B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Revision inc 1937 info and bigger map |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked''' | <big>'''B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked'''</big> | ||
<blockquote>- a sub-section of the '''[[Bengal and North-Western Railway]]'''(B&NWR) page</blockquote> | <blockquote>- a sub-section of the '''[[Bengal and North-Western Railway]]'''(B&NWR) page</blockquote> | ||
In 1905 there was 1468 miles(2363km) of metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) in the B&NWR Network, (902 miles plus the 566 miles ‘[[Tirhoot State Railway]]’) | In 1905 there was 1468 miles(2363km) of metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) in the B&NWR Network, (902 miles plus the 566 miles ‘[[Tirhoot State Railway]]’(TSR)) | ||
<br>By 1918 | <br>By 1918 the B&NWR System had increased to 2046 miles(3293km) = 1242 miles plus 804 miles TSR | ||
<br>By 1937 the B&NWR System had increased to 2107 miles(3391km) = 1270 miles plus 800 miles TSR plus 39 miles [[Masharak-Thawe Extension Railway]] | |||
The ‘[[Tirhoot State Railway]]’ was worked in conjunction with the B&NWR. [[Tirhoot State Railway |''See separarate page for full information'']] | The ‘[[Tirhoot State Railway]]’ was worked in conjunction with the B&NWR. [[Tirhoot State Railway |''See separarate page for full information'']] | ||
[[File:B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked 1937.png|right| B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked , 1937]] | |||
===B&NWR Mainline & Branches=== | ===B&NWR Mainline & Branches=== | ||
The following is generally based on the 1918 Administration Report for Railways | The following is generally based on the 1918 Administration Report for Railways | ||
<ref name=Admin1918>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n165/mode/1up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 157-162]; Retrieved 16 Apr 2020</ref> and the 1937 History of Indian Railways, Railway Branch | <ref name=Admin1918>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n165/mode/1up "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 157-162]; Retrieved 16 Apr 2020</ref> and the 1937 History of Indian Railways, Railway Branch | ||
| Line 22: | Line 26: | ||
* Jarwal Road to Bahramghat, 5 miles(8km) (including [[Elgin Bridge, Barabanki|Elgin Bridge]]) opened 18 December 1896 | * Jarwal Road to Bahramghat, 5 miles(8km) (including [[Elgin Bridge, Barabanki|Elgin Bridge]]) opened 18 December 1896 | ||
