Indian Midland Railway: Difference between revisions
→Personnel: 'George Barclay Bruce' and 'Robert White' added with link and reference |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Indian Midland Railway''' (IMR) was a state agency formed in 1885 to undertake the working of several existing broad gauge([[Rail_gauge# | The '''Indian Midland Railway Company''' (IMR) was a state agency formed in 1885 to undertake the working of several existing broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) lines, and the construction and working of further BG lines centred on [[Jhansi]]. | ||
The record of March 1885 states “An agreement was come to with the promoters of the Bhopal, Gwalior, and Cawnpore Railways (605 miles) in February last, as to the general terms on which a Company, to be called the Indian Midland Railway Company, was to be formed for undertaking the line in question, and a contract embodying in legal form the necessary provisions is now under consideration. The agreement is similar to that made with the Southern Mahratta Railway Company, with the modification suggested by the recent Select Committee on Indian Railways, and provides for the grant of interest at 3½ per cent on an estimated capital of £5,000,000, with one-fourth of the net earnings besides. For the first seven years, the Government also guarantee that the Company shall receive not less than 4 per cent interest per annum. <ref>[https://hansard.parliament.uk/Commons/1885-03-23/debates/20da8f0e-9f2f-4d11-86c6-2be044eeb631/Railways(India)%E2%80%94BhopalGwaliorAndCawnporeRailway ‘Hansard House of Commons Parliament’ - ‘Railways (India)—Bhopal, Gwalior, And Cawnpore Railway, 23 March 1885,’ Volume 296 ]; Retrieved 2 May 2020</ref>. | |||
The IMR had a comparatively brief existence before being amalgamated in 1900 with the [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]](GIPR). | |||
[[File: Indian Midland Railway.png|thumb|Indian Midland Railway]] | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
The following information is generally based on ‘The Administration Report for Railways, 1918’”<ref name =AdminGIPR>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n74/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 65 (pdf74)]; Retrieved 2 May 2020</ref>. | |||
The | *1886, the initial section of IMR, from [[Bhopal]] to [[Agra|Agra Cantonment]] was completed by May 1881. The railway connected to the ‘[[Rajputana-Malwa State Railway]]’(RMSR) near the Cantonment Station at Agra (The RMSR only existed until 1885 when it became part of the ‘[[Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway]]’(BB&CIR)) . The entire line was amalgamated into GIPR, 1900 becoming the [[Great_Indian_Peninsula_Railway_-_Lines_owned_and_worked#GIPR_Midland_Mainline |‘GIPR Midland Mainline’ ]] | ||
** ‘Bhopal-Jhansi Section’ via Bina; 1880, 180 miles(290km) | |||
** ‘Jhansi-Gwalior Section’; 1880, 60 miles(97km) | |||
** ‘Gwalior-Dholpur Section’; 1879-80-81, 40 miles(64km) - originally ‘[[Scindia State Railway]]’ - ''see Note A'' | |||
** ‘Dholpur-Agra Cantonment Section’; 1878, 36 miles(58km) - originally ‘[[Scindia State Railway]]’ - ''see Note A'' | |||
<blockquote>''Note A:-'' These two sections, described in some documents as the ‘[[Agra-Gwalior Railway]]’, completed 1881; Indian State line, owned by Gwalior Durbar. This railway was known as ‘[[Scindia State Railway]]’ and was handed over to the IMR under a Contract dated March 1890. <ref> British Library IOR/L/F/8/13 (953) ‘Contract with the Indian Midland Railway Company Limited as to the handing over of the Sindia State Railway’, 18 March 1890</ref></blockquote> | |||
* 1886-88 ‘Jhansi- Cawnpore Section’ , was under construction when the IMR was formed. ; from [[Jhansi ]] to [[Cawnpore]], 1886-88, 136 miles(219km); later known as the ‘Cawnpore Branch’- ''see Note B'' | |||
<blockquote>''Note B:-'' Early records describe part of this as the ‘[[Jhansi-Konch-Kalpi Railway]]’. In fact the line, when constructed, ran from [[Jhansi]] to [[Kalpi]] on onward to [[Cawnpore]]. Konch was only connected in 1903 by the GIPR ‘[[Ait-Kunch Branch Railway]]’. </blockquote> | |||
==Lines worked and developed by IMR== | ==Lines worked and developed by IMR== | ||
