Difference between revisions of "Madras Railway"
(<sup> and ==Notes== changed to ==Ref==;) |
(‘Major Stations Infobox ‘ revised) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|company12details= | |company12details= | ||
|headquarters= [[Madras]] | |headquarters= [[Madras]] | ||
| − | |workshop= [[Perambur|Perambore]] | + | |workshop= [[Madras]], [[Perambur|Perambore]], Podanur <br>''See'' [[M&SMR Railway Workshops]] |
| − | |stations= [[Bezwada]], [[Bangalore]], [[Calicut]], [[Cochin]], [[Coimbatore]], [[Erode]], [[Guntakal]], [[Mangalore]], [[Nellore]], [[Ootacamund]], [[Rajahmundry]], [[Renigunta]] | + | |stations= '''[[Madras]] ''', [[Bezwada]], [[Bangalore]], [[Calicut]], [[Cochin]], [[Coimbatore]], [[Erode]], [[Guntakal]], [[Mangalore]], [[Nellore]], [[Ootacamund]], [[Rajahmundry]], [[Renigunta]] |
| + | ''See also separate page'' [[Madras_Railways_%26_Stations#Madras_Stations| ''' Madras Stations''']] ''for details'' | ||
|system1date= 1951 | |system1date= 1951 | ||
|system1details= [[Southern Railway]] {IR zone) | |system1details= [[Southern Railway]] {IR zone) | ||
| Line 88: | Line 89: | ||
}} | }} | ||
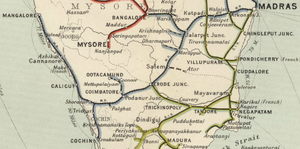
| + | [[File: Madras Railway Map 1909, north section.png|thumb| Madras Railway Map 1909, north section]] | ||
| + | [[File: Madras Railway Map 1909, south section.png|thumb| Madras Railway Map 1909, south section]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==First Company Formation== | ||
| + | The '''Madras Railway Company'''(MR) was incorporated on 8 May 1845 | ||
| + | <ref>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_rail_transport_in_India#1832%E2%80%931852:_Industrial_railways Wikipedia ‘History of Rail Transport in India’]; Retrieved 4 May 2020</ref> and the prospectus stated “the securing the introduction of the railway system into the territories under the presidency of Madras .... to depute to India a skilful engineer ...with two engineer officers ... to suggest some feasible line of moderate length as an experiment for railway communication in India” | ||
| + | <ref>[https://books.google.fr/books?id=6WhDAAAAcAAJ&pg=PA639&lpg=PA639&dq#v=onepage&q&f=false Google Books ‘Allen's Indian Mail,’ 1845, page 639]; Retrieved 4 May 2020</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The proposal was for an initial 70 mile line between [[Madras]] and the military base at [[Arcot]]. [[Robert Stephenson]] agreed to act as Consulting Engineer based in London. The subsequent recession removed the financial incentive for railways in India and the Madras scheme was dissolved the following year | ||
| + | <ref>[https://books.google.fr/books?id=BzErDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA155&lpg=PA155#v=onepage&q&f=false Google Books “Robert Stephenson – The Eminent Engineer” edited by Michael R. Bailey; page 155-57]; Retrieved 4 May 2020</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Second Company Formation== | ||
The '''Madras Railway Company'''(MR) was formed provisionally in July 1852 to acquire lands in the “East Indies” and to construct and work a railway or railways in that territory. In December of that year the railway company contracted with the [[East India Company]] to construct and maintain an “experimental line of railway” from [[Madras]] to (or towards) the west coast of India. | The '''Madras Railway Company'''(MR) was formed provisionally in July 1852 to acquire lands in the “East Indies” and to construct and work a railway or railways in that territory. In December of that year the railway company contracted with the [[East India Company]] to construct and maintain an “experimental line of railway” from [[Madras]] to (or towards) the west coast of India. | ||
| − | <ref> [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/228649/8330.pdf H.M. Government “Statute Law Repeals: Nineteenth Report : Draft Statute Law (Repeals) Bill; April 2012"; pages 130-132, paragraphs 3.65-3.73] Retrieved on | + | <ref> [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/228649/8330.pdf H.M. Government “Statute Law Repeals: Nineteenth Report : Draft Statute Law (Repeals) Bill; April 2012"; pages 130-132, paragraphs 3.65-3.73] Retrieved on 5 May 2020</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | The Chief Engineer from 1853-6 was [[George Barclay Bruce]]. "He had then laid out and partly constructed about 500 miles of the Madras railway, he developed a system of carrying out works without contractors using direct labour. Also he developed the brick wells sunk by native divers system to construct the [[Poiney Viaduct]], a major hurdle on the route <ref >[http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/George_Barclay_Bruce Grace's Guide "George Barclay Bruce"]; Retrieved on 24 Jun 2016</ref>. . | ||