* Bahramghat to Burhwal , 4 miles(6.5km) opened 24 November 1896 | * Bahramghat to Burhwal , 4 miles(6.5km) opened 24 November 1896 | ||
'''B&NWR Branches ''' metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]). | '''B&NWR Branches ''' metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]). | ||
Revision as of 10:28, 19 April 2020
B&NWR Lines Owned and Worked
- a sub-section of the Bengal and North-Western Railway(B&NWR) page
In 1905 there was 1468 miles(2363km) of metre gauge(MG) in the B&NWR Network, (902 miles plus the 566 miles ‘Tirhoot State Railway’(TSR))
By 1918 the B&NWR System had increased to 2046 miles(3293km) = 1242 miles plus 804 miles TSR
By 1937 the B&NWR System had increased to 2107 miles(3391km) = 1270 miles plus 800 miles TSR plus 39 miles Masharak-Thawe Extension Railway
The ‘Tirhoot State Railway’ was worked in conjunction with the B&NWR. See separarate page for full information
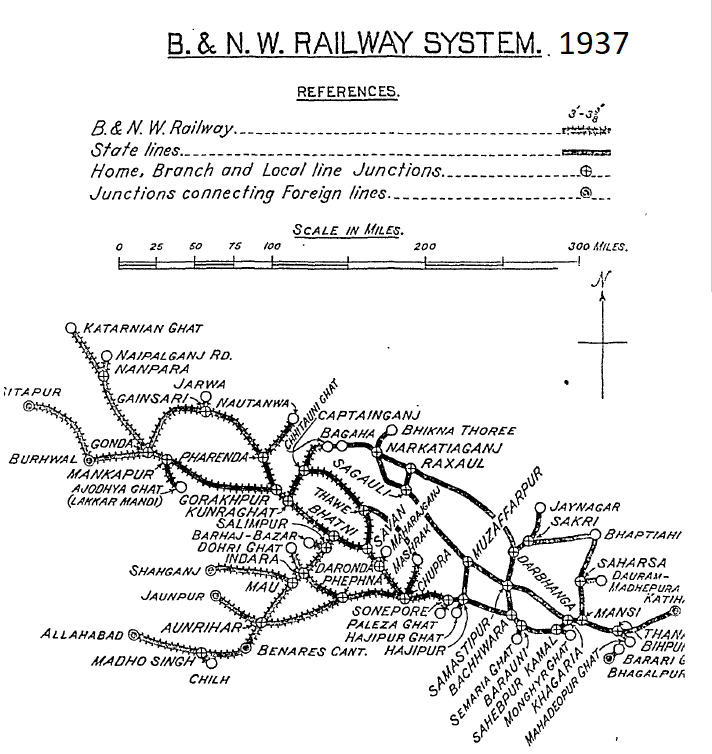
B&NWR Mainline & Branches
The following is generally based on the 1918 Administration Report for Railways [1] and the 1937 History of Indian Railways, Railway Branch [2]
B&NWR Mainline metre gauge(MG), total 277 miles(446km) consisting of following sections:-
- Sonepur to Mankapur , 221 miles(354km) opened 15 January 1885
- Mankapur to Gonda , 17 miles(27km) opened 2 April 1884
- Gonda to Colonelganj , 18 miles(30km) opened (29 October 1891) 1 February 1892
- Colonelganj to Jarwal Road, 11 miles(18km) opened 1 February 1892
- Jarwal Road to Bahramghat, 5 miles(8km) (including Elgin Bridge) opened 18 December 1896
- Bahramghat to Burhwal , 4 miles(6.5km) opened 24 November 1896
B&NWR Branches metre gauge(MG).
- Branches from B&NWR Mainline
- ‘Digha Ghat Branch B&NWR’, Sonpor to Palaza Ghat, 6 miles, 1885 The B&NWR at Palaza Ghat was connected to East Indian Railway ‘Digha Ghat Branch EIR’ by the Digha Ghat Steam Ferry [3]
- ‘Mashrak Branch’, Chapra to Mashrak, 26 miles, 1910
- ‘Maharajganj Branch’, Daronda to Maharajganj, 4 miles, 1907
- ‘Saran-Captainganj Branch’, Saran to Captainganj, 79 miles, 1907-13
- ‘Bagaha Branch’, Gorakhpur to Bagaha, 62 miles, 1907-13
- ‘Gorakhpur-Gonda Branch’, Gorakhpur to Gonda, 135 miles, 1886-1906 in stages
- ‘Jarwa Branch’, Gainsari to Jarwa, 9 miles, 1906
- ‘Katarnian Ghat Branch’, Nanpira to Katarnian Ghat, 42 miles, 1896
- ‘Silapur Branch’, Burwhal to Silapur, 59 miles, 1911
- ‘Chupra-Benares-Allahabad Branch’, 201 miles, first section opened 1891, this included the ‘Ganga-Gogra Doab Mainline’ see below extended to Jhusi 1909, Izat Bridge 1912, Allahabad 1913.
