Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway: Difference between revisions
1909 Railway Map Section added |
m →History: link removed |
||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
The JBR had its beginnings in a section of metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railway built for the [[Rajputana-Malwa Railway]] between [[Marwar]] and [[Luni]]. Later this section was extended to [[Jodhpur]] and formed the first ''' | The JBR had its beginnings in a section of metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) railway built for the [[Rajputana-Malwa Railway]] between [[Marwar]] and [[Luni]]. Later this section was extended to [[Jodhpur]] and formed the first '''Jodhpur Railway'''. | ||
[[Walter Home]] was, in April 1882, deployed from the [[Public Works Department]] Railways Branch, appointed as Manager for the construction of the Jodhpur Railway and also in-charge of the Marwar State Public Works Department . He built the Jodhpur Railway from scratch over the ensuing 25 years. | [[Walter Home]] was, in April 1882, deployed from the [[Public Works Department]] Railways Branch, appointed as Manager for the construction of the Jodhpur Railway and also in-charge of the Marwar State Public Works Department . He built the Jodhpur Railway from scratch over the ensuing 25 years. | ||
Revision as of 07:31, 15 November 2016
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Marwar to Kuchaman Merta to Bhatinda | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 710 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1882 1884 1885 |
Marwar to Pali section opened Pali to Luni section opened Luni to Jodhpur section opened | |
| 1889 | Joint system formed | |
| 1891 | Jodhpur to Bikaner section opened | |
| 1902 | Bhatinda reached | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Bhatinda, Bikaner, Hissar, Gigasar, Jodhpur, Kuchaman, Luni, Mahajan, Marwar, Merta, Nagaur, Palana | |
| System agency | ||
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1889 | Joint system formed | |
| 1924 | System split between the two States | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1889 | Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | |
| 1900 | Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway | |
| 1910 | Pipar-Bilara Light Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Jodhpur | |
| Workshops | ||
| Major Stations | Bhatinda, Bikaner, Hissar, Hyderabad, Jodhpur, Kuchaman, Luni, Marwar | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1924 | Bikaner State Railway Jodhpur State Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 834 miles (1905) 1331 miles (1921) | |
| 2' 6" NG | 25 miles (1921) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
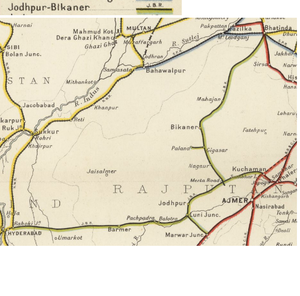
The Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) was a metre gauge (MG) system, jointly owned and operated by the Princely Jodhpur State and Bikhaner State until 1924 when the system was split between the newly-formed Jodhpur State Railway and Bikhaner State Railways.
History
The JBR had its beginnings in a section of metre gauge(MG) railway built for the Rajputana-Malwa Railway between Marwar and Luni. Later this section was extended to Jodhpur and formed the first Jodhpur Railway.
Walter Home was, in April 1882, deployed from the Public Works Department Railways Branch, appointed as Manager for the construction of the Jodhpur Railway and also in-charge of the Marwar State Public Works Department . He built the Jodhpur Railway from scratch over the ensuing 25 years.
In 1889, the two States of Jodhpur and Bikhaner formed the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) to promote railway development jointly within the Rajasthan Agency.
In 1891, rapid progress was made in constructing the railway from Jodhpur to Bikaner, later (1901-1902) extended to Bhatinda where the JBR connected with the Metre Gauge(MG) section of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway, and the Broad Gauge(BG) North Western and the Southern Punjab Railways. [1]
By 1906 the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway was having operations over 828 miles in the territories of Sind (under British control) and in territories of the States of Jodhpur and Bikaner. In October 1906 Walter Home resigned.
In 1924, the JBR was split into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the Jodhpur and Bikhaner State Railways, formed to work the lines.
JBR Lines and extensions
- Mirpur Khas-Jhudo Railway, opened 1909 as a section of JBR; then by JSR.
- Mirpur Khas-Khadro Railway, opened 1912 as a section of JBR; then by JSR.
Lines worked by JBR at some time
- Hyderabad-Umarkot Railway; surveyed 1890. Section opened 1892 as part of Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway (British Section). Worked by JBR until 1924; then by JSR.
- Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway (British Section). Fully opened 1901. Worked by JBR until 1924; then by JSR.
- Pipar Road-Ravi Light Railway, opened 1910 as part of Pipar-Bilara Light Railway. Worked by JBR, 1910; then JSR, 1924
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [2] gives the following: -
- L/F/8/20/1684 “Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway System, Reprint of Contracts; 1922”
- L/PWD/8/228 “ File 181A Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway; 1901”