North Western Railway: Difference between revisions
→Railways absorbed into NWR: Kandahar State Railway link corrected |
'Stations' infobox revised with link |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
|timeline5details= [[Southern Punjab Railway]] merged into NWR | |timeline5details= [[Southern Punjab Railway]] merged into NWR | ||
|presidency= [[Bengal]] | |presidency= [[Bengal]] | ||
|stations= | |stations= ''see'' '''Major Stations Infobox''' ''below'' | ||
|system1date= 1886 | |system1date= 1886 | ||
|system1details= State agency | |system1details= State agency | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
|company8= | |company8= | ||
|company8details= [[Southern Punjab Railway]] | |company8details= [[Southern Punjab Railway]] | ||
|company9= | |company9=] | ||
|company9details= [[Kalka-Simla Railway]] | |company9details= [[Kalka-Simla Railway]]] | ||
|company10= | |company10= | ||
|company10details= | |company10details= | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|company12details= | |company12details= | ||
|headquarters= [[Lahore]] | |headquarters= [[Lahore]] | ||
|workshop= [[Moghalpura]] | |workshop= [[Lahore|Lohore(Moghalpura)]], [[Karachi]], [[Multan]], [[Saharanpur]]<br>''see also'' [[NWR Railway Workshops]] | ||
|stations= [[Amritsar]], [[Ferozepore]], [[Hyderabad]], [[Meerut]], [[Multan]], [[Peshawar]], [[Quetta]], [[Rawalpindi]], [[Saharanpur]], [[Sibi]] | |stations= [[Amritsar]], [[Ferozepore]], [[Ghaziabad]], [[Hyderabad]], [[Meerut]], [[Multan]], [[Peshawar]], [[Quetta]], [[Rawalpindi]], [[Saharanpur]], [[Sibi]] | ||
[[Ghaziabad]] was the connection to [[Delhi]] - [[Delhi_Railways_%26_Stations#Delhi_Stations| ''see separate page'' - '''Delhi Stations''']] for details | |||
|system1date= 1947 | |system1date= 1947 | ||
|system1details= [West] [[Pakistan Railways]] | |system1details= [West] [[Pakistan Railways]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 88: | ||
|auxillary forces= [[North-Western Railway Battalion]] | |auxillary forces= [[North-Western Railway Battalion]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File: North-Western Railway Map 1909, south-west section.png|thumb| North-Western Railway Map 1909, south-west section]] | |||
[[File: North-Western Railway Map 1909, north-east section.png|thumb| North-Western Railway Map 1909, north-east section]] | |||
The '''North-Western State Railway''' (NWR) was formed in January 1886 from the merger of the [[Sind, Punjab and Delhi Railway]], the [[Indus Valley State Railway]], the [[Punjab Northern State Railway]], the eastern section of the [[Sind-Sagar Railway]] and the southern section of the [[Sind-Pishin State Railway]]. | The '''North-Western State Railway''' (NWR) was formed in January 1886 from the merger of the [[Sind, Punjab and Delhi Railway]], the [[Indus Valley State Railway]], the [[Punjab Northern State Railway]], the eastern section of the [[Sind-Sagar Railway]] and the southern section of the [[Sind-Pishin State Railway]]. | ||
| Line 92: | Line 96: | ||
== History == | ==History== | ||
The military and strategic concerns of Afghan-Indian border were such that [[Francis Langford O'Callaghan]], was posted from the [[State Railways]] as "engineer-in-chief for a number of demanding railway projects, surveys and constructions on the north-west frontier" <ref name=biog>[http://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/abs/10.1680/bdoceigbai.58347.457 Institution of Civil Engineers "Biographical Dictionary of Civil Engineers in Great Britain and Ireland - O'Callaghan, Francis Langford "]; Retrieved on 9 Jul 2016</ref>. These were initially military and strategic projects and became part of the NWR network on formation in 1886. The [[Bolan Pass Railway Construction]] was completed in 1886. The [[Khwaja Amran Railway Survey]] in 1887 included the [[Khojak Tunnel]] and the [[Chaman Extension Railway]]<ref>[http://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V21_020.gif "The Imperial Gazetteer of India" v. 21, p. 14.]; Retrieved on 13 Jul 2016</ref>. The [[Khojak Tunnel]] opened in 1891 and the railway reached [[Chaman]] on the Afghan border. | |||