- ‘Mirzapur Ghat Extension’, Madho Singh to Mirzapur Ghat, 7 miles, 1999 extended 1912, part of Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines’ see below
- ‘Bhatni Benares Chord’, Bhatni to Aunrihar, 79 miles, 1896-99, part of Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines’ see below
- ‘Barhaj Branch’, 13 miles, Salimpur to Barhaj-Bazaar, 1907
- ‘Dohri Ghat Branch’, 33 miles, Phephna via Daronda to Dohri Ghat, 1899-1901,
- ‘Shahganj Branch’, 62 miles, Mau to Shahganj, 1898-1903, part of Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines’ see below
- ‘Janupur Branch’, 36 miles, Aunrihar to Janupur, 37 miles, part of Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines’ see below
Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines

The ‘Ganga-Gogra Doab Lines’ were the classification given by the B&NWR to the lines in this area, and were part of the ‘B&NWR Mainline branches’ above.
The lines run through an especially fertile area of land between the Ganges and Gogra rivers known as the Doab. Doab literally means land lying between two confluent rivers, the Ganges (Ganga) and the Gogra. Most of the trade was born by these rivers and the railway has many spur lines to ghats on both rivers. The lines comprised:-
- ‘Ganga-Gogra Doab Mainline’ between Sonopore on the North Western Railwayand Allahabad , 200 miles (322km), opened in stages from 1899 to 1912. This was part of the B&NWR ‘Chupra-Benares-Allahabad Branch’ (see above) . The line ran from Sonpore on the main North western line along the river to Allahabad. It reached Revelganj first by April 1889 then crossed the river Ghaghara River by the Inchcape Bridge which opened in 1912. Then on to Phephna , Gahazipur and Aunrihar to Benares, connecting with the East Indian Railway. Then on to Madhosingh crossing the Izat Bridge into the city of Allahabad. The line from Allahabad to Benares was proposed and surveyed in 1907.
- Branches from ‘Ganga-Gogra Doab Mainline’
- ‘Mirzapur Ghat Extension’, Mado Sihgh to Mirzapur Ghat, 7 miles, 1899 extended 1912. Running from Mado Singh to Chilh to a ghat to connect to Mirzapur on the other side of the river Ganges. No evidence of the line now exists.
- ‘Bhatni Benares Chord’, Bhatni to Aunrihar, 79 miles, 1896-99. Opened from Bhatni to Turtipar in December 1896 a distance of 17.23 miles (7.73kim) This was followed to Mau in June 1898. The final link opened in March 1899 to Aunrihar about 24.85miles (40km) east from Benares.
- ‘Shahganj Branch’, Mau to Shahganj, 62 miles, 1898-1903. Branch to meet with the East Indian Railway Shahganji opened in stages from Mau to Azamgarh in 1898 and to Shahganj in 1903
- ‘Janupur Branch’, Aunrihar to Janupur, 37 miles, 1904. Connected the main line running along the Ganges valley to the East Indian Railway at Jaunpur.
Tirhoot State Railway Network
- ‘Tirhoot State Railway’(TSR), opened 1874. Temporary famine relief line; worked by B&NWR 1886-1890; then independent but included as part of B&NWR network.
Lines worked by B&NWR
- ‘Benares City Branch Railway’, opened as branch of Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway(O&RR) 1899; however worked by B&NWR
- ‘Cawnpore-Barabanki Railway’, opened 1896; worked jointly between B&NWR and Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway(R&KR) networks
- ‘Darbhanga State Railway’, opened 1883-84 as Nirmali Branch of Tirhoot State Railway(TSR); worked by B&NWR 1886-1890; then reverted to TSR
- ‘Nirmali Branch Railway’, alternative name for Darbhanga State Railway
- ‘Masharak-Thawe Extension Railway’, opened 1931, worked by B&NWR
- ‘Patna-Baraich Railway’, constucted by B&NWR under arrangement with Government of India(GoI); first phase opened 1884 and worked by B&NWR.
- ‘Sagauli-Raxaul Railway’,opened 1899, included under B&NWR, 1904
References
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 157-162; Retrieved 16 Apr 2020
- ↑ US Archive.org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’ pages 11-20, pdf 32-41; Retrieved 16 Apr 2020
- ↑ ‘Imperial Gazetteer of India’, v. 22, p. 90. ; Retrieved 16 Apr 2020