Bhavnagar State Railway
| Bhavnagar State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1880 | Bhavnagar State Railway system formed | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1911 | Bhavnagar State Railway | |
| 1911 | Dhrangadra Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Bhavnagar | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | Bhavnagar, Dhola, Wadhwan | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1948 | Saurashtra Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 206 miles (1921) 307 miles (1944) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Bhavnagar State Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Dhola to Wadhwan Bhavnagar to Mahuva | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 307 miles (1944) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1880 | First section opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bombay | |
| Stations | Bhavnagar, Dhandhuka, Dhola, Jasdan, Kundla, Limbdi, Mahuva, Palitana, Wadhwan | |
| System agency | ||
| 1880 | Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway | |
| 1911 | Own agency | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Bhavnagar State Railway (BSR) was a Metre Gauge(MG) railway line formed and built by the Princely Bhavnagar State in Bhavnagar State in the Kathiawar Peninsula .
Soon after the formation of BSR in 1880 the company absorbed the Princely ‘Kathiawar State Railway’
Initially worked by an administrative coalition as the ‘Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway’, the BSR operated as an independent system from 1911 under the administration of the Bhavnager Durbar. [1]
For some years after 1911, the BSR also worked the ‘Dhrangadra Railway’.
In 1948 the BSR was merged to form the ‘Saurashtra Railway’.
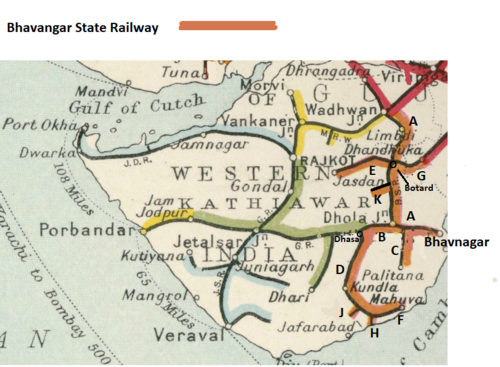
History
- 1878 November: The building of a metre gauge(MG) railway from Bhavnagar to Wadhwan was sanctioned [2]. The line was to interchange at Wadhwan with the Bombay, Baroda Central India Railway(BB&CIR) ‘Viramgam-Wadhwan Branch Line’ that had opened as a broad gauge(BG) line in 1873 (converted to MG in 1902)[3].
- 1879 March: Mr. Alexander Izat was appointed as the Engineer-in-Chief. He was earlier the Chief Engineer of the Dhond-Manmad State Railway (which had opened in 1878). Mr. R. Proctor Sims who was Bhavnagar's State Engineer had carried out the survey from Bhavnagar to Botad. The survey from Dhasa to Dhoraji was carried out under Mr. Ford who held analogous post in Gondal. An engineer from BB &CIR, Mr. Hargreaves did the survey from Botad to Wadhwan [4].
- 1879 July: The Agreement was signed, whilst mainly between Bhavnagar State and Gondal State also involved the British Administration, (taking charge of the security of the line) and others due to the number of different States that the line passed through [5].
- 1880 December: The ‘Bhavnagar-Wadhwan Mainline’, 104 miles(167km), opened from Bhavnagar to Wadhwan [6], and to the junction with the Bombay, Baroda Central India Railway(BB&CIR), 106 miles(171km) [7]. Built and financed by the Princely Bhavnagar State.
- Line ‘A’ on map
- 1881 January: The ‘Dhoraji Branch Line’, 89 miles(143km) opened. This branch from Dhola Junction (between Bhavnagar and Wadhwan) to Dhasa, 15 miles(24km) [6] and from Dhasa via Jetasar to Dhoraji, 74 miles(119km) [8]. Funded in proportion to the distance in each Territory being approximately 2/3rd Bhavnagar State and 1/3rd Gondal State [9].
- Line ‘B’ on map
- 1881: The 'Bhavnagar-Gondal State Railway' was formed as an administrative coalition between the 'Bhavnagar State Railway' and the ’Gondal State Railway' - see separate page for further information.
- 1888: When the ‘Junagadh State Railway’ from Junagadh to Jetalsar opened in 1888 and on to Verval the coalition briefly became the 'Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Verval Railway'(BGJVR)
- 1889: When the ‘Porbandar State Railway’ extension from Dhasa reached Porbandar the coalition finally became the ‘Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway’(BGJPR) - see separate page for further information]].
This ‘Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway’(BGJPR) coalition was also described in some records as the ‘Kathiawar Railway’, the ‘Kathiawar Union Railway’ and the ‘Kathiawar State Railway’.
- 1910 November: The ‘Palitina Branch’ Line, 17 miles(27km) opened from Sihor to Palitina [6].
- Line ‘C’ on map
- 1911: The BGJPR administrative coalition was dissolved in 1911 with the constituents going their independent ways.
The Bhavnagar State Railway (BSR) was formed under the administration of the Bhavnager Durbar. [6].
