Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway: Difference between revisions
1918 Admin link changed and text changed Info moved to new page. ‘O&RR Lines Owned and Worked’ . Change infobox to 1867 |
Stations infoboxes revised and ‘Stations’ heading added |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|timeline5details= State purchases O&RR | |timeline5details= State purchases O&RR | ||
|presidency= Bengal | |presidency= Bengal | ||
|stations= [[Aligarh]], [[Bareilly]], [[Cawnpore]], [[Delhi]], [[Lucknow]], [[Moradabad]], [[ | |stations= [[Aligarh]], [[Allahabad]], [[Bareilly]], ''' [[Cawnpore]] ''', ''' [[Delhi]] ''', '''[[Lucknow]] ''', [[Moradabad]], [[Saharanpur]], | ||
''See also heading '''Stations''' for major stations marked'' '''bold''' | |||
|system1date= 1889 | |system1date= 1889 | ||
|system1details= Oudh and Rohilkand State Railway | |system1details= Oudh and Rohilkand State Railway | ||
| Line 71: | Line 72: | ||
|headquarters= [[Lucknow]] | |headquarters= [[Lucknow]] | ||
|workshop= [[Alambagh]], [[Charbagh]] <br>See also [[O&RR Railway Workshops]] | |workshop= [[Alambagh]], [[Charbagh]] <br>See also [[O&RR Railway Workshops]] | ||
|stations= | |stations= See heading '''Stations''' for major stations | ||
|system1date= 1925 | |system1date= 1925 | ||
|system1details= [[East Indian Railway]] | |system1details= [[East Indian Railway]] | ||
| Line 89: | Line 90: | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File: Oudh & Rohilkhand Railway Map | [[File:Oudh & Rohilkhand Railway 1909 Map.png|600px|right|Oudh & Rohilkhand Railway]] | ||
The '''Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway''' (O&RR) was formed around 1872 by taking over the interests of the ‘[[Indian Branch Railway]]’ / ‘Awadh Rohilkhand Railway‘ - [[Indian Branch Railway| ''see separate page for details'']]. | The '''Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway''' (O&RR) was formed around 1872 by taking over the interests of the ‘[[Indian Branch Railway]]’ / ‘Awadh Rohilkhand Railway‘ - [[Indian Branch Railway| ''see separate page for details'']]. | ||
The O&RR operated under a Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) guarantee. And was acquired by the State on 1 Jan 1889<ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n140/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 131 (pdf 140) | The O&RR operated under a Government of India([[Government of India |GoI]]) guarantee. And was acquired by the State on 1 Jan 1889<ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n140/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 131 (pdf 140) ]; Retrieved 24 Oct 2020</ref>. | ||
In 1925, the O&RR was merged into the ‘[[East Indian Railway]]’(EIR) when the latter came into state management. | In 1925, the O&RR was merged into the ‘[[East Indian Railway]]’(EIR) when the latter came into state management. | ||
| Line 111: | Line 108: | ||
O&RR were given operating rights of the opening in 1905 of the [[Allahabad-Fyzabad Railway]] which included the [[Curzon Bridge, Allahabad]] over the river Ganges. This line and bridge were constructed by [[State Railways]] and connected to the [[East Indian Railway]](EIR) to the south of the river Ganges and a junction to the O&RR mainline. Thus providing a direct link from Allahbad to Lucknow and the hill stations beyond. <ref name=ICE>[http://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/imotp.1908.17544 Institution of Civil Engineers "The Curzon Bridge at Allahabad" by Robert Richard Gales, 1908]; Retrieved 16 Jul 2016</ref>. | O&RR were given operating rights of the opening in 1905 of the [[Allahabad-Fyzabad Railway]] which included the [[Curzon Bridge, Allahabad]] over the river Ganges. This line and bridge were constructed by [[State Railways]] and connected to the [[East Indian Railway]](EIR) to the south of the river Ganges and a junction to the O&RR mainline. Thus providing a direct link from Allahbad to Lucknow and the hill stations beyond. <ref name=ICE>[http://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/imotp.1908.17544 Institution of Civil Engineers "The Curzon Bridge at Allahabad" by Robert Richard Gales, 1908]; Retrieved 16 Jul 2016</ref>. | ||
The O&RR was merged into the [[East Indian Railway]](EIR) in 1925 when the latter came into state management. | |||
==O&RR Lines owned and Worked== | |||
