Difference between revisions of "South Indian Railway - Lines Owned and Worked"
(Full revision based on 1937 History) |
(Link and text Changes) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
On 1 Jan 1908 the ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Section’ of the ‘[[Madras Railway]]’ including the ‘[[Tirupattur-Krishnagiri Railway]]’, with the [[Morappur-Dharmapuri Railway| ‘Morappur-Dharmapuri Section’]] and the [[Nilgiri Mountain Railway| ‘Nilgiri Railway’]] were transferred to the ‘South Indian Railway Company’ . | On 1 Jan 1908 the ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Section’ of the ‘[[Madras Railway]]’ including the ‘[[Tirupattur-Krishnagiri Railway]]’, with the [[Morappur-Dharmapuri Railway| ‘Morappur-Dharmapuri Section’]] and the [[Nilgiri Mountain Railway| ‘Nilgiri Railway’]] were transferred to the ‘South Indian Railway Company’ . | ||
<br>At the same time the ‘Katpadi-Dharmaram Section’ and the ‘Pakala-Gudur Section’ were handed over from the SIR to the M&SMR . | <br>At the same time the ‘Katpadi-Dharmaram Section’ and the ‘Pakala-Gudur Section’ were handed over from the SIR to the M&SMR . | ||
| − | <br>At the same date the SIR were given | + | <br>At the same date, 1908, the SIR were given “Running Powers “ over the [[Mysore-Bangalore Railway| ‘Madras-Bangalore Section’]] of the M&SMR. |
| + | <ref>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n145/mode/1up “Administration Report for Railways, 1918” page 136(pdf 145)]; Retrieved 21 Feb 2021</ref>. This arrangement lasted until 1919 when [[Mysore State]] successfully sought the reversion of the ‘[[Mysore-Bangalore Railway]]’ | ||
<br>Also the working of the ‘[[Shoranur-Cochin Railway|Shoranur-Cochin Indian State Railway]] was transferred to the SIR from the M&SMR | <br>Also the working of the ‘[[Shoranur-Cochin Railway|Shoranur-Cochin Indian State Railway]] was transferred to the SIR from the M&SMR | ||
==South Indian Railway System== | ==South Indian Railway System== | ||
| − | The following is based on the “1937 History of Indian Railways”<ref name=HistA>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 192-213, pdf 233-256]; Retrieved 8 Oct 2020</ref> , and also where extra information is available from the “1918 Administration Report on Railways” <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/ | + | The following is based on the “1937 History of Indian Railways”<ref name=HistA>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 192-213, pdf 233-256]; Retrieved 8 Oct 2020</ref> , and also where extra information is available from the “1918 Administration Report on Railways” <ref name=Admin>[https://archive.org/stream/BombayBarodaAndCentralIndiaRailwaySystem/Bombay_Baroda_And_Central_India_Railway_System#page/n145/mode/1up “Administration Report for Railways, 1918” pages 138-152 (pdf 145-160)]; Retrieved 21 Feb 2021</ref> |
The SIR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge,. It was the description applied for the actual ‘SIR Proper’ lines which comprised both broad gauge ([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) and metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) lines plus a number of BG ane MG lines on behalf of other parties. In addition the SIR worked two narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) lines on behalf of other parties:- | The SIR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge,. It was the description applied for the actual ‘SIR Proper’ lines which comprised both broad gauge ([[Rail_gauge#Broad_Gauge|BG]]) and metre gauge([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) lines plus a number of BG ane MG lines on behalf of other parties. In addition the SIR worked two narrow gauge([[Rail_gauge#Narrow_Gauge|NG]]) lines on behalf of other parties:- | ||
| Line 45: | Line 46: | ||