Bhavnagar State Railway
With the dissolving of the BGJPR the ‘Bhavagar State Railway’(BSR) continued to develop :-
- 1911-12: The ‘ Kundla Extension’, 36 miles(58km) from the mainline at Dhasa to Kundla (Savar Kundla) [6].
- Line ‘D’ on map
- 1913: The ‘Jasdan Branch’, 33 miles(54km) from the mainline at Botard to Jasdan, this was partly funded by the Jasdan Darbar [6].
- Line ‘E’ on map
- 1921-22: The ‘Mahuva Extension’, 42 miles(68km), a further extension from Kundla via Rajula Junction to Mahuva. **Line ‘F’ on map
- 1922: The ‘Dhandhuka Branch’, 30 miles(48km), from the mainline at Botard to Dhandhuka where it connected to the BB&CIR network.
- Line ‘G’ on map
- 1922: The ‘Rajula Town and Quarry Branch’, 6 miles(10km) from Rajula Junction to Rajula Town and a spur to the nearby quarries at Rajula.
- Line ‘J’ on map
- 1923: The ‘Port Albert Victor Branch’, 7½ miles(12km), which became an important oil terminal.
- Line ‘H’ on map
- 1929: The ‘ Ningala-Gadhada Branch’ , 9½ miles(15km),
- Line ‘K’ on map - this line does not appear on the 1931 Map and there is no evidence of this route on modern maps [10].
- 1948: The BSR was merged to form the ‘Saurashtra Railway’’ - see separate page
Lines Worked by BSR
- ‘Dhrangadra Railway’ - see separate page from opening in 1898 worked by BGJPR and from 1911 by BSR.
- ‘Bhavnagar Tramway’- see separate page, built by Bhavnagar State, first section opened 1926 , extended 1938 and worked by BSR.
- ‘Wadhwan-Sayla Tramway’ - see separate page built by an Agency of BSR, opened in 1924 and worked by BSR.
Personnel Records
No Staff Lists have been found.
The Records show the following deployed to the 'Kathiawar State Railway' ,which became ‘Bhanagar State Railway’.
- Trevredyn Rashleigh Wynne deployed from the Railway Branch of the Public Works Department, 1879-83, to the Kathiawar State Railway as Assistant Engineer, later promoted to Executive Engineer.
- John Edwin Dallas, Assistant Engineer, also from the Railway Branch was P.A. to the Engineer-in-Chief Kathiawar State Railway, from 1881.
- Ernest Ifill Shadbolt, also from the Railway Branch was Executive Engineer, Kathiawar State Railway, 1887-91.
The following are recorded as 'on loan' to Bhanagar and Gondal Railway from the Public Works Department(PWD)
- Ernest Ifill Shadbolt, PWD Assistant Engineer from 1874 to 1884 'services lent to Bhavnagar and Gondal States' Railways [11].
- Alexander Izat, 1879, Engineer-in-Chief [12], on loan
- Richard Gardiner Lieut-Col. R.E. from PWD, 1887, Manager and Engineer-in-Chief of 'Bhavnagar-Gondal Railway' until retirement in 1893.[13].
- Willoughby Verner Constable, 1887, Officiating Manager of 'Bhavnagar, Gondal and States Railways' [14].
- Horace Chaloner Knox, 1890, Executive Engineer employed with 'Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway' [15].
Further Information
See Bhavnagar-Gondal-Junagad-Porbandar Railway for period to 1911
and Kathiawar Peninsula Railway and Tramway Systems gives a map, timeline and relates this railway to others in the Kathiawar Peninsula.
References
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 169; Retrieved 30 Jan 2016
- ↑ ‘Bhavanagar.com’ “History of Bhavanagar” by ’ Manoj Pande; Retrieved 19 Jun 2019
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 22 (pdf31) ; Retrieved 10 May 2020
- ↑ Wikipedia ‘Bhavangar State Railway’; Retrieved 19 Jun 2019
- ↑ British Library IOR/V/1384 ‘India States Administration Reports – Kathiawar 1865-1875 No 50A of 1867, para 2
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 169(pdf177); Retrieved 19 Jun 2019
- ↑ ‘1884 Gazetteer of Bombay Presidency, Volume 8 Kathiawar -Railways pages 221-222(pdf249-250); Retrieved 10 May 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 181 (pdf189); Retrieved 10 May 2020
- ↑ .‘1884 Gazetteer of Bombay Presidency’, Volume 8 Kathiawar -Railways pages 221-222(pdf249-250); Retrieved 18 Jun 2019
- ↑ Kathiawar Economics’,1943, by A B Trivedi, 1943 Digital Library of India Archive.org Page 192); Retrieved 18 Jun 2019
- ↑ “Indian Biographical Dictionary” 1915 page 390; Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Wikipedia "Bhavnagar State Railway"; Retrieved on 7 Jul 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 499 (pdf page 462) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 466 (pdf page 429) Retrieved on 17 May 2016
- ↑ India Civil List 1890, page 41