ‘Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway’ and the NG ‘Powayan Light Railway’. The three railways were worked using shared facilities, classified as the ‘Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway System’ but retaining separate identities. See ‘Lines Worked’ and ‘Records' below
In 1906 the R&KR extended the line from Bareilly to Soron where it joined existing MG line to Kasganj. The ‘Kasganj-Soron Section’ had been constructed by the State Government in 1885 as part of the ‘Rajputana-Malwa Railway’(RMR) ‘Cawnpore-Achnera Line ‘and in 1906 was passed to the R&KR. The extensions from Moradabad to Kashipur, Kashipur to Ramnagar and Lalkuan to Kashipur were completed by 1908 [1].
The railway was progressively extended and by 1912 the R&KR covered 256 miles(412km); and the R&KR also worked the ‘Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway ‘296 miles(476km) and together with the ‘Powayan Light Railway’; giving a total network of 592 miles(953km) [2].
The lines from Pilibhit to Carewganj and Shabaznager were completed by 1916 [1]
The 1918 “Administration Report” [3] gives a total of 610 miles(982km) for the ‘Rohilkund and Kumaon System’ comprising the actual ‘R&KR’ 259 miles(417km); the ‘Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway ’ 312 miles(502km); and the ‘Powayan Light Railway’ (39 miles(63km)
The 1937 “History of Indian Railways” [4] gives a total of 571 miles(919km) for the ‘Rohilkund and Kumaon System’ comprising the actual ‘R&KR’ unchanged at 259 miles(417km); the ‘Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway ’ unchanged at 312 miles(502km). The ‘Powayan Light Railway’ having closed in WW1
Company History
The Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway Company, Limited, was a Joint Stock Company with limited liability, having its registered office in London[5] . The company was privately owned and worked from formation in 1882
In 1883 Alexander Izat was appointed Director, prior to this he was employed by the Railway Branch - Public Works Department (PWD) where he had served in various parts of India and was instrumental in initiating and carrying out many metre-gauge extensions[6]. He represented R&KR at the Indian Railway Conference Association and remained as Director, until his retirement in 1904. In 1918 he is recorded as being R&KR Chairman with headquarters in London [3]
The R&KR remained a private Company until nationalisation in 1943 when it was amalgamated with the Bengal and North-Western Railway(B&NWR), with which it had been closely associated, and the Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway, to form the Oudh and Tirhut Railway(O&TR).
In turn, in 1952, the Oudh and Tirhut Railway became part of 'North Eastern Railway', a zone of Indian Railways.
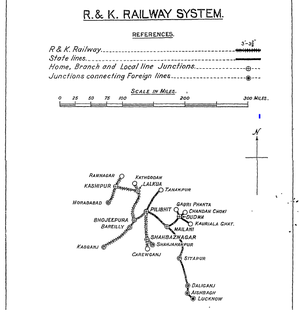
Lines owned and operated by R&KR
Information mainly based on the “Administration Report for Railways 1918” [3].
- Bhojeepura-Kathgodam R&KR Mainline from Bhojeepura (near Bareilly to Kathgodam , 1884; 54 miles(84km)
- ‘Kasganj Extension Line’ from Bareilly to Soron, 1885; to Kasganj, 1906; 63 miles(100km).
- ‘Ramnagar Extension Line’ from Moradabad via the ‘Ramganga Bridge' to Ramnagar, 1907-8; 48 miles(76km)
- ‘Kashipur Extension Line’ from Lalkua to Kashipur, 1907; 36 miles(57km). This line surveyed as ‘Kichha-Kashipur Extension Survey’ - see separate page
- ‘Shahjahanpur Extension Line’ from Pilibhit 1911; reaching Shahjahanpur 1916; 56 miles(89km)
Lines worked by R&KR
- Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway(LBSR), was formed in 1891 from the merger of the Lucknow-Sitapur-Sihramau Railway and Bareilly-Pilibheet Provincial State Railway [5]. The metre gauge(MG) railway formed an alternative northern "loop" between the cities of Lucknow and Bareilly to the broad gauge(BG) main line of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway. The MG of 198 miles (317km) in 1891; extended to 312 miles(500km) by 1918 [3] and the same in 1937[7].