The following is generally based on the “1937 History of Railways”<ref name=Hist196>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 196-197, pdf 239-240]; Retrieved 2 Oct 2020</ref> and formed the ''actual'' ‘SIR Metre Gauge’ [[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]); other MG railways were worked by SIR ,these were individually listed but classified as the ‘SIR System Metre Gauge’ | The following is generally based on the “1937 History of Railways”<ref name=Hist196>[https://ia801605.us.archive.org/30/items/in.ernet.dli.2015.36650/2015.36650.India-Railway-Board-History-Of-Indian-Railways-Constructed-And-In-Progress.pdf US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 196-197, pdf 239-240]; Retrieved 2 Oct 2020</ref> and formed the ''actual'' ‘SIR Metre Gauge’ [[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]); other MG railways were worked by SIR ,these were individually listed but classified as the ‘SIR System Metre Gauge’ | ||
<br>''See separate pages for detailed information'' | <br>''See separate pages for detailed information'' | ||
| − | * ‘[[Madras-Dhanushkodi Mainline]]’, 425 miles(684km) | + | * ‘[[Madras-Dhanushkodi Mainline]]’, 425 miles(684km) from Madras to Dhanushkodi opened in stages [[Madras-Dhanushkodi Mainline|''- see separate page'']]. The metre gauge ([[Rail_gauge_#Metre_Gauge|MG]]) Mainline and Branches, developed from the ex-[[Great Southern of India Railway]](GISR) lines which were converted to MG and continued to be expanded over the years by SIR. From [[Madras]] the Mainline ran southwards via Chingleput, Villupuram , Cuddalore , Mayavaram, Tanjore , Trichinopoly, Madura to Manmadura to Mandapam, where it connected to the [[Pamban Branch Railway| ‘Pamban Railway’]] by way of the ‘[[Pamban Viaduct]]’ with the Island of [[Pambam]] to [[Dhanushkodi ]], from where there was a ferry connection to [[Ceylon]]. |
** ‘[[Arkonam Branch Line]]’, 39 miles(63km), opened 1880-81 from [[Chingleput]] to Conjaeeraram ; the Conjaeeraram th [[Arkonam]] section opened 1865 as a BG line and converted to MG in 1878 | ** ‘[[Arkonam Branch Line]]’, 39 miles(63km), opened 1880-81 from [[Chingleput]] to Conjaeeraram ; the Conjaeeraram th [[Arkonam]] section opened 1865 as a BG line and converted to MG in 1878 | ||
** [[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section| ‘Katpadi Branch Line’]], 99 miles(159km), opened 1890-91 from Villuparam to Katpadi. Originally part of the '[[Villupuram-Guntakal State Railway]]', from 1908 becoming the ‘[[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section]]’ final ly to become the [[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section| ‘Katpadi Branch Line’]] | ** [[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section| ‘Katpadi Branch Line’]], 99 miles(159km), opened 1890-91 from Villuparam to Katpadi. Originally part of the '[[Villupuram-Guntakal State Railway]]', from 1908 becoming the ‘[[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section]]’ final ly to become the [[Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section| ‘Katpadi Branch Line’]] | ||
| Line 54: | Line 55: | ||
** [[Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway | ‘Tranquebar Branch Line’]], 18 miles(29km), opened 1926 from Mayavaram to Tranquebar. Also described as the ‘[[Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway]]’ | ** [[Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway | ‘Tranquebar Branch Line’]], 18 miles(29km), opened 1926 from Mayavaram to Tranquebar. Also described as the ‘[[Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway]]’ | ||
** ‘[[Mayavaram -Arantangi Railway]]’, 99 miles(159km), opened 1894 from Mayavaram Junction to Mutupet Railway. Originally a [[Tanjore District Board Railway|Tanjore Distriict Board]] line described as the ‘[[Mayavaram Mutupet Railway]]’, 53 miles(85km) and extended in 1902-03, a further 46 miles(74km) to [[Arantangi ]]. | ** ‘[[Mayavaram -Arantangi Railway]]’, 99 miles(159km), opened 1894 from Mayavaram Junction to Mutupet Railway. Originally a [[Tanjore District Board Railway|Tanjore Distriict Board]] line described as the ‘[[Mayavaram Mutupet Railway]]’, 53 miles(85km) and extended in 1902-03, a further 46 miles(74km) to [[Arantangi ]]. | ||
| − | ** [[Nidamangalam-Mannargudi Railway| ‘ Mannargudi Branch Line]]’, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1915 from Nidamangalam to Mannargudi. Originally a [[Tanjore District Board Railway|Tanjore Distriict Board]] line. ** ‘[[Tirutturaipundi -Point Calimere Railway]]’, 28 miles(45km), opened 1919 from Tirutturaipundi to Agastiyampalli, 23 miles(37km) and extended a further 5 miles(8km) to Point Calimere in 1930 | + | ** [[Nidamangalam-Mannargudi Railway| ‘ Mannargudi Branch Line]]’, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1915 from Nidamangalam to Mannargudi. Originally a [[Tanjore District Board Railway|Tanjore Distriict Board]] line. |
| + | ** ‘[[Tirutturaipundi -Point Calimere Railway]]’, 28 miles(45km), opened 1919 from Tirutturaipundi to Agastiyampalli, 23 miles(37km) and extended a further 5 miles(8km) to Point Calimere in 1930 | ||
** ‘[[Nagore Branch Line]]’, 53 miles(km), opened 1861 as a BG line from [[Tanjore]] to Nagapatam , and converted to MG in 1875, extended 1899 from Nagapatam to [Nagore]] | ** ‘[[Nagore Branch Line]]’, 53 miles(km), opened 1861 as a BG line from [[Tanjore]] to Nagapatam , and converted to MG in 1875, extended 1899 from Nagapatam to [Nagore]] | ||
** ‘[[Trichinopoly-Tuticorin Railway]]’, 195 miles(314km) , from Trichinopoly to Tuticorin. The section from Trichinopoly Junction to Madura , 96 miles(154km) originally was part of the ‘MG Branch Line’, the section from [[Madura]] to [[Tuticorin]], 99 miles(158km) opened in 1876 and was named ‘[[Tuticorin Branch Line]]’ | ** ‘[[Trichinopoly-Tuticorin Railway]]’, 195 miles(314km) , from Trichinopoly to Tuticorin. The section from Trichinopoly Junction to Madura , 96 miles(154km) originally was part of the ‘MG Branch Line’, the section from [[Madura]] to [[Tuticorin]], 99 miles(158km) opened in 1876 and was named ‘[[Tuticorin Branch Line]]’ | ||
| Line 101: | Line 103: | ||
==Further Information== | ==Further Information== | ||
See '''[[South Indian Railway|South Indian Railway Main Page]]''', and each separate Individual Page | See '''[[South Indian Railway|South Indian Railway Main Page]]''', and each separate Individual Page | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Railways]] | [[Category:Railways]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:38, 30 January 2021
South Indian Railway - Lines Owned and Worked
- a sub section of the main South Indian Railway(SIR) page
Contents
History
The following summary is taken from the 1937 ‘History of Indian Railways’[1].
The ‘South Indian Railway’ was formed by the amalgamation on 1 July 1874 of the ‘Great Southern of India Railway’ and the ‘Carnatic Railway’, which on 1 Jan 1891 was purchased by the State and handed over, together with the ‘Villupuram-Guntakal State Railway’ for working as one undertaking, to a new company – the ‘South Indian Railway Company’.
The ‘Dharmavaram-Guntakal Section’ was made over from the SIR to the ‘Southern Mahratta Railway’ in 1893, which in 1908 became the ‘Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway (M&SMR’ ).
On 1 Jan 1908 the ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Section’ of the ‘Madras Railway’ including the ‘Tirupattur-Krishnagiri Railway’, with the ‘Morappur-Dharmapuri Section’ and the ‘Nilgiri Railway’ were transferred to the ‘South Indian Railway Company’ .
At the same time the ‘Katpadi-Dharmaram Section’ and the ‘Pakala-Gudur Section’ were handed over from the SIR to the M&SMR .
At the same date, 1908, the SIR were given “Running Powers “ over the ‘Madras-Bangalore Section’ of the M&SMR.