The “Administration Report on Railways 1918” <ref name=Admin/> gives the ‘Lines Opened’ as 1510 miles(2430km) of the O&RR [[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|‘Broad Gauge (BG)]] lines. | The “Administration Report on Railways 1918” <ref name=Admin/> gives the ‘Lines Opened’ as 1510 miles(2430km) of the O&RR [[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|‘Broad Gauge (BG)]] lines. | ||
A small number of branches and extensions were constructed after 1918 by the O&RR before merger into the EIR. These are listed under the ‘EIR System’ in the “History of Indian Railways 1937”<ref name=Hist>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 84, pdf 113]; Retrieved 17 Oct 2020</ref> | |||
[[O&RR Lines Owned and Worked | <big>'''O&RR Lines Owned and Worked '''</big> - ''see separate page'']] | |||
==Stations== | |||
See separate pages for details of the Stations and Rail System into the following major Cities:- | |||
* [[Cawnpore_Railways_and_Stations#Cawnpore_Stations| ‘Cawnpore Stations’]] | |||
* [[Delhi_Railways_%26_Stations#Delhi_Stations| ‘Delhi Stations’]] | |||
* [[Lucknow_Railways_and_Stations#Original_Lucknow_Station| ‘Lucknow Stations]] | |||
==O&RR Workshops== | ==O&RR Workshops== | ||
The O&RR established workshops at [[Alambagh]] (1865) and [[Charbagh]] (1867) to provide capacity for the major broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) line from [[Benares]] to [[Lucknow]], to the north of the River Ganges, | The O&RR established workshops at [[Alambagh]] (1865) and [[Charbagh]] (1867) to provide capacity for the major broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) line from [[Benares]] to [[Lucknow]], to the north of the River Ganges, | ||
[[O&RR Railway Workshops| <big>'''O&RR Railway Workshops'''</big> ''-see separate page for details'']] | |||
==Records== | ==Records== | ||
Latest revision as of 09:34, 8 March 2021
| Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Oudh & Rohilkhand Railway Logo | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Benares to Saharanpur Allahabad to Fyzabad (1905) | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad | 1165 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1867 | Benares to Lucknow opened by Indian Branch Railway | |
| 1874 | Lucknow to Moradabad open | |
| 1876 | Moradabad to Saharanpur open | |
| 1887 | Link with East Indian Railway at Moghal Sarai | |
| 1889 | State purchases O&RR | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Aligarh, Allahabad, Bareilly, Cawnpore , Delhi , Lucknow , Moradabad, Saharanpur,
See also heading Stations for major stations marked bold | |
| System agency | ||
| 1889 | Oudh and Rohilkand State Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1889 | State agency takes over running of O&RR | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1889 | Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway | |
| Cawnpore-Burhwal Railway | ||
| Hardwar-Dehra Railway | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Lucknow | |
| Workshops | Alambagh, Charbagh See also O&RR Railway Workshops | |
| Major Stations | See heading Stations for major stations | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1925 | East Indian Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 1187 miles (1905) | |
| Metre gauge | 80 miles (1905) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway Battalion | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
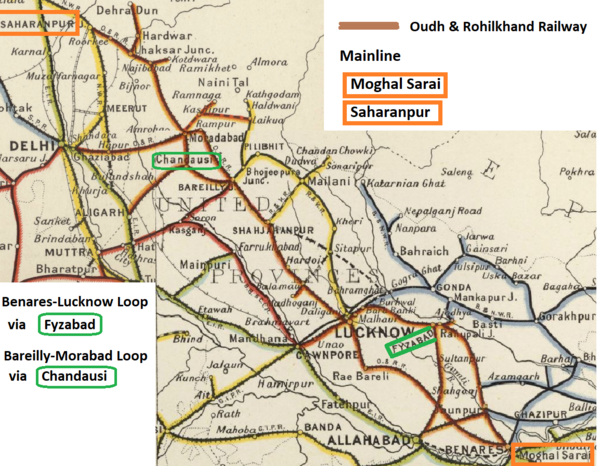
The Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway (O&RR) was formed around 1872 by taking over the interests of the ‘Indian Branch Railway’ / ‘Awadh Rohilkhand Railway‘ - see separate page for details.
The O&RR operated under a Government of India(GoI) guarantee. And was acquired by the State on 1 Jan 1889[1].
In 1925, the O&RR was merged into the ‘East Indian Railway’(EIR) when the latter came into state management.
Alternative Name: Early records give the spelling Oude and Rohilkund Railway
History
The “1870-71 Annual Report for Indian Railways for the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway “ gives:- ‘Broad Gauge (BG) ‘Lines Sanctioned’ ‘ 733 miles(1180km), with 42 miles(68km) open, nil opened in 1870/71 and 679 miles(1092km) to be finished’. The Report also details the ‘progress of the railway and the commercial summery’ - see separate pages for details.
