Punjab Northern State Railway: Difference between revisions
Complete Revision with map, new text & IOR references ref Steve Moore |
→Personnel Records: Sedgwick added 1879 |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
* [[Francis Joseph Edward Spring]] was deployed from the Indian Imperial Civil Service's engineering section in 1873 as Consulting Engineer for the survey of the PNSR and the construction of various parts of that Railway and Bridges. He remained attached to the PNSR until 1878. | * [[Francis Joseph Edward Spring]] was deployed from the Indian Imperial Civil Service's engineering section in 1873 as Consulting Engineer for the survey of the PNSR and the construction of various parts of that Railway and Bridges. He remained attached to the PNSR until 1878. | ||
* [[W Sedgwick|Capt. W. Sedgwick]], Officiating Manager PNSR 1879 [[Indian_Railway_Conference_Association#Railway_Conference| ‘Railway Conference’ delegate]] | |||
The following from the Railway Branch of the [[Public Works Department]] were deployed to the PNSR | '''Railway Branch''' The following from the Railway Branch of the [[Public Works Department]] were deployed to the PNSR | ||
* [[Henry Francis Storey]], 1868-78, Employed on the construction of the [[Alexandra Bridge]] over the Chenab river (<ref>[http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/Henry_Francis_Storey "Grace's Guide - Henry Francis Storey”]; Retrieved on 30 May 2016</ref> | * [[Henry Francis Storey]], 1868-78, Employed on the construction of the [[Alexandra Bridge]] over the Chenab river (<ref>[http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/Henry_Francis_Storey "Grace's Guide - Henry Francis Storey”]; Retrieved on 30 May 2016</ref> | ||
*[[Henry Thomas Geoghegan]], 1868, Executive Engineer <ref>[https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=b2NPAAAAMAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&hl=en_GB&pg=GBS.PA501 Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 501 (pdf page 464)] Retrieved on 18 May 2016</ref>. | *[[Henry Thomas Geoghegan]], 1868, Executive Engineer <ref>[https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=b2NPAAAAMAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&hl=en_GB&pg=GBS.PA501 Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 501 (pdf page 464)] Retrieved on 18 May 2016</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 10:16, 26 April 2020
Punjab Northern State Railway(PNSR)
The route of what became the PNSR, was first surveyed in 1857 and years of political and military debate followed as described under Lahore & Peshawar Railway .
Finally, following further exchanges, the line was constructed by the of Government of India (GoI). The Punjab Northern State Railway(PNSR) was created in 1870-71 to construct and operate the railway from Lahore to Peshawar. The first section of the line was opened in 1873 and Lahore and Peshawar were connected in 1883 [1] with the completion of the Attock Bridge over the river Indus. It was the first railway in India to have been taken under GOI control in 1886.
Early History
The railway was first designed as a broad gauge(BG) line, but the Government Railway Gauge policy changed and the metre gauge(MG) was adopted for the PNSR see separate page ‘Railway Gauge’ .
The ‘1871-72 Report on Railways’ [2] states:-
“Having been originally designed for the 5' 6"gauge (BG), fresh plans and drawings had to be prepared when it was determined to adopt the new metre gauge of 3' 3 3/8" (MG) This led to the suspension of operations for a time, but during the past year there has been much activity in pushing on the works, and considerable progress has been made. It is estimated approximately that the line will be constructed for 10,000/. a mile. The expenditure had amounted on the 31st December last to 660,868/. The bridges over the Ravee(Ravi), Chenab, and Jhelum rivers are amongst the most formidable works yet undertaken in India, and will not be finished so soon as the rest of the line, but the sections between the rivers may possibly be opened this year.”
Line Opening
- Lahore via Lala Musa to Jhelum Section. This first section of 103 miles(165km) of the PNSR opened in stages from Sept 1873 [3] to Sept 1876 [4] as a metre gauge (MG) line in accordance with Government Railway Gauge policy at the time (See separate page ‘Railway Gauge’ ). This policy was reversed in Jan 1874 and the conversion of this section to broad gauge(BG) was completed in 1878 [3]. During the conversion this remained an ‘open line’ whilst the earthworks and bridgework were undertaken to permit the wider gauge [5]
- Jhelum to Rawalpindi Section. This section of the PNSR opened as a BG line in 1880 with a length of 70½ miles(113km), using temporary diversions allowing 1 in 50 gradients. Later from 1888 to 1897 a series of realignments improved the gradient to 1 in 100, giving a line length of 76¾ miles(121km)
- Rawalpindi to Peshawar Section . The surveys for this extension commenced in 1876-77 with three plans and estimates submitted as far as Attock. The final section to Peshawar was submitted in 1877-78. The first section from Rawalpindi opened in 1881 and extended in stages to reach Peshawar in 1883 [6].
Bridge Constructions
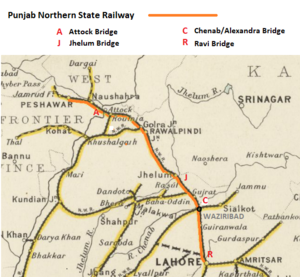
Several major bridges required construction to complete the PNSR line between from Lahore and Peshawar (See separate pages for details ):-
- Ravi Bridge(marked R on map), over the River Ravi situated between Sadiq Pura, Lahore and Shahdara Bagh. The construction work on this bridge was started in 1871 to MG designs , opened 12 Apr 1875 and remained open during the BG conversion, which required bridge strengthening. The BG line opened 6 Oct 1878 between [[Lahore]) and Jhelum.