[2]. This arrangement lasted until 1919 when Mysore State successfully sought the reversion of the ‘Mysore-Bangalore Railway’
Also the working of the ‘Shoranur-Cochin Indian State Railway was transferred to the SIR from the M&SMR
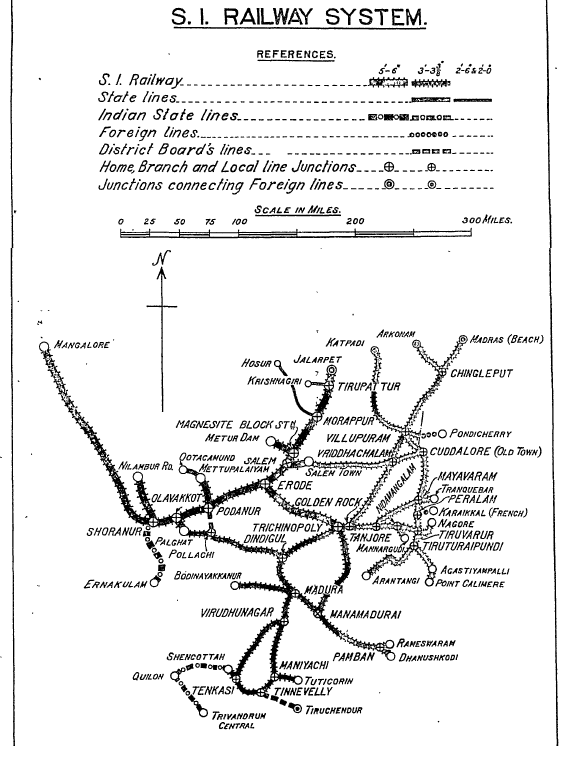
South Indian Railway System
The following is based on the “1937 History of Indian Railways”[3] , and also where extra information is available from the “1918 Administration Report on Railways” [4]
The SIR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge,. It was the description applied for the actual ‘SIR Proper’ lines which comprised both broad gauge (BG) and metre gauge(MG) lines plus a number of BG ane MG lines on behalf of other parties. In addition the SIR worked two narrow gauge(NG) lines on behalf of other parties:-
The ‘SIR System‘ comprised
- Broad Gauge (BG) in 1918 was 450 miles(724km); and by 1937 was 664 miles(1069km)
- Metre Gauge (MG) in 1918 was 1281 miles(2062km); and by 1937 was 1769 miles(2847km)
- Narrow Gauge(NG) in 1918 was 99 miles(159km); and by 1937 was 99 miles(159km)
SIR Broad Gauge
The Broad Gauge BG) Mainline with branches was originally named the ‘Jalarpet-Mangalore Mainline ’, owned and worked by ‘Madras Railway’ up to 31 Dec 1907, then transferred on 1 Jan 1908 to the ‘South Indian Railway’(SIR)[4]. Later development was undertaken by SIR by the addition of Branch lines [1]
This formed the actual ‘SIR Broad Gauge’ BG); other BG railways were worked by SIR and were listed separately but classified as part of the ‘SIR System Broad Gauge’
See separate pages for detailed information
- ‘SIR Broad Gauge Mainline’, 418 miles(673km), opened in stages from 1861 to 1907 from Jalarpet to Mangalore See separate pages for details
- ‘Mettupalaiyam Branch Line’, 26 miles(42km), opened 1873 from Podanur via Coimbatore to Mettupalaiyam
- ‘Palghat Branch Line’, 2½ miles(4km), opened 1888 from Palakkad Junction(Olavakode) to Palghat
- ‘Erode Branch Line’, 88 miles(142km), opened 1862-67 from Trichinoply Junction to Erode originally as a BG line but was converted to metre gauge(MG) in 1879. Reconverted to BG in 1920
- ‘Nilambur Branch Line’, 41 miles(68km) , opened 1927 from Shoranur to Nilambur Road. Also described as the ‘Shoranur-Nalambur Railway'.