The 42 miles(68km) line from Lucknow to Cawnpore, constructed by the ‘Indian Branch Railway’ had opened in 1867. In 1874, the line was extended to Moradabad and in 1876, to Saharanpur where the O&RR met the North Western Railway(NWR). On 31 December 1888, the GoI assumed both ownership and management of the O&RR.
O&RR were given operating rights of the opening in 1905 of the Allahabad-Fyzabad Railway which included the Curzon Bridge, Allahabad over the river Ganges. This line and bridge were constructed by State Railways and connected to the East Indian Railway(EIR) to the south of the river Ganges and a junction to the O&RR mainline. Thus providing a direct link from Allahbad to Lucknow and the hill stations beyond. [2].
The O&RR was merged into the East Indian Railway(EIR) in 1925 when the latter came into state management.
O&RR Lines owned and Worked
The “Administration Report on Railways 1918” [1] gives the ‘Lines Opened’ as 1510 miles(2430km) of the O&RR ‘Broad Gauge (BG) lines.
A small number of branches and extensions were constructed after 1918 by the O&RR before merger into the EIR. These are listed under the ‘EIR System’ in the “History of Indian Railways 1937”[3]
O&RR Lines Owned and Worked - see separate page
Stations
See separate pages for details of the Stations and Rail System into the following major Cities:-
O&RR Workshops
The O&RR established workshops at Alambagh (1865) and Charbagh (1867) to provide capacity for the major broad gauge(BG) line from Benares to Lucknow, to the north of the River Ganges,
O&RR Railway Workshops -see separate page for details
Records
An on-line search of the India Office Records (IOR) records held at the British Library relating to this railway [4] gives the following: -
- L/AG/46/16; “Records of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway Company”; 1862-1888
- V/24/3582; “India. Public Works Department: Administration and progress report of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway, 1872/73-1875/76”
Personnel
Unfortunately, there are no O&RR staff records held in the India Office Records at the British Library.
1905 Civil List The following from the Public Works Department, are recorded as deployed to the O&RR:-
- William Edward Meares, 1890, Executive Engineer[5].
- George Frederick Wilson, 1898, Manager [6].
- Bernard Baxter, 1901, Engineer-in-Chief [7]
Thacker's Directories The following for Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway Personnel 1872 have been indexed in Grace's Guide:-
Various Other Records - Chronological Order
- Henry Burdett Hederstedt, date unspecified (probably late 1860's, O&RR Chief Engineer, 'a position he held for nearly 20 years' and 1881-87, Dufferin Bridge over the Ganges at Benares, as O&RR Chief Engineer [8] in charge of construction.
- Frederick Thomas Granville Walton, 1868-88, O&RR) Engineer.'During this time he was initially in charge of the construction of the Ramganga River Bridge and Lines'; 1881-87, Dufferin Bridge over the Ganges at Benares, O&RR Engineer-in-Charge of construction; 1889-96, O&RR Engineer-in-Chief [9].
- William Arthur Brunton, 1868-70, District Engineer, O&RR [10].
- J H Jenkins Agent for O&RR 1879 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
- J Hartwell Deputy Agent O&RR 1880 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
- J G Cooke Locomotive Superindent 1880 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
- Richard Arthur Sargeaunt, 1889-92, O&RR Manager [11].
- Henry Parsall Burt, 1901-02, Manager [12], posted from State Railways.
- William Danvers Waghorn, 1914, Agent [13], posted from State Railways.
Also see
- Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway Battalion
- School fees subsidies-Railway subordinates’ children c 1935 for subsidies applying from 1921
External links
- History of The Oudh & Rohilkhand Railway oldmartiniansassociation.co.uk
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 131 (pdf 140) ; Retrieved 24 Oct 2020
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "The Curzon Bridge at Allahabad" by Robert Richard Gales, 1908; Retrieved 16 Jul 2016
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 84, pdf 113; Retrieved 17 Oct 2020
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 29 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 565 (pdf page 528) Retrieved on 29 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books "India List and India Office List, 1905" page 648 (pdf page 611) Retrieved on 29 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 435 (pdf page 398) Retrieved on 29 May 2016
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "Obituary Henry Burdett Hederstedt" Retrieved on 21 Jul 2016
- ↑ Grace's Guide "Frederick Thomas Granville Walton" Retrieved on 21 Jul 2016
- ↑ Google Books "The Archaeology of an Early Railway System: The Brecon Forest Tramroads" by Stephen Hughes, page 126; Retrieved 14 Jun 2016
- ↑ Google Books "India List and India Office List -1905" page 607; Retrieved on 19 Aug 2016
- ↑ The Indian Biographical Dictionary "Burt, Henry Parsall"; Retrieved on 12 Jul 2016
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "Biographical Dictionary - Waghorn, William Danvers"; Retrieved on 12 Jul 2016