Great Indian Peninsula Railway - Lines owned and worked
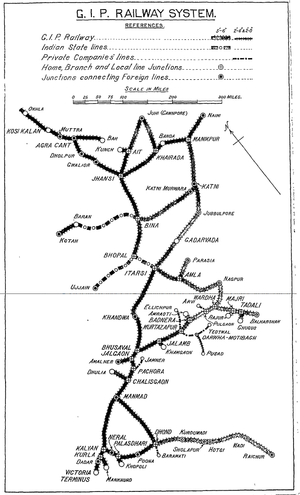
Great Indian Peninsula Railway - Lines owned and worked
- a sub-section of the Great Indian Peninsula Railway (GIPR) page
The GIPR operated an extensive network of railways of broad gauge(BG). In 1905 the route mileage was 1562 miles(2514km) and by 1918 was 2553 miles(4109km) divided into three sections ‘North East Division’, ‘South East Division’ and ‘Midland Division’ and their associated branches.
By 1937 the ‘GIPR Railway System’ had become 3727 miles(5998km)[1].
The GIPR also managed, worked and maintained a number of lines on behalf of other parties.
The information below is mainly from the “Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918" [2] and subsequent additions and variations referenced from the 1937 ‘History of Railways’) [1].
GIPR North East Mainline

The ‘GIPR North East Mainline’ , from Bombay to Jubbulpore, 615 miles(990km), opened in stages from 1853, reaching Jubbulpore in 1870
Shown in Green on GIPR North East Division Map
- ‘Bombay(Victoria Terminus)-Kalkan Section’; 1853-54, 33 miles(53km)
- ‘Kalkan-Thal Ghat(Igatpuri) Section’; 1860-65, 52 miles(84km)
- ‘Thal Ghat (Igatpuri)-Jalagon Section’, via Manmad Junction and Chalisgaon; 1861-63, 176 miles(283km)
- ‘Jalagon-Bhusaval Section’ ; 1863, 15 miles(24km)
- ‘Bhusawal-Khandwa Section’; 1865-66, 77 miles(124km)
- ‘Khandwa-Jubbulpore Section’, via Itarsi Junction; 1868-70, 262 miles(422km)
- ‘Jubbulpore-Naini Extension’ opened 1867 by the East_Indian_Railway as the ‘EIR Jubbulpore Branch’ and trasferred to GIPR in 1925[1].
GIPR North East Branches
Shown in Pink on GIPR North East Division Map
- ‘Nagpur Branch, NE line’; Bhusawal Junction to Baderna 1863-65, Bederna via Wardha Junction to Nagpur 1867: 243 miles(391km)
- ‘Khamgaon Branch’ NE line’, branch from ‘Nagpur Branch’; Jalamb to Khamgaon , 1870, 8 miles(13km)
- ‘Amraoti Branch, NE line’ branch from ‘Nagpur Branch’; Baderna to Amraoti , 1871, 5½ miles(9km)
- ‘Balharshah Branch, NE line’, Wardha to Warora, 1875-79, extended from Warora to Balharshah 1898, 82 miles(132km); with branch line Majri to Rajur, 1925, 37 miles[1].
- ‘Mohpani Branch, NE line’, branch from ‘Khandwa- Jubbulpore Section’; Gadarvada to Mohpani , 1872; extended to Goitoria 1896 and to new coal-fields 1900,
- ‘Jalagon-Amainer Branch, NE line’; Jalagon to Amainer, 1900, 34 miles(55km)
- ‘Chalisgaon-Dhulia Branch, NE line’; Chalisgaon to Dhulia , 1900, 35 miles56km)
- ‘Bombay Harbour Branch, NE line’; 1910, 6 miles(10km), extended 1925 from Victoia Tezrminus to Bray Road, giving total 10 miles(16km) [1].
- ‘Itsari-Nagpur Branch, NE line’ Itsari to Parasia; 1913-15, 134 miles(216km); finally extended to Nagpur 1923-24, giving total 278 miles(447km) [1].
- ‘Mahim Chord, NE line’; Ravali to Mahim, 1914, 1¼ miles(2km)
- ‘Kurla Branch, NE line’; Kurla to Mandala, 1924-27, 4 miles(7km) [1].
- ‘Ghugus Extension, NE line’,Tadali to Ghugus, 1918, 9 miles(14km) [1].
- ‘Agra-Bah Section, NE line’, Agra to Bah, 1918, 43 miles(69km) [1].