| − | + | The first section of line, from [[Madras]] to [[Arcot]], was not opened to traffic until 1 July 1856. | |
In 1859, its object was given as "the construction and working of a railway from Madras to the western coast at [[Beypore]], with branches to [[Bangalore]] and the [[Neilgherries]]; also of a line from Madras, ''via'' [[Bellary]], to join the line from [[Bombay]] - total, about 820 miles." <ref>"Money Market and City Intelligence", ''The Times'', Wednesday, 15 June 1859, #23333, 7a.1</ref> | In 1859, its object was given as "the construction and working of a railway from Madras to the western coast at [[Beypore]], with branches to [[Bangalore]] and the [[Neilgherries]]; also of a line from Madras, ''via'' [[Bellary]], to join the line from [[Bombay]] - total, about 820 miles." <ref>"Money Market and City Intelligence", ''The Times'', Wednesday, 15 June 1859, #23333, 7a.1</ref> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 112: | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
Headquartered in Madras, whence its lines radiated, the Madras Railway was built to Broad Gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]). | Headquartered in Madras, whence its lines radiated, the Madras Railway was built to Broad Gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[1870-71_Report_on_Railways#Progress_on_State_lines._Paragraphs_5-10.3B_Pages_3-4| “1870-71 Annual Report for Indian Railways for the Madras Railway“]] gives:- [[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge| | ||
| + | ‘Broad Gauge (BG)]] Line sanctioned 862 miles(1387km), Line opened 1870/71 125 miles(201km), | ||
| + | giving total Line length 832 miles(1339km) and 30 miles(48km) to be finished’. The Report also details the | ||
| + | [[1870-71_Report_on_Railways#Madras_Railway._Paragraphs_65.2C66.3B_Page_35|‘progress of the railway and the commercial summery’]] - ''see separate pages for Report details.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1887, July-September, the engineer [[Charles Albert Bull]] is recorded as being deployed from the Railway Branch of the [[Public Works Department]] to undertake a survey, this would be to continue the expansion of the MR network. | ||
In 1901 the southern part of [[East Coast State Railway]](ECSR), renamed [[Madras (North-East) Railway]] was transferred to MR. | In 1901 the southern part of [[East Coast State Railway]](ECSR), renamed [[Madras (North-East) Railway]] was transferred to MR. | ||
| Line 102: | Line 124: | ||
It was the last [[Guaranteed Railways|guaranteed railway]] to fall to Government of India ([[Government of India |GoI]]) ownership (31 December 1907). | It was the last [[Guaranteed Railways|guaranteed railway]] to fall to Government of India ([[Government of India |GoI]]) ownership (31 December 1907). | ||
| − | + | On 1 Jan 1908, the northern portion (ie the north east, north west and [[Bangalore]] branches) was merged with the [[Southern Mahratta Railway]](SMR) to form the [[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway]](M&SMR). The southern section of [[Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline]] section, became part of the [[South Indian Railway]](SIR). | |
The [[Government of India |GoI]] took over the management of the M&SMR on 1 April 1944. | The [[Government of India |GoI]] took over the management of the M&SMR on 1 April 1944. | ||
| Line 108: | Line 130: | ||
On 14 April 1951, M&SMR together with SIR and MSR became [[Southern Railway]], a zone of [[Indian Railways]]. | On 14 April 1951, M&SMR together with SIR and MSR became [[Southern Railway]], a zone of [[Indian Railways]]. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Madras Railway - Construction and Bridges== |
| − | + | [[Madras Railway Bridges and Constructions|'''Madras Railway Bridges and Constructions''' - ''see separate page for details '']] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | *[[ | + | ==Madras Railway Lines== |