Later renamed the [[North Western Railway]], by 1905 it was the longest railway under one administration and the strategic railway of the north-west frontier. In 1947, one part became the nucleus of [[Pakistan Railways|Pakistan's railways]], with 4976 of the old system's 6861 miles lying within the new state; the part lying in India was reorganised and renamed as [[Eastern Punjab Railway]]. | Later renamed the [[North Western Railway]], by 1905 it was the longest railway under one administration and the strategic railway of the north-west frontier. In 1947, one part became the nucleus of [[Pakistan Railways|Pakistan's railways]], with 4976 of the old system's 6861 miles lying within the new state; the part lying in India was reorganised and renamed as [[Eastern Punjab Railway]]. | ||
== | ==North Western Railway - Lines operated and worked== | ||
[[North_Western_Railway_-_Lines_operated_and_worked|''See seperate page for full details'' '''NWR - Lines operated and worked''']] | |||
<br>Comprising:- | |||
*[[North_Western_Railway_-_Lines_operated_and_worked#NWR_Commercial_Section_BG|'''NWR Commercial Section''']] | |||
*[[ | *[[North_Western_Railway_-_Lines_operated_and_worked#NWR_Military.2FStrategic_Section|'''NWR Frontier (Military) Section''']] | ||
*[[North_Western_Railway_-_Lines_operated_and_worked#NWR_Narrow_Gauge_System|'''NWR Narrow Gauge System''']] | |||
*[[ | *[[North_Western_Railway_-_Lines_operated_and_worked#NWR_System_.E2.80.93_BG_Lines_Worked_as_part_of_the_NWR_System|'''NWR System – BG Lines Worked as part of the NWR System''']] | ||
*[[ | |||
*[[ | |||
== | ==NWR Coal Supplies== | ||
From an early daate the NWR estabished their own collieries to supply coal for their operations.''See separate pages for more information'':- | |||
*[[ | *[[Khost Colliery Tramway|Khost Colliery ]] - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1877 and closed on unknown date. | ||
*[[Dandot Light Railway|Dandot Colliery]] - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed 1911. | |||
*[[Sharigh Colliery]] - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed on unknown date. | |||
*[[Bhaganwala Colliery Railway|Bhaganwala Colliery]] - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed 1899. | |||
*[[ | |||
*[[ | |||
== | ==NWR Sleeper Supplies== | ||
''See separate pages for further information'' | |||
*[[ | *[[Changa Manga Forest Tramway|Changa Manga Forest Operation]]. By 1884 the NWR found itself starved of sleepers that were vital in running services on its network. This operation had been established in 1864 and started supply of sleepers in 1884 | ||
*[[Marala Sleeper Works Railway|Marala Sleeper Works]], opened 1917, closed and transferred 1922-23 | |||
*[[Dhilwan Sleeper Works Railway|Dhilwan Sleeper Works]], opened 1923 | |||
*[[ | |||
*[[ | |||
== | ==NWR Quarries== | ||
*[[ | *[[Paikhel Quarry Railway|Paikhel Quarry Railway]], owned by NWR, in use 1939-42 | ||
==FIBIS resources== | ==FIBIS resources== | ||
*FIBIS Gallery Album [http:// | ''See separate pages for more information'':- | ||
**[http:// | *FIBIS Gallery Album [http://gallery.fibis.org/index.php?/category/17 Railways/NWR/H V O WATERS Collection] He served as a travelling Inspector of Coaching and Goods Accounts, NWR 1907-1917. Includes a | ||
**[http://gallery.fibis.org/picture.php?/521/category/17 map] of the railway network. To enlarge, click on the icon at the top left hand corner of the map. | |||
== Records == | ==Records== | ||
An on-line search of the [[India Office Records]] (IOR) records held at the [[British Library]] relating to this railway <ref>[http://searcharchives.bl.uk/primo_library/libweb/action/search.do?vid=IAMS_VU2 “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search]; Retrieved 30 May 2016</ref> | |||
gives several entries, the most relevant as follows: - | |||
*L/AG/46/34; “Records of the India Office relating to the North Western State Railway”; 1893-1924 | |||
*L/F/8/18/1419; “North Western Railway, Book of contracts relating to lines worked by the NorthWestern Railway Office of the Chief Examiner of Accounts”; date unspecified | |||