- ’Salem-Mettur Dam Branch’, 23 miles(39km), opened 1929 from Salem to Mettur Dam and included the assisted siding from Mechori Road to Mettur Dam
SIR System Broad Gauge
In addition to the actual ‘SIR Broad Gauge’ lines, listed above, the following BG lines were worked by SIR and finally classified as part of the ‘SIR Broad Gauge System’
See separate pages for detailed information
- ‘Shoranur-Cochin Railway'. 65 miles(106km), opened 1902 from Shoraur to Ernakulam as a BG branch line. Funded by the Cochin Durbar and originally worked by the ‘Madras Railway’, from 1908 made over to the SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’. In 1938 the ‘Cochin Harbour Extension Railway', opened 1938, a 7 mile(11km) from Cochin to Cochin Harbour
- ‘Suramangalam-Salem Railway’, 3.9 miles (6.3km), District Board owned, opened 1917 as a BG line and worked by SIR . This short line converted into mixed gauge by addition of a MG rail in 1931, the MG line being part of the ‘Salem-Vriddhachalam Railway’ See MG Branches below
SIR Metre Gauge
The following is generally based on the “1937 History of Railways”[5] and formed the actual ‘SIR Metre Gauge’ MG); other MG railways were worked by SIR ,these were individually listed but classified as the ‘SIR System Metre Gauge’
See separate pages for detailed information
- ‘Madras-Dhanushkodi Mainline’, 425 miles(684km) from Madras to Dhanushkodi opened in stages - see separate page. The metre gauge (MG) Mainline and Branches, developed from the ex-Great Southern of India Railway(GISR) lines which were converted to MG and continued to be expanded over the years by SIR. From Madras the Mainline ran southwards via Chingleput, Villupuram , Cuddalore , Mayavaram, Tanjore , Trichinopoly, Madura to Manmadura to Mandapam, where it connected to the ‘Pamban Railway’ by way of the ‘Pamban Viaduct’ with the Island of Pambam to Dhanushkodi , from where there was a ferry connection to Ceylon.
- ‘Arkonam Branch Line’, 39 miles(63km), opened 1880-81 from Chingleput to Conjaeeraram ; the Conjaeeraram th Arkonam section opened 1865 as a BG line and converted to MG in 1878
- ‘Katpadi Branch Line’, 99 miles(159km), opened 1890-91 from Villuparam to Katpadi. Originally part of the 'Villupuram-Guntakal State Railway', from 1908 becoming the ‘Villupuram-Katpadi Railway Section’ final ly to become the ‘Katpadi Branch Line’
- ‘Pondicherry Branch Line’, 10 ½ miles(17km), opened 1879 from Villupuram to Ginga River including the bridge over the Pondicherry River.
- ‘Villupuram-Trichinopoly Railway’, 108 miles(173km) , opened 1927-29 from Villupuram to Golden Rock (Trichinopoly)
- ‘Cuddalore-Vriddhachalam Railway’, 35 miles(56km), opened 1928 from Cuddalore to Vriddhachalam. The line from Cuddalore Old Town to Wharf, 1½ Miles(2.4km), which had opened 1899 , listed in the 1918 Report was probably absorbed into this line.
- ‘Salem-Vriddhachalam Railway’, 86 miles(138km), opened 1931 from Salem to Vriddhachalam . The first 3.9miles(6.3km) from Salem Junction to Salem Town had opened in 1917 and described as the ‘Suramangalam-Salem Railway’, owned by the Salem District Board as a BG line and converted to mixed gauge (MG and BG) in 1931.
- ‘Tranquebar Branch Line’, 18 miles(29km), opened 1926 from Mayavaram to Tranquebar. Also described as the ‘Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway’
- ‘Mayavaram -Arantangi Railway’, 99 miles(159km), opened 1894 from Mayavaram Junction to Mutupet Railway. Originally a Tanjore Distriict Board line described as the ‘Mayavaram Mutupet Railway’, 53 miles(85km) and extended in 1902-03, a further 46 miles(74km) to Arantangi .