| − | + | The Madras Railway (MR) constructed and worked an extensive network of broad gauge([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) lines. | |
| − | *[[ | + | |
| + | In addition, in 1901, the southern part of [[East Coast State Railway]](ECSR), renamed [[Madras (North-East) Railway]] was transferred to MR and became part of the MR network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The MR contract expired on 31 Dec 1907, at this point the BG route mileage was 1449 miles(2331km) | ||
| + | *From 1 Jan 1908 the [[Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline]] section, being 417 miles(671km), was transferred from MR to the [[South Indian Railway]](SIR). | ||
| + | *The remaining BG lines, 1032 miles(1660km) were taken over by the [[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway]](M&SMR) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The MR also worked several lines on behalf of other parties. The metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) [[Nilgiri Mountain Railway]] and the [[Shoranur-Cochin Railway]]; together with the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) [[Morappur-Dharmapuri-Hosur Railway|Morappur-Dharmapuri]] and [[Tirupattur-Krishnagiri Railway|Tirupattur-Krishnagiri]] famine protection railways owned by the [[Government of India]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Madras Railway – Lines owned and worked]]''' gives details of the Mainline routes together with Branches, the line lengths and dates of opening | ||
| + | *'BG Lines - owned and worked by Madras Railway(MR)' | ||
| + | **Madras-Jalapet SW Mainline (and Royauram Branch Line; Ranipet Branch Line, Bangalore Branch Line) | ||
| + | **Arkonam-Raichur NW Mainline | ||
| + | **Madras-Waltair NE Mainline (and Samalkot Junction-Cocanada Branch Line; Waltair-Vizagapatam Branch Line) | ||
| + | **[[Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline]] (and Mettupalaiyam Branch Line; Palghat Branch Line) | ||
| + | *'Railways worked by Madras Railway(MR)' - giving details of lines worked by MR on behalf of other parties and the reallocation of these arrangements to SIR and M&SMR from 1908 onwards | ||
| − | == | + | ==Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Workshops== |
| − | + | The [[Madras Railway - Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Workshops]] was moved from Madras, established in [[Perambur]] in 1863 and progressively extended. In 1901 a major expansion commenced by the Deputy Locomotive Superintendent Mr [[A Pilkington]] under the orders of Mr [[C E Phillips]], Locomotive Superintendent at that time. These workshops became the M&SMR workshops in 1908. | |
== Records == | == Records == | ||
| − | + | Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the [http://www.fibis.org/store/fibis-books-and-publications/bff-0004-research-sources-for-indian-railways-1845-1947/ Fibis shop]. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the [[India Office Records]] (IOR) held at the [[British Library]] | |
| + | |||
| + | An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway <ref>[http://searcharchives.bl.uk/primo_library/libweb/action/search.do?vid=IAMS_VU2 “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search]; Retrieved 26 Jan 2016</ref> | ||
| + | gives many references. The most important being:- | ||
| + | *'''L/AG/46/15''' “Records of the Madras Railway Company; 1852-1937” | ||
| + | *'''L/AG/46/33''' “Records of the India Office relating to the Madras and Southern MahrattaRailway Company; 1882-1930” | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Personnel== | ||
| + | Unfortunately there are no Staff agreements held at the [[British Library]] in the [[India Office Records]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following have been identified from various sources:- | ||
| + | *[[Henry Burdett Hederstedt]], date unspecified but probably in the early 1860's for a short time, Madras Railway, 'joined the staff' <ref name=biog>[http://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/imotp.1915.16286 Institution of Civil Engineers "Obituary Henry Burdett Hederstedt"] Retrieved on 21 Jul 2016</ref>, he later moved on to [[Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway]], Chief Engineer,. | ||