- ‘Baran-Kotah Section, NE line’, Baran to Kotah,1907-09, 40 miles(64km) [1] Not listed in 1918 Report
- ‘Cawnpore-Banda Section, NE line’, Cawnpore to Banda, 1913-14, 76 miles(122km) [1] Not listed in 1918 Report
GIPR South East Mainline

The ‘GIPR South East Mainline’ from Kalyan to Raichur, 409 miles(658km), opened in stages from 1856, reaching Raichur in 1871.
Shown in Yellow on GIPR South East Division Map
- ‘Kalkan-Bhore Ghat(Khandala) Section’; 1856-63, 44 miles(71km)
- ‘‘Bhore Ghat Khandala)-Poona Section’; 1858, 42 miles(68km)
- ‘Poona-Barsi Junction Section’; 1858-59, 115 miles(185km)
- ‘Barsi Junction-Gulburga Section’; to Sholapur, 1860 via Hotgi Juction to Gulberga, 1870, 119 miles(192km)
- ‘Galburga-Raichur Section’, via Wadi Junction and Kistna Viaduct; 1870-71, 89 miles(143km)
GIPR South East Branches
Shown in Purple on GIPR South East Division Map
- ‘Khopoli Branch, SE line’; Palasdhari(Padusdhurree) to Khopoli(Campoolie) 1856: 7¼ miles(12km). This section became a branch line on the opening of the Bhor Ghat in 1863.
- ‘Manmad Branch, SE line’; Dhond to Manmad: 145 miles(233km) at Madmad connected to the ‘GIPR North East Mainline’‘. Originally the ‘Dhond-Manmad State Railway’; opened 1878. A 'chord' line connecting the GIPR south-eastern main line to Madras with the GIPR north-eastern main line to Allahabad, passed to GIPR 1880.
GIPR Midland Mainline

The ‘GIPR Midland Mainline’ from Bhopal to Agra Cantonment, 316 miles(509km), opened 1878-81, originally by the ‘Indian Midland Railway’. The line was extended to connect to the ‘Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway ‘(BB&CIR) at Agra in 1905 and the ‘Agra-Delhi Chord Railway’ in 1906, a further 3½ miles (6km).
Shown in Red on GIPR Midland Division Map'
- ‘Bhopal-Jhansi Section’ via Bina; 1880, 180 miles(290km)
- ‘Jhansi-Gwalior Section’; 1880, 60 miles(97km)
- ‘Gwalior-Dholpur Section’; 1879-80, 40 miles(64km)
- ‘Dholpur-Agra Cantonment Section’; 1878, 36 miles(58km)
GIPR Midland Branches
Shown in Blue on GIPR Midland Division Map
- ‘Ait-Kunch Branch Railway’ opened 189?. Indian State line initially worked by ‘Indian Midland Railway’(IMR); then worked by GIPR
- ‘Bina-Saugur-Katni Branch’; from Bina to Saugur 1889, Katni 1898-99, 162 miles(261km]; in 1890 a short connection to ‘Bengal Nagpur Railway’(BNR) at Katni Murwara and in 1899 a short connection to ‘East Indian Railway’(EIR) near Agra
- ‘Bina-Goona-Baran Railway’, opened 1895. Owned by State of Gwalior and Udaipur Durbar; worked by Indian Midland Railway(IMR); amalgamated into GIPR , 1900; extended with the Baran-Kotah Railway’, opened 1908.
- ‘Cawnpore Branch’; from Jhansi to Cawnpore, 1886-88, 136 miles(219km);
- ‘Moth Quarry Branch’, 3 mile(5km) branch from ‘Cawnpore Branch’, 1907
- ‘Manikpur Branch’; from Jhansi via Banda to Manikpur, 1889, 180 miles(290km)
- ‘Bhopal-Ujjain Railway’, opened c.1895. Indian State line worked by IMR
Former IMR Lines transferred to GIPR
Note these generally incorporated into the GIPR network above
See separate pages for further information
- ‘Indian Midland Railway’(IMR). State agency formed 1882 to work several branch lines centred on Jhansi, amalgamated into GIPR, 1900
- ‘Agra-Gwalior Railway’, opened 1881; Indian State line, owned by Gwalior Durbar, known as Scindia State Railway, working taken over by IMR 1885; then in 1900 becoming part of GIPR 'Midland Section Mainline'.