* | * ‘[[Bhopal State Railway]]’, [[Itarsi]] to [[Hoshangabad]] Section’, 11 miles(17km) opened in 1882 and reached [[Bhopal]] in Nov 1884, a total length of 45 miles(72km) <ref name=Admin79>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n79/mode/1up “Administration Report on Railways 1918” pages 70-71 (pdf78-79 ]; Retrieved 24 Mar 2018</ref>. Initially worked by the 'Indian Midland Railway Company'(IMR) under a Contract of 2 Oct 1885; amalgamated into GIPR,1900. The ‘Bhopal State Railway’ was an Indian State broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) line , funded by Begum, Nawab of the [[Princely states|Princely ]][[Bhopal State]] to connect [[Bhopal]] to the [[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]](GIPR) line at [[Itarsi]]. The line comprised two sections, one in the territory of Her Highness the Begum of Bhopal, which joined to the ‘British Section’ to form the [[Bhopal-Itarsi Railway]], together forming the ‘[[Bhopal State Railway]]’ | ||
* | * ‘[[Jhansi-Manikpore State Railway]]’ ; a further section of the IMR, opened in 1889; amalgamated into GIPR,1900 | ||
* | * ‘[[Bina-Katni Railway]]’ - a further section of the IMR, opened in 1889; amalgamated into GIPR,1900 | ||
* | * ’[[Bina-Goona-Baran Railway]]’ - opened by IMR, 1889, amalgamated into GIPR, 1900 | ||
* | * ‘[[Cawnpore-Kalpi-Jhansi Railway]]’ - line completed 1888 by IMR; amalgamated into GIPR,1900 | ||
* ‘[[Bhopal-Ujjain Railway]]’ - opened c.1895, Indian State line worked by IMR; amalgamated into GIPR, 1900 | |||
* | |||
== Records == | == Records == | ||
| Line 62: | Line 69: | ||
==Personnel == | ==Personnel == | ||
The following found from various sources – see individual pages:- | |||
*[[Archibald Crellin Cregeen]] from the [[Public Works Department]](PWD) Railway Branch, was in 1886 appointed IMR Agent and Chief Engineer. This position he held until 1888. | *[[Archibald Crellin Cregeen]] from the [[Public Works Department]](PWD) Railway Branch, was in 1886 appointed IMR Agent and Chief Engineer. This position he held until 1888. | ||
*[[Hugh Lewin Monk]],1887 March, deployed from the Railway Branch of the PWD to the Indian Midland Railway Company, on loan from State Railways until 1888 (March) | *[[Hugh Lewin Monk]],1887 March, deployed from the Railway Branch of the PWD to the Indian Midland Railway Company, on loan from State Railways until 1888 (March) | ||
| Line 68: | Line 76: | ||
==Further Information== | ==Further Information== | ||
See '''[[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]]''' | See '''[[Great Indian Peninsula Railway]]''' | ||
<br> and '''[[Great_Indian_Peninsula_Railway_-_Lines_owned_and_worked#Former_IMR_Lines_transferred_to_GIPR |GIPR Lines Owned and Worked]]''' | |||
<br>also [[Great_Indian_Peninsula_Railway_-_Lines_owned_and_worked#GIPR_Midland_Mainline|''' GIPR Midland Division''']] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:15, 4 July 2020
| Indian Midland Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Bhopal to Cawnpore Bina to Katni Jhansi to Agra Jhansi to Manikpur Ait to Kunch (branch) | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 807 miles | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1885 | Company formed | |
| 1889 | Lines from Jhansi to Gwalior, Kanpur, Manikpur, and Bhopal opened for traffic | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | Agra, Banda, Bhopal, Cawnpore, Dholpur, Jhansi, Saugor | |
| System agency | ||
| State line worked by GIPR | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
The Indian Midland Railway Company (IMR) was a state agency formed in 1885 to undertake the working of several existing broad gauge(BG) lines, and the construction and working of further BG lines centred on Jhansi.
The record of March 1885 states “An agreement was come to with the promoters of the Bhopal, Gwalior, and Cawnpore Railways (605 miles) in February last, as to the general terms on which a Company, to be called the Indian Midland Railway Company, was to be formed for undertaking the line in question, and a contract embodying in legal form the necessary provisions is now under consideration. The agreement is similar to that made with the Southern Mahratta Railway Company, with the modification suggested by the recent Select Committee on Indian Railways, and provides for the grant of interest at 3½ per cent on an estimated capital of £5,000,000, with one-fourth of the net earnings besides. For the first seven years, the Government also guarantee that the Company shall receive not less than 4 per cent interest per annum. [1].
The IMR had a comparatively brief existence before being amalgamated in 1900 with the Great Indian Peninsula Railway(GIPR).
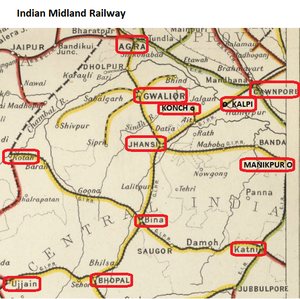
History
The following information is generally based on ‘The Administration Report for Railways, 1918’”[2].