| + | *[[Frederick Charles Bullmore]],1865 appointed to 'Madras Railway'. He was successively engaged in superintending the construction of three districts of the North-West line, aggregating a length of 40 miles, and was in 1867 promoted from the fourth to the third class. 1877 he re-entered service and was employed until his decease in 1887 in the maintenance of various divisions <ref>[https://www.gracesguide.co.uk/Frederick_Charles_Bullmore Grace's Guide 'Frederick Charles Bullmore']; Retrieved 3 Apr 2020</ref>. | ||
| + | *[[Henry Thomas Geoghegan]], from the [[Public Works Department]] was in 1885 posted as Superintending Engineer for the Madras State Railway Survey <ref>[https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=b2NPAAAAMAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&hl=en_GB&pg=GBS.PA501 Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 501 (pdf page 464)] Retrieved on 30 May 2016</ref>. | ||
| + | *[[Henry James Oddie]], from the PWD was in 1890 posted as Executive Engineer <ref> India Civil List 1890, page 41</ref>. | ||
| + | *[[A M Saunders]], Agent and Manager Madras Railway 1879 and 1880 [[Indian_Railway_Conference_Association#Railway_Conference| ‘Railway Conference’ delegate]] | ||
| + | *[[F H Trevithick]], Locomotive Superintendent Madras railway 1880 [[Indian_Railway_Conference_Association#Railway_Conference| ‘Railway Conference’ delegate]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further Information== | ||
| + | See '''[[Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway]]'''(M&SMR) for information from 1908 onwards. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | *[https://madrascourier.com/insight/how-the-madras-rail-evolved-into-the-third-largest-rail-system/ "How the Madras Rail Evolved into the Third Largest Rail System"] 13 April 2018 ''Madras Courier'' | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 15:44, 14 March 2021
| Madras Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 Madras Central Railway Station | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Madras to Bangalore Madras to Raichur Madras to Waltair (Vizagapatam) Jalarpet to Mangalore | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 904 miles (1905) | |
| Broad gauge | 497 miles (1905) - North East line | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1845 | Company formed | |
| 1856 | First section of line open to traffic | |
| 1889 | Branch line Calicut-Azikhal Railway opened | |
| 1907 | Line acquired by State | |
| 1908 | Jalarpet to Mangalore transferred to South Indian Railway | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Madras | |
| Stations | Bezwada, Calicut, Coimbatore, Erode, Guntakal, Nellore, Rajahmundry, Renigunta | |
| System agency | ||
| Own agnecy | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
| Madras Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
| [[Image:|150px| ]] | ||
| System timeline | ||
| 1907 | Merged with Southern Mahratta Railway to form Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway | |
| Constituent companies / lines | ||
| Madras Railway | ||
| Kolar Gold Fields Railway | ||
| 1903 | Nilgiri Mountain Railway | |
| Shoranur-Cochin Railway | ||
| Key locations | ||
| Headquarters | Madras | |
| Workshops | Madras, Perambore, Podanur See M&SMR Railway Workshops | |
| Major Stations | Madras , Bezwada, Bangalore, Calicut, Cochin, Coimbatore, Erode, Guntakal, Mangalore, Nellore, Ootacamund, Rajahmundry, Renigunta
See also separate page Madras Stations for details | |
| Successor system / organisation | ||
| 1951 | Southern Railway {IR zone) | |
| System mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 1411 miles (1905) | |
| Metre gauge | 82 miles (1905) | |
| Associated auxiliary force | ||
| Madras Railway Volunteers | ||
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
Contents
First Company Formation
The Madras Railway Company(MR) was incorporated on 8 May 1845 [1] and the prospectus stated “the securing the introduction of the railway system into the territories under the presidency of Madras .... to depute to India a skilful engineer ...with two engineer officers ... to suggest some feasible line of moderate length as an experiment for railway communication in India” [2].