- ’Bhopal State Railway’ opened 1884. Indian State line, initially worked by IMR as Bhopal-Itarsi (Indian State Section).
- ‘Bhopal-Itarsi Railway’, opened 1882. State(British) Section; worked by IMR, 1885.
- ‘Bina-Katni Railway’, opened 1889. Part of IMR.
- ‘Cawnpore-Kalpi-Jhansi Railway’, opened 1886. Line completed 1888 by IMR.
- ‘Dhond-Manmad State Railway’, opened 1878. A 'chord' line connecting GIPR main lines; constructed by GoI and handed to GIPR, 1880.
- ‘Jhansi-Bina Bhopal Railway’, opened 1889. Part of IMR.
- ‘Jhansi-Gwalior and Katni Railway’, opened 1889. Part of IMR.
- ‘Jhansi-Konch-Kalpi Railway’, opened 1886. Part of IMR.
- ‘Jhansi-Manikpore State Railway’, opened 1889. Part of IMR.
- ‘Kunch- Madhggarh Railway’. Project in 1906 by IMR/GIPR as extension to ‘Ait-Kunch Branch Railway’
Railways absorbed into GIPR
Note these generally incorporated into the GIPR network above
See separate pages for further information
- ‘Allahabad-Jubbulpore line’, opened 1867. Built by East Indian Railway(EIR); transferred to GIPR, 1925
- ‘Amraoti State Railway, opened 1871. Branch railway to Baderna on GIPR. Worked by GIPR and finally taken over.
- ‘Dhond-Manmad State Railway’; opened 1878. A 'chord' line connecting the GIPR south-eastern main line to Madras with the GIPR north-eastern main line to Allahabad, passed to GIPR 1880.
Lines worked by GIPR at some time - alphabetical order
Broad Gauge (BG) and Narrow Gauge (NG) as indicated.
See separate pages for further information
- ‘Ambaji-Taranga Light Railway’ NG, opened 1919-20. Unassisted Company formed 1917; apparently worked by GIPR
- ‘Cawnpore-Banda Railway’ BG, opened 1913-14. Worked by GIPR , 1914
- ‘Central Provinces Railway Co Ltd’(CPR). A British owned company, formed 1910, operating a group of NG lines; all worked by GIPR ; under GoI management, 1925
- ‘Darwha-Pusad Railway’ opened 1931. Part of CPR
- ‘Dhond-Baramati Railway’ NG, opened 1914-15. Part of CPR
- ‘Ellichpur-Murtazapur-Yeotmal Railway’ NG, opened first section opened as ‘Yavatmal Murtijapur Railway’ 1903, extended to Ellichpur 1913 . Known informally as ‘Shakuntala Railway’. Part of CPR
- ‘Pachora-Jamner Light Railway’ NG, opened 1919. Part of CPR
- ‘Pulgaon-Arvi Railway’ NG, opened 1917-18. Part of CPR
- ‘Gwalior Light Railway’ NG, opened 1899. Owned by State of Gwalior; worked by GIPR; renamed ‘Scindia State Railway’ 1944
- ‘Ujjain-Agar Branch Railway’ NG, opened 1932. Part of ‘Gwalior Light Railway’
- ‘Khamagaon-Jalna Railway’ NG. The date of opening of the railway is not known; the railway was under consideration in 1906.
- ‘Khamgaon Branch Railway’ BG. Short branchline of 12km between Jalamb and Khamgaon; worked by GIPR. The date of opening of the railway is not known.
- ‘Salsette Trombay Railway’ Std.Gauge, opened 1928. Operated by GIPR, closed 1934
- ‘Kurla-Trombay Railway’, opened 1928. Part of ‘Salsette Trombay Railway’; worked by GIPR
- ‘Nizam's Railway’ BG, opened 1874. Worked by GIPR until 1878; then by GoI; became ‘Nizam's Guaranteed State Railway’, 1886
- ‘Pench Valley Coalfield Railway’ NG, opened 1913. Private Branch Line to [‘[Itarsi-Nagpur Railway]]’; worked by GIPR
- ‘Wardha Valley Railway’ BG, opened 1874. Worked by GIPR, also called ‘Wardha Coal Railway’
- ‘Wardha-Warora Railway’ BG, opened 1877, managed by GIPR by 1905
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India – Railway Department’, page 96, pdf 125; Retrieved 18 Apr 2020
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; pages 64-68, pdf pages 73-77; Retrieved 10 Apr 2020