- ‘ Mannargudi Branch Line’, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1915 from Nidamangalam to Mannargudi. Originally a Tanjore Distriict Board line.
- ‘Tirutturaipundi -Point Calimere Railway’, 28 miles(45km), opened 1919 from Tirutturaipundi to Agastiyampalli, 23 miles(37km) and extended a further 5 miles(8km) to Point Calimere in 1930
- ‘Nagore Branch Line’, 53 miles(km), opened 1861 as a BG line from Tanjore to Nagapatam , and converted to MG in 1875, extended 1899 from Nagapatam to [Nagore]]
- ‘Trichinopoly-Tuticorin Railway’, 195 miles(314km) , from Trichinopoly to Tuticorin. The section from Trichinopoly Junction to Madura , 96 miles(154km) originally was part of the ‘MG Branch Line’, the section from Madura to Tuticorin, 99 miles(158km) opened in 1876 and was named ‘Tuticorin Branch Line’
- ‘Dindigul-Pollachi Railway’, 75 miles(121km), opened 1928 from Dindigul to Pollachi
- ‘Pollachi-Palghat Railway’, 34 miles(55km), opened 1928 from Pollach to Palghat
- ‘Madura-Manamadura Section’, 29 miles(47km), opened 1902 from Madura to Manamadura, originally part of the Mainline
- ‘Madura-Bodinayakanur Railway’, 66 miles(106km), opened 1928 from Madura to Bodinayakanur
- ‘Rameswaram Branch Line’, 7 miles(11km), opened 1906 from Pamban to Rameswaram . Originally named the ‘Pamban Branch Railway’ as part of the ‘‘Madras-Dhanushkodi Mainline’, detailed above.
- ‘Virudhunagar-Tenkasi Railway’, 75 miles(121km), opened 1927 from Virudhunagar to Tenkasi
- ‘Tinnevelly Branch Line’, 18 miles(30km), opened 1876 from Maniyachi to Tinnevelly
- ‘Pulliarpati Quarry Branch Line’ , 4½ miles(7km), opened 1898 from Tanjore to Pulliarpati Quarry. Listed in the 1918 Report - presume abandoned as not listed in the 1937 Report'
- ‘Capper Quarry Branch Line’, 0.9 mile(1.5km), opened 1900 from [Mainline Junction to Capper Quarry . Listed in the 1918 Report - presume abandoned as not listed in the 1937 Report'
- ‘Livingopuram Salt Branch Line’, 2.4 miles(4km) from Tuticorin to Livingopuram. Listed in the 1918 Report - presume abandoned as not listed in the 1937 Report'
SIR System Metre Gauge
In addition to the actual ‘SIR Metre Gauge’ lines, listed above, the following MG lines were worked by SIR and finally classified as part of the ‘SIR Metre Gauge System’
See separate pages for further information.
- ‘Nilgiri Mountain Railway', MG, 17 miles(27km), opened 1899 from Mettupalaiyam to Coonoor. Initially worked by ‘Madras Railway Co’, then from 1908 worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’. The line was extended to Ootacamund a further 12 miles(19km), was constructed by the Government and opened 1908[6].
- ‘Karaikkal-Peralam Railway', MG, 15 miles(24km), opened 1898 which connected the French enclave of Karaikkal with the rest of British India at Peralam . Financed by French Govt, constructed by Great Southern of India Railway and became part of the ‘SIR System’[7].
- ‘Podanur-Pollachi Railway', MG, 25 miles(40km), opened 1905. Coimbatore District Board owned, worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’ [8].
- ‘Pondicherry Railway', MG, 17 miles(27km), opened 1879. Connecting the French enclave of Pondicherry to the ‘SIR Mainline’ at Villupuram, worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’[9].
- ‘Tinnevelly-Tiruchendur Railway’, MG, 38 miles(61km), opened 1923 constructed by the SIR on behalf of the Tinnevelly District Board connecting Tiruchendur to the SIR at Tinnevelly, worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’[10].