- 1886, the initial section of IMR, from Bhopal to Agra Cantonment was completed by May 1881. The railway connected to the ‘Rajputana-Malwa State Railway’(RMSR) near the Cantonment Station at Agra (The RMSR only existed until 1885 when it became part of the ‘Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway’(BB&CIR)) . The entire line was amalgamated into GIPR, 1900 becoming the ‘GIPR Midland Mainline’
- ‘Bhopal-Jhansi Section’ via Bina; 1880, 180 miles(290km)
- ‘Jhansi-Gwalior Section’; 1880, 60 miles(97km)
- ‘Gwalior-Dholpur Section’; 1879-80-81, 40 miles(64km) - originally ‘Scindia State Railway’ - see Note A
- ‘Dholpur-Agra Cantonment Section’; 1878, 36 miles(58km) - originally ‘Scindia State Railway’ - see Note A
Note A:- These two sections, described in some documents as the ‘Agra-Gwalior Railway’, completed 1881; Indian State line, owned by Gwalior Durbar. This railway was known as ‘Scindia State Railway’ and was handed over to the IMR under a Contract dated March 1890. [3]
- 1886-88 ‘Jhansi- Cawnpore Section’ , was under construction when the IMR was formed. ; from Jhansi to Cawnpore, 1886-88, 136 miles(219km); later known as the ‘Cawnpore Branch’- see Note B
Note B:- Early records describe part of this as the ‘Jhansi-Konch-Kalpi Railway’. In fact the line, when constructed, ran from Jhansi to Kalpi on onward to Cawnpore. Konch was only connected in 1903 by the GIPR ‘Ait-Kunch Branch Railway’.
Lines worked and developed by IMR
- ‘Bhopal State Railway’, Itarsi to Hoshangabad Section’, 11 miles(17km) opened in 1882 and reached Bhopal in Nov 1884, a total length of 45 miles(72km) [4]. Initially worked by the 'Indian Midland Railway Company'(IMR) under a Contract of 2 Oct 1885; amalgamated into GIPR,1900. The ‘Bhopal State Railway’ was an Indian State broad gauge(BG) line , funded by Begum, Nawab of the Princely Bhopal State to connect Bhopal to the Great Indian Peninsula Railway(GIPR) line at Itarsi. The line comprised two sections, one in the territory of Her Highness the Begum of Bhopal, which joined to the ‘British Section’ to form the Bhopal-Itarsi Railway, together forming the ‘Bhopal State Railway’
- ‘Jhansi-Manikpore State Railway’ ; a further section of the IMR, opened in 1889; amalgamated into GIPR,1900
- ‘Bina-Katni Railway’ - a further section of the IMR, opened in 1889; amalgamated into GIPR,1900
- ’Bina-Goona-Baran Railway’ - opened by IMR, 1889, amalgamated into GIPR, 1900
- ‘Cawnpore-Kalpi-Jhansi Railway’ - line completed 1888 by IMR; amalgamated into GIPR,1900
- ‘Bhopal-Ujjain Railway’ - opened c.1895, Indian State line worked by IMR; amalgamated into GIPR, 1900
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [5] gives many references. The most important being:-
- L/F/5/126 “Indian Midland Railway Co.; Copies of agreements with the Secretary of State etc; 1885-1903”
- L/AG/46/14 “Records of the Indian Midland Railway Company; 1882-1911”
- L /AG/46/32 “Records of the India Office relating to the Indian Midland Railway Company; 1885-1911”
- L/F/8/13/915/1 “Indian Midland Railway, Preliminary agreement Secretary of State; 1885”
Unfortunately, there are no IMR Staff appointments held in the India Office Records at the British Library.
Personnel
The following found from various sources – see individual pages:-
- Archibald Crellin Cregeen from the Public Works Department(PWD) Railway Branch, was in 1886 appointed IMR Agent and Chief Engineer. This position he held until 1888.
- Hugh Lewin Monk,1887 March, deployed from the Railway Branch of the PWD to the Indian Midland Railway Company, on loan from State Railways until 1888 (March)
- George Barclay Bruce from 1894 was the Consulting Engineer to the IMR and the GIPR, based in London, in partnership with Robert White [6].
Further Information
See Great Indian Peninsula Railway
and GIPR Lines Owned and Worked
also GIPR Midland Division
References
- ↑ ‘Hansard House of Commons Parliament’ - ‘Railways (India)—Bhopal, Gwalior, And Cawnpore Railway, 23 March 1885,’ Volume 296 ; Retrieved 2 May 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 65 (pdf74); Retrieved 2 May 2020
- ↑ British Library IOR/L/F/8/13 (953) ‘Contract with the Indian Midland Railway Company Limited as to the handing over of the Sindia State Railway’, 18 March 1890
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” pages 70-71 (pdf78-79 ; Retrieved 24 Mar 2018
- ↑ British Library “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 23 Jan 2016
- ↑ Grace's Guide "George Barclay Bruce"; Retrieved on 24 Jun 2016