- Chenab/Alexandra Bridge(marked C on map), over the River Chenab between Wazirabad and Gujrat . Construction started in 1871 as MG and opened 22 Jan 1876 by Edward VII the King-Emperor when he was Prince of Wales. Converted to BG , which required alterations to the longitudinal bearers and opened 6 Oct 1878 between [[Lahore]) and Jhelum.
- Jhelum Bridge(marked J on map), over the River Jhelum , started in 1871 and opened 14 Sep 1876 taking the MG line to Jhelum. Converted to BG , which required alterations and opened 6 Oct 1878 between [[Lahore]) and Jhelum.
- Attock Bridge(marked A on map), over the River Indus between Attock and Khairabad. The construction started in 1880 and completed in 1883
Minor Bridges mentioned in the 1876-77 Report [5]:- Chikori Bridge, which had to be rebuilt; Chumb Bridge, 5 openings of 37' 6' girder; Dekh Bridge, 3 openings of 37' 6' girder; Ghilanwala Bridge, 4 openings. The 1877-78 Report refers to the Bagh Butcha Bridge and the Chikori Nullah Bridge with the problems of conversion to the BG specification. The 1878-79 Report details the Jhelum to Rawlpindi Section with bridges over the large rivers Dina, Bukrala, Sohawa, Bishendorh, Bykhan and Sohan.
Branch Line
- Lala Musa -Mayo Salt Mines Railway - see separate page. Branch line, metre gauge. In August 1878 orders were received to proceed with the works of this line on a project prepared in the year 1872. [7]
Later History
With others, the Punjab Northern State Railway was merged with the Sind, Punjab and Delhi Railway in 1886 to form the ‘North-Western State Railway’ (later becoming the North Western Railway ).
Records
The British Library ‘India Office Records’ IOR/R/V/24/3590; "Public Works Department: Railways" which includes "Annual Progress Reports on the construction of the Punjab Northern State Railway, 1876-1879” has been downloaded by FIBIS and provides full detailed information.
Personnel Records
There are no PNSR Staff agreements held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
- Francis Joseph Edward Spring was deployed from the Indian Imperial Civil Service's engineering section in 1873 as Consulting Engineer for the survey of the PNSR and the construction of various parts of that Railway and Bridges. He remained attached to the PNSR until 1878.
- Capt. W. Sedgwick, Officiating Manager PNSR 1879 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
Railway Branch The following from the Railway Branch of the Public Works Department were deployed to the PNSR
- Henry Francis Storey, 1868-78, Employed on the construction of the Alexandra Bridge over the Chenab river ([8]
- Henry Thomas Geoghegan, 1868, Executive Engineer [9].
- Robert Trefusis Mallet, 1868, Executive Engineer [10].
- Hugh Lewin Monk, 1870-73, Assistant Engineer [11]
- Horace Bell, 1874, Executive Engineer during Construction [12]
- Joseph Bonus, 1877-81, Superintending Engineer and Engineer-in-Chief for the construction from Rawalpindi(Pindi) to Peshawar section [13].
- James Condor, 1875, Executive Engineer [14].
- Thomas Gracey Col. R.E., 1879, Engineer-in-Chief Pindi-Kohat Section. [15].
- Frederick Lewis Dibblee, 1879-80, PNSR Engineer-in-Chief, Jhelum division; later Superintending Engineer, Rawal-Pindi(Rawalpindi) section . [16]
- Ernest Lindsay Marryat,1880-86 PNSR Manager [17].
- Richard Arthur Sargeaunt, 1884-87, PNSR Offg Manager [18].
The Annual Reports [5] mention the following:-
- J Bonus, Lieut-Col, Engineer-in-Chief, Punjab Northern State Railway (1877-78)
- Mr Johnson, Engineer Ravi division of the Lahore-Jhelum section (1877-78).
References
- ↑ Google Books "Engines of Change: The Railroads that made India" by Ian J. Kerr, page 84 Retrieved on 12 Jul 2016
- ↑ Google Books ‘Report on Railways 1871-72’ “Punjab Northern State Railway”page 36 pdf 596; Retrieved 24 June 2018
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 106, pdf page 115; Retrieved 18 Dec 2017
- ↑ British Library ‘India Office Records’ IOR/V/24/3590 ; "Public Works Department: Railways, 1876-79" which contains “Punjab State Railway Administration report of the Construction of the Railway from its commencement to the end of the Financial year 1878-79 (31st March 1879).” Page 6, para 27
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 IOR/V/24/3590 ‘1876-77 and 1877-78 Annual Progress Reports
- ↑ “Administration Report on Railways 1918” page 106(pdf115); Retrieved 18 Nov 2018
- ↑ 1878-79 Report Para 43
- ↑ "Grace's Guide - Henry Francis Storey”; Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 501 (pdf page 464) Retrieved on 18 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 560 (pdf page 523 Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ British Library - "Photographs Album details for shelfmark Photo 1085/9"; Retrieved 30 May 2016
- ↑ "Grace's Guide - Horace Bell”; Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books "India List and India Office List -1905" page 444; Retrieved on 19 Aug 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 465 (pdf page 428) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 506 (pdf page 469) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Biography "Life of Frederick Lewis Dibblee"; Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ Google Books "India List and India Office List -1905" page 562; Retrieved on 19 Aug 2016
- ↑ Google Books "India List and India Office List -1905" page 607; Retrieved on 19 Aug 2016