The proposal was for an initial 70 mile line between Madras and the military base at Arcot. Robert Stephenson agreed to act as Consulting Engineer based in London. The subsequent recession removed the financial incentive for railways in India and the Madras scheme was dissolved the following year [3].
Second Company Formation
The Madras Railway Company(MR) was formed provisionally in July 1852 to acquire lands in the “East Indies” and to construct and work a railway or railways in that territory. In December of that year the railway company contracted with the East India Company to construct and maintain an “experimental line of railway” from Madras to (or towards) the west coast of India. [4]
The Chief Engineer from 1853-6 was George Barclay Bruce. "He had then laid out and partly constructed about 500 miles of the Madras railway, he developed a system of carrying out works without contractors using direct labour. Also he developed the brick wells sunk by native divers system to construct the Poiney Viaduct, a major hurdle on the route [5]. .
The first section of line, from Madras to Arcot, was not opened to traffic until 1 July 1856.
In 1859, its object was given as "the construction and working of a railway from Madras to the western coast at Beypore, with branches to Bangalore and the Neilgherries; also of a line from Madras, via Bellary, to join the line from Bombay - total, about 820 miles." [6]
History
Headquartered in Madras, whence its lines radiated, the Madras Railway was built to Broad Gauge(BG).
The “1870-71 Annual Report for Indian Railways for the Madras Railway“ gives:- ‘Broad Gauge (BG) Line sanctioned 862 miles(1387km), Line opened 1870/71 125 miles(201km), giving total Line length 832 miles(1339km) and 30 miles(48km) to be finished’. The Report also details the ‘progress of the railway and the commercial summery’ - see separate pages for Report details.
In 1887, July-September, the engineer Charles Albert Bull is recorded as being deployed from the Railway Branch of the Public Works Department to undertake a survey, this would be to continue the expansion of the MR network.
In 1901 the southern part of East Coast State Railway(ECSR), renamed Madras (North-East) Railway was transferred to MR.
It was the last guaranteed railway to fall to Government of India (GoI) ownership (31 December 1907).
On 1 Jan 1908, the northern portion (ie the north east, north west and Bangalore branches) was merged with the Southern Mahratta Railway(SMR) to form the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(M&SMR). The southern section of Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline section, became part of the South Indian Railway(SIR).
The GoI took over the management of the M&SMR on 1 April 1944.
On 14 April 1951, M&SMR together with SIR and MSR became Southern Railway, a zone of Indian Railways.
Madras Railway - Construction and Bridges
Madras Railway Bridges and Constructions - see separate page for details
Madras Railway Lines
The Madras Railway (MR) constructed and worked an extensive network of broad gauge(BG) lines.
In addition, in 1901, the southern part of East Coast State Railway(ECSR), renamed Madras (North-East) Railway was transferred to MR and became part of the MR network.
The MR contract expired on 31 Dec 1907, at this point the BG route mileage was 1449 miles(2331km)
- From 1 Jan 1908 the Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline section, being 417 miles(671km), was transferred from MR to the South Indian Railway(SIR).
- The remaining BG lines, 1032 miles(1660km) were taken over by the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(M&SMR)
The MR also worked several lines on behalf of other parties. The metre gauge(MG) Nilgiri Mountain Railway and the Shoranur-Cochin Railway; together with the 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG) Morappur-Dharmapuri and Tirupattur-Krishnagiri famine protection railways owned by the Government of India.