- Powayan Light Railway, from the 17 Dec 1900 worked by R&KR, a 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) line of 39 miles(62km) length [3] and dismantled in WW1 [4] see separate page for information
Lines Surveyed/Proposed by R&KR
- ‘Kichha-Kashipur Extension Survey’ - see separate page surveyed 1894-98 which became the ‘R&KR Kasganj Extension Line’ listed above
- ‘Kathgodam-Nainital Branch’, proposed by private enterprise in 1895 for the development of Kuaon and Nainitial districts. It was to be a 2ft/610mm narrow gauge(NG) line, 13 miles(21km) line at estimated cost RS.12 lakhs. The concession lapsed in 1898 [8].
- ‘Philibhit-Sitapur Railway’, sanctioned for survey 1905-6; MG line from Pilibhit - Bisalpur to Shahjahanpur and thence to Sitapur, a length of about 105 miles(168km) [8].
- 'Philibhit - Shahjahanpur Section’ was constructed by R&KR as ’Shahjahanpur Extension Line’, opened 1911-16 - see above;
- ‘Shahjahanpur - Sitapur Section’ was constructed the East Indian Railway]](EIR] as a broad gauge(BG) line from Rosa (just south of Shahjahanpur ) to Sitapur Cantonment and opened in 1910-14 and became the EIR ‘‘Rosa-Sitapur Branch’
- ‘Dudhwa Branch Extension’ and ‘Ramnager Ghat Extension’, first proposed in 1895 by the Agents, the R&KR, on behalf of the Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway(LBSR) - see for information [8].
- ‘Pilibhit-Barmedo Branch’, surveyed in 1903 by the Agents, the R&KR, on behalf of the Lucknow-Bareilly State Railway(LBSR) - see for information [8]
Records
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [9] gives many references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/35 “ Records of the India Office relating to the Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway Company; 1882-1931"
- L/F/7/2382-2391 “Collection 380: Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway, date unspecified"
Personnel Records
There are no personnel or staff records held in the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
There is a photograph dated 1911 in the British Library ‘Satow Collection’:
"Miscellaneous Portrait Groups of Railway Officials" Photo 1082/13(4) with the following Catalogue Note [10]:-
Officers of Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway, Feb. 1911. Group portrait of railway officials, with identifications written on mount as follows:
- front row, seated on ground: Kellie, Edwards, Welsh;
- second row, seated: Bruce, Izat, Finlayson, Robb, Ralston;
- third row, standing: Steyn, Bannister, Storrar, O'Brien, Irons, Young, Smith;
- back row, standing: Sandes, Donaldson, Will, Clark, Addis
The R&KR officers detailed above have not been identified at the present time.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 ‘Government of India’ - “NorthEastern Railway – From the pages of History” ; Retrieved 1 Jun 2019
- ↑ Google Books “The Making of India: The Untold Story of British Enterprise” by Kartar Lalvani, page 218; Retrieved 8 Dec 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 196; Retrieved 8 Dec 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 183 pdf 224; Retrieved 24 Sept 2020
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 British Library ‘India Office Records’ L/F/8/13/977 “Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway- Contract for advance of capital and as to debentures supplemental to the Contact dated 8 Sep 1890” , 1892
- ↑ Grace's Guide "Alexander Izat"; Retrieved on 18 Jul 2016
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 190 pdf 231; Retrieved 24 Sept 2020
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 “Histories of (Indian)Railway Projects ...up to June 1906” page 42; Retrieved 3 Oct 2017
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 27 Jan 2016
- ↑ India Office Records “Officers of R. & K. Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway, Feb. 1911". Photo 1082/13(4)); Retrieved on 21 Jul 2016