Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway: Difference between revisions
Link added |
JBR Railway Workshops added ti infobox |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|company12details= | |company12details= | ||
|headquarters= [[Jodhpur]] | |headquarters= [[Jodhpur]] | ||
|workshop= | |workshop= [[Jodhpur]], [[Bikaner]] <br>see also [[JBR Railway Workshops]] | ||
|stations= [[Bhatinda]], [[Bikaner]], [[Hissar]], [[Hyderabad, Sind|Hyderabad]], [[Jodhpur]], [[Kuchaman]], [[Luni]], [[Marwar]] | |stations= [[Bhatinda]], [[Bikaner]], [[Hissar]], [[Hyderabad, Sind|Hyderabad]], [[Jodhpur]], [[Kuchaman]], [[Luni]], [[Marwar]] | ||
|system1date= 1924 | |system1date= 1924 | ||
Latest revision as of 09:35, 4 March 2020
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Marwar to Kuchaman Merta to Bhatinda | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 710 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1882 1884 1885 |
Marwar to Pali section opened Pali to Luni section opened Luni to Jodhpur section opened | |
| 1889 | Joint system formed | |
| 1891 | Jodhpur to Bikaner section opened | |
| 1902 | Bhatinda reached | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Bhatinda, Bikaner, Hissar, Gigasar, Jodhpur, Kuchaman, Luni, Mahajan, Marwar, Merta, Nagaur, Palana | |
| System agency | ||
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1889 | Joint system formed | |
| 1924 | System split between the two States | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1889 | Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway | |
| 1900 | Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway | |
| 1910 | Pipar-Bilara Light Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Jodhpur | |
| Workshops | Jodhpur, Bikaner see also JBR Railway Workshops | |
| Major Stations | Bhatinda, Bikaner, Hissar, Hyderabad, Jodhpur, Kuchaman, Luni, Marwar | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1924 | Bikaner State Railway Jodhpur State Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 834 miles (1905) 1331 miles (1921) | |
| 2' 6" NG | 25 miles (1921) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| n/a | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
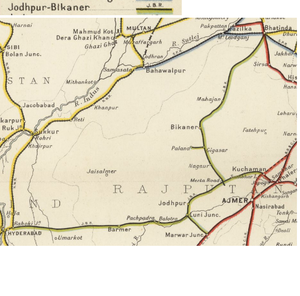
The Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) was a metre gauge (MG) system, jointly owned and operated by the Princely Jodhpur State and Bikaner State until 1924 when the system was split between the newly-formed Jodhpur State Railway and Bikaner State Railways.
History
Jodhpur Railway
The JBR had its beginnings as the Jodhpur Railway with the decision by Maharaja Jaswant Singh, to build a railway line from Bitoora to his capital city Jodhpur. Douglas Joscelyne, an executive engineer, was posted from the Public Works Department [1] to Rajputana for this work. The construction on Bitoora-Pali section was commenced on February 16, 1881 and was completed on February 28, 1882 as a metre gauge(MG) line[2].
Bitoora became known as Marwar Junction with a connection to MG Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway(BB&CIR) MG Rajputana Section between Ajmer and Palanpur that had opened in 1881.
Walter Home succeeded Joscelyne in April 1882, deployed from the Public Works Department Railways Branch, appointed as Manager for the construction of the Jodhpur Railway and also in-charge of the Marwar State Public Works Department. He built the Jodhpur Railway from scratch over the ensuing 25 years [3].
The first section of Jodhpur Railway from Marwar Junction to Pali was opened for traffic in 1882, extended Luni 1884 and reached Jodhpur in 1885 railways [2].
In 1887, a proposal was put forward for linking up Jodhpur with other important towns of the State like Nagaur and Makrana and with a possible rail link to Bikaner. Both these were given due consideration in forming the expansion proposals of Jodhpur Railway. The outcome were agreements dated July 13 and 30 1889, between the British Government, Maharaja of Jodhpur and Maharaja of Bikaner for the construction of a railway from Jodhpur to Bikaner [4]..
This agreement of 1889 was unique, in that, it was first of its kind in which two native rulers decided to co-operate and invest in an enterprise for the benefit of both and public at large. The title of Jodhpur Railway was changed to Jodhpur Bikaner Railway (JBR). Walter Home now the Manager of JBR was promoted and placed in the list of Superintending Engineers [3].
Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway
In 1889, the two States of Jodhpur and Bikaner formed the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway (JBR) to promote railway development jointly within the Rajasthan Agency.
In 1891, rapid progress was made in constructing the railway from Jodhpur to Bikaner, later (1901-1902) extended to Bhatinda where the JBR connected with the Metre Gauge(MG) section of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway, and the Broad Gauge(BG) North Western and the Southern Punjab Railways. [5]
By 1906 the Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway was having operations over 828 miles in the territories of Sind (under British control) and in territories of the States of Jodhpur and Bikaner. In October 1906 Walter Home resigned.
In 1924, the JBR was split into its two constituent parts, with two new systems, the Jodhpur and Bikaner State Railways, formed to work the lines.
The JBR Network
Jodhpur Section - 1918 grand total, 687 miles(1105km) [6].