Madras Railway – Lines owned and worked gives details of the Mainline routes together with Branches, the line lengths and dates of opening
- 'BG Lines - owned and worked by Madras Railway(MR)'
- Madras-Jalapet SW Mainline (and Royauram Branch Line; Ranipet Branch Line, Bangalore Branch Line)
- Arkonam-Raichur NW Mainline
- Madras-Waltair NE Mainline (and Samalkot Junction-Cocanada Branch Line; Waltair-Vizagapatam Branch Line)
- Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline (and Mettupalaiyam Branch Line; Palghat Branch Line)
- 'Railways worked by Madras Railway(MR)' - giving details of lines worked by MR on behalf of other parties and the reallocation of these arrangements to SIR and M&SMR from 1908 onwards
Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Workshops
The Madras Railway - Locomotive, Carriage and Wagon Workshops was moved from Madras, established in Perambur in 1863 and progressively extended. In 1901 a major expansion commenced by the Deputy Locomotive Superintendent Mr A Pilkington under the orders of Mr C E Phillips, Locomotive Superintendent at that time. These workshops became the M&SMR workshops in 1908.
Records
Refer to FIBIS Fact File #4: “Research sources for Indian Railways, 1845-1947” - available from the Fibis shop. This Fact File contains invaluable advice on 'Researching ancestors in the UK records of Indian Railways' with particular reference to the India Office Records (IOR) held at the British Library
An on-line search of the IOR records relating to this railway [7] gives many references. The most important being:-
- L/AG/46/15 “Records of the Madras Railway Company; 1852-1937”
- L/AG/46/33 “Records of the India Office relating to the Madras and Southern MahrattaRailway Company; 1882-1930”
Personnel
Unfortunately there are no Staff agreements held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
The following have been identified from various sources:-
- Henry Burdett Hederstedt, date unspecified but probably in the early 1860's for a short time, Madras Railway, 'joined the staff' [8], he later moved on to Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway, Chief Engineer,.
- Frederick Charles Bullmore,1865 appointed to 'Madras Railway'. He was successively engaged in superintending the construction of three districts of the North-West line, aggregating a length of 40 miles, and was in 1867 promoted from the fourth to the third class. 1877 he re-entered service and was employed until his decease in 1887 in the maintenance of various divisions [9].
- Henry Thomas Geoghegan, from the Public Works Department was in 1885 posted as Superintending Engineer for the Madras State Railway Survey [10].
- Henry James Oddie, from the PWD was in 1890 posted as Executive Engineer [11].
- A M Saunders, Agent and Manager Madras Railway 1879 and 1880 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
- F H Trevithick, Locomotive Superintendent Madras railway 1880 ‘Railway Conference’ delegate
Further Information
See Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway(M&SMR) for information from 1908 onwards.
External links
- "How the Madras Rail Evolved into the Third Largest Rail System" 13 April 2018 Madras Courier
References
- ↑ Wikipedia ‘History of Rail Transport in India’; Retrieved 4 May 2020
- ↑ Google Books ‘Allen's Indian Mail,’ 1845, page 639; Retrieved 4 May 2020
- ↑ Google Books “Robert Stephenson – The Eminent Engineer” edited by Michael R. Bailey; page 155-57; Retrieved 4 May 2020
- ↑ H.M. Government “Statute Law Repeals: Nineteenth Report : Draft Statute Law (Repeals) Bill; April 2012"; pages 130-132, paragraphs 3.65-3.73 Retrieved on 5 May 2020
- ↑ Grace's Guide "George Barclay Bruce"; Retrieved on 24 Jun 2016
- ↑ "Money Market and City Intelligence", The Times, Wednesday, 15 June 1859, #23333, 7a.1
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 26 Jan 2016
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "Obituary Henry Burdett Hederstedt" Retrieved on 21 Jul 2016
- ↑ Grace's Guide 'Frederick Charles Bullmore'; Retrieved 3 Apr 2020
- ↑ Google Books " India List and India Office List, 1905" page 501 (pdf page 464) Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ India Civil List 1890, page 41