Southern Mahratta Railway
| Southern Mahratta Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Hotgi to Guntakal Guntakal to Bezwada Gadag to Poona Bellary to Rayadrug (branch) | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 1042 miles (1905) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1884 | First sections opened to traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Madras, Bombay | |
| Stations | Bagalkot, Belgaum, Bellary, Bezwada, Bijapur, Cumbum, Gadag, Guntakal, Guntur, Harihar, Hospet, Hotgi, Londa, Miraj, Nandyal, Poona, Rayadrug, Tadepalli | |
| System agency | ||
| 1882 | Worked by Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| 1907 | Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Southern Mahratta Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1882 | Contracted to work Mysore State Railway | |
| 1907 | Merged with Madras Railway to form Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| 1882 | Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| 1899-1919 | Birur-Shimoga Railway | |
| Guntakal-Mysore Frontier Railway | ||
| 1887-1938 | Hindupur-Yesvantpur Railway | |
| Hospet-Kottur Railway | ||
| Kolhapur State Railway | ||
| 1891-1919 | Mysore-Nanjangud Railway | |
| 1887-1938 | Mysore State Railway | |
| 1902 | West of India Portuguese Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Dharwar | |
| Workshops | Dharwar/Hubli See M&SMR Railway Workshops | |
| Major Stations | Bangalore, Bellary, Gadag, Guntakal, Hotgi, Kolhapur, Marmagao, Mysore, Poona | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1907 | Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| System mileage | ||
| Metre gauge | 1687 miles (1905) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Southern Mahratta Railway Rifle Corps | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Southern Mahratta Railway(SMR) was also variously called the Southern Maratha Railway and the Southern Maharastra Railway.

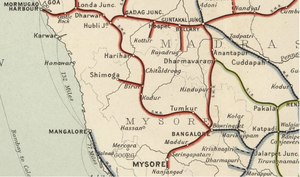
History
In 1881 the Bombay Eastern Deccan Railway was under construction with William Michell the Engineer-in-Charge. This line immediately upon opening became the Bijapur Branch of the Southern Mahratta Railway. [1]
The Southern Mahratta Railway (SMR) was founded in 1882 to construct a metre gauge(MG) railway between Hotgi and Gadag (opened to traffic in 1884), one of the "famine lines" set up with a guarantee. In the same year (1882), it was contracted by the Indian State of Mysore to work the several metre gauge lines that the Mysore State had built or was in the course of construction.
In 1888, a line was extended from Londa towards the Portuguese colony of Goa where it connected with the Marmagao line at Castle Rock. (From 1902 this line was leased as the West of India Portuguese Railway. By 1890, this line extended from Londa eastwards via Guntakal to Bezwada, and northwards to Poona, turning the SMR from an assortment of branches to a real railway network.
In 1908, the SMR , with a route mileage of 1687 miles(2715km), merged with sections of the ‘South Indian Railway’ to form the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway - M&MSR Metre Gauge Division - see separate page for details
Railways absorbed into/worked by SMR
- Birur-Shimoga Railway a MG branch line in the Indian State of Mysore, opened in 1899, 38 miles(61km). Worked by SMR and from 1908 by M&SMR until 1919. See Birur-Shimoga Railway.
- Bellary-Kistna State Railway constructed before 1890; surveyed for Hindpur extension 1892-94; worked by SMR and from 1908 by M&SMR; became M&SMR, 1908
- Guntakal-Mysore Frontier Railway opened c.1893. Worked by SMR, 1893 and from 1908 by M&SMR
- Hindupur-Yesvantpur Railway opened 1893. Also known as Hindupur (Yesvantpur)-Mysore Frontier Railway, worked by SMR became M&SMR, 1908
- Hospet-Kottur Railway opened c.1905. Originally worked by SMR and from 1908 by M&SMR
- Kolhapur State Railway opened after 1888. Worked by SMR, 1891; and from 1908 by M&SMR
- West of India Portuguese Railway opened 1886-87. Worked by SMR, 1902nd from 1908 by M&SMR
- Sangli State Railway opened in 1907 as a short 5 mile(8km) link from SMR Miraj Junction to Sangli, Worked by SMR, 1907 and from 1908 by M&SMR
Records
An on-line search of the India Office Records (IOR) records held at the British Library relating to this railway [2] gives several entries, the most relevant as follows: -
- L/F/8/12/901; “Southern Mahratta Railway Company Limited, Contract as to construction, maintenance, management and working by the Southern Mahratta RailwayCompany Limited of a railway intended to be called the Southern Mahratta Railway “1 Jun 1882”
- L/F/8/13/916 ; “Southern Mahratta Railway Company Limited, West Deccan Contract”; 28 Oct 1885
- L/F/8/16/1178; “Southern Mahratta Railway Company Limited, Contract”; 26 Jun 1907
Personnel
Unfortunately, there are no SMR Staff agreements held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
The following personnel , from the Public Works Department, are recorded as being ‘on loan’ to the Southern Mahratta Railway Company:-
References
- ↑ "Grace's Guide - William Michell”; Retrieved on 3 May 2016
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 30 May 2016
- ↑ "Obituaries of Frederick Lewis Dibblee" now archived.
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 456 (pdf page 419) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 566 (pdf page 529) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 456 (pdf page 419) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
Further Information
See Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway for period after 1908