- ‘Travancore Railway’, MG, originally named the ‘Tinnevelly-Quilon Railway', comprised two sections worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’ [11]:-
- 'Travancore Railway - British Section' , 50 miles(80km) ,opened 1902-03 from Tinnevelly to frontier of Travancore State.
- 'Travancore Railway - Indian State Section' , 58 miles(93km), opened 1904 from the frontier of Travancore State to Quilon
- ‘Quilon-Trivandrum Extension Railway’, 40 miles(64km), opened 1918 from Quilon to Chakai and further extended in 1931 to Trivandrum Central.
SIR System Narrow Gauge lines worked by SIR
The following Narrow Gauge (NG) were worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR NG System’
See separate pages for further information.
- ‘Morappur-Hosur Railway’, 2ft 6in/762mm NG, 73 miles(118km), opened 1906 from Morappur to Dharmapuri ; extended from Dharmapuri to Hosur in 1913. Worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’[12]
- ‘Tirupattur-Krishnagiri Railway' 2ft 6in/762mm NG, 25 miles(40km), opened 1905 as a famine protection line; worked by ‘Madras Railway’(MR) until 31 December 1907; then working passed to SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’[13]
- ‘Golden Rock- Sircarpalayam Tramway’ 2ft/610mm NG Tramway, 2¾ miles(4.4km) for carrying materials to the water pumping staion. Worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’[14]
District Board Lines worked by SIR
The following metre gauge MG) lines were worked by SIR under arrangements with and finally incorporated into the ‘SIR MG System ‘and included in the above.
See separate pages for further information.
- ‘Tanjore District Board Railways’, the first of District Board Railway, formed by raising funds to construct feeder lines; worked by SIR.:-
- ‘‘Mayavaram Mutupet Railway’, MG, 53 miles(85km) ), opened 1894 from Mayavaram Junction to Mutupet Railway. Originally a Tanjore District Board line worked by SIR. Extended in 1902-03, a further 46 miles(74km) to Arantangi and renamed the ‘Mayavaram Arantangi Railway’, 99 miles(159km).
- ‘ Mannargudi Branch Line’, MG, 8½ miles(14km), opened 1915 from Nidamangalam to Mannargudi. Originally a Tanjore District Board line, worked by SIR.
- ‘Mayavaram-Tranquebar Railway', MG, 19 mile(30km) , opened 1926 from Mayavaram to Tranquebar . Originally a Tanjore District Board line worked by SIR.
- ‘Podanur-Pollachi Railway', MG, 25 miles(40km), opened 1905. Coimbatore District Board owned, worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’
- ‘Tinnevelly-Tiruchendur Railway’, MG, 38 miles(61km), opened 1923 constructed by the SIR on behalf of the Tinnevelly District Board connecting Tiruchendur to the SIR at Tinnevelly, worked by SIR as part of the ‘SIR System’
- ‘Suramangalam-Salem Railway’, 3.9 miles (6.3km), Salem District Board owned, opened 1917 as a BG line and worked by SIR . This short line converted into mixed gauge by addition of a MG rail in 1931, the MG line being part of the ‘Salem-Vriddhachalam Railway’
Further Information
See South Indian Railway Main Page, and each separate Individual Page
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 192-194, pdf 233-237; Retrieved 8 Oct 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report for Railways, 1918” page 136(pdf 145); Retrieved 21 Feb 2021
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 192-213, pdf 233-256; Retrieved 8 Oct 2020
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 “Administration Report for Railways, 1918” pages 138-152 (pdf 145-160); Retrieved 21 Feb 2021
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ pages 196-197, pdf 239-240; Retrieved 2 Oct 2020
- ↑ ibid page 203 pdf 246
- ↑ ibid page 204 pdf 247
- ↑ ibid page 206 pdf 249
- ↑ ibid page 206 pdf 249
- ↑ ibid page 208 pdf 251
- ↑ ibid page 208 and 211 pdf 251 and 254
- ↑ ibid page 211 pdf 254
- ↑ ibid page 212 pdf 255
- ↑ ibid page 213 pdf 256