- Main Line, MG,342 miles(550km)
- Kuchman Road-Jodhpur, opened 1891-93, 137 miles
- Jodhpur- Luni Junction, opened 1885, 20 miles
- Luni Junction-Balotra, opened 1887, 50 miles
- Balotra-Barmer, opened 1899, 60 miles. This section formed part of the ‘Shadipalli-Balotra Railway’ - see separate page .
- Barmer-Jodhpur Frontier, opened 1900, 74 miles. This section formed part of the ‘Shadipalli-Balotra Railway’ - see separate page
- Pachpadra Branch Line, MG, 10 miles(16km)
- Balotra-Pachpadra, opened 1887, 10 miles
- Marwar Junction Extension Line, MG, 44 miles(71km)
- Luni Junction-Marwar Pali, opened 1884, 25 miles
- Maewar Pali-Marwar Junction, opened 1882, 19 miles
- Phalodi Branch Line, MG, 79 miles(127km)
- Jodhpur-Osian, opened 1913, 34 miles
- Osian-Phalodi, opened 1914, 45 miles
- Merta City Branch Line, MG, 19 miles(31km)
- Merta Road-Merta City, opened 1905, 19 miles
- Bhagu Extension Line, MG, 59 miles(95km)
- Merta Road-Nagaur, opened 1891, 35 miles
- Nagaur-Bhagu, opened 1891, 24 miles
- Marwar Frontier Line, MG, 61 miles(98km)
- Degana-Marwar Frontier, opened 1909, 61 miles
- Ladna Extension Line, MG, 5 miles(8km)
- Jaswantgarg-Ladna, opened 2015, 5 miles
- Sanderao Extension Line, MG, 78 miles(125km)
- Marwar Junction-Sanderao, sanctioned for construction 1914, 78 miles
Bikaner Section - 1918 grand total, 630 miles(1013km) [7].
- Main Line, MG, 249 miles(401km)
- Bhagu(Marwar Frontier)-Bikaner, opened 1891, 48 miles
- Bikaner-Dumera, opened 1898, 42 miles
- Dulmera-Suratgarh, opened 1901,71 miles
- Suratgarh-Bhatinda, opened 1902, 88 miles
- Hisar Extension Line, MG, 136 miles(219km)
- Marwar Frontier to Ratangarh, opened 1909-10, 30 miles
- Ratangarh-Churu, opened 1910, 26 miles
- Churu-Hisar, opened 1911, 80 miles
- Bikaner-Ratangarh Chord Line, MG, 85 miles(137km)
- Bikaner-Ratangarh, opened 1912, 85 miles
- Sardarshahr Extension Line, MG, 27 miles(43km)
- Hudera(2 miles from Ratangarh)- Sardarshahr, opened 1916, 27 miles
- Hanumangarh-Sadupur Line, MG, 105 miles(169km)
- Hanumangarh-Sadupur, sanctioned for construction 1915, 105 miles
- Bikaner-Kolayat Line, MG, 27 miles(43km)
- Bikaner-Kolayat , sanctioned for construction 1915, 27 miles
Lines worked by JBR
Jodhpur-Hyderabad Railway (British Section) – MG, 1918 grand total, 124 miles(200km) [8].
- Hyderabad-Shadipali, opened 1892 as a broad gauge(BG) line; converted to MG in 1901, 56 miles. The section extended eastward from Shadalpi as far as Umarkot and was also known as the is Hyderabad-Umarkot Railway.
- Shadipali-Jodhpur Frontier, opened 1900, 68 miles
Mirpur Khas-Jhudo Railway , MG, 50 miles(80km) [9].
Owned, managed and maintained by JBR, worked as part of the JBR network
- Jamro Junction-Jhudo, opened 1909, 50 miles.
Mirpur Khas-Khadro Railway, MG, 49 miles(79km) [10].
Owned, managed and maintained by JBR, worked as part of the JBR network.
- Mirpur Khas-Khadro, opened 1912, 49 miles.
Pipar Road-Ravi Light Railway , 2ft/610mm narrow gauge(NG), 25 miles(40km) [11].
Constructed as a steam tramway and initially worked by Jodhpur Durbar, taken over by JBR
- Pipar Road-Bhavi, opened 1910, 19 miles
- Bhavi-Bilara, opened 1912, 6 miles
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [12] gives the following: -
- L/F/8/20/1684 “Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway System, Reprint of Contracts; 1922”
- L/PWD/8/228 “ File 181A Jodhpur-Bikaner Railway; 1901”
Further Information after 1924
References
- ↑ “The India List and Indian Civil List for 1905” page 535 ; Retrieved 19 Nov 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page185, pdf page 194; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 “Eminent Railwaymen of Yesteryears – Walter Home” by R R Bhandari, July 2008, reproduced by Indian Railways Fan Club; Retrieved 19 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page186, pdf page 195; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ "Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 185 to 192 (pdf193); Retrieved 19 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page185, pdf page 193; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page187, pdf page 195; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page188, pdf page 197; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page189-91, pdf page 198; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” pages 190-192, pdf page 200; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 192, pdf page 201; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 18 Nov 2016