[[File:Viceregal Crockery of the North Western Railways.JPG |thumb| Viceregal Crockery of the North Western Railway]] | |||
== | ==Personnel== | ||
There are no staff agreements for NWR personnel held at the [[British Library]] in the [[India Office Records]]. | |||
'''[[North Western Railway Personnel]]''' gives details of NWR staff from several sources:- | |||
*“India Civil List 1890” <ref>Fibis Records, scans of original ” </ref> and the " India List and India Office List, 1905" <ref>[https://play.google.com/books/reader?id=b2NPAAAAMAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&hl=en_GB&pg=GBS.PR14 " India List and India Office List, 1905"] Retrieved on 30 May 2016</ref> for [[Public Works Department]] Railway Branch or [[:Category:State Railways|State Railways]] personnel deployed to NWR gives a number of entries. The most notable of these have been listed. | |||
*"Grace's Guide ” for notable personnel <ref>[http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/Main_Page “Grace’s Guide”]; Retrieved 30 May 2016</ref> | |||
*"National Archives from the RAIL collection” <ref>[http://discovery.nationalarchives.gov.uk/details/r/C241 “National Archives” ”]; Retrieved 30 May 2016</ref> | |||
==Associated Auxiliary Force== | |||
*[[North-Western Railway Battalion]]. Includes mention of armoured trains | *[[North-Western Railway Battalion]]. Includes mention of armoured trains | ||
== Institutions == | == Institutions == | ||
*[[Schools#F|North Western Railway School]], Fairlawn, [[Mussoorie]]. | *[[Schools#F|North Western Railway School]], Fairlawn, [[Mussoorie]]. | ||
*[http://www.panoramio.com/photo/54984118 Picture of the teachers and students of St. Andrew School, Pakistan Railways (then NWR) at Lahore, set up in the late 19th century] panoramio.com | *[https://web.archive.org/web/20170519215908/http://www.panoramio.com/photo/54984118 Picture of the teachers and students of St. Andrew School, Pakistan Railways (then NWR) at Lahore, set up in the late 19th century] panoramio.com, now archived. | ||
== Recommended reading == | ==Recommended reading== | ||
*Berridge, Percy Stuart Attwood. ''Couplings to the Khyber: the story of the North Western Railway''. Newton Abbot: David & Charles, 1969. | *Berridge, Percy Stuart Attwood. ''Couplings to the Khyber: the story of the North Western Railway''. Newton Abbot: David & Charles, 1969. | ||
| Line 176: | Line 161: | ||
Monthly staff magazine. Some editorial content published in Urdu . No BL holdings. 2 copies (November 1942, December 1945) are held in the Berridge Papers, [[University of Cambridge - Centre of South Asian Studies|Cambridge South Asian Archive]]. | Monthly staff magazine. Some editorial content published in Urdu . No BL holdings. 2 copies (November 1942, December 1945) are held in the Berridge Papers, [[University of Cambridge - Centre of South Asian Studies|Cambridge South Asian Archive]]. | ||
== External | ==External links== | ||
*Terry Case, [http://members.tripod.com/shankardubai/nwrhome.htm ''North Western Railway'']. Includes a section about [http://shankardubai.tripod.com/halwaters.htm Hal Waters] (refer photograph album above) | *Terry Case, [http://members.tripod.com/shankardubai/nwrhome.htm ''North Western Railway'']. Includes a section about [http://shankardubai.tripod.com/halwaters.htm Hal Waters] (refer photograph album above) | ||
| Line 184: | Line 169: | ||
*[http://web.archive.org/web/20130127073836/http://pakistaniat.com/2010/03/01/journeys-to-remember-quetta-lahore-by-rail-in-1925/ Quetta to Lahore by Rail 1925] ''All Things Pakistan'', now an archived website | *[http://web.archive.org/web/20130127073836/http://pakistaniat.com/2010/03/01/journeys-to-remember-quetta-lahore-by-rail-in-1925/ Quetta to Lahore by Rail 1925] ''All Things Pakistan'', now an archived website | ||
*[http://www.indiaofthepast.org/contribute-memories/read-contributions/life-back-then/350-breakup-of-the-north-western-railway-and-the-anglo-indian-community "Breakup of the North Western Railway and the Anglo-Indian community"] by Kenneth Hugh Staynor. indiaofthepast.org | *[http://www.indiaofthepast.org/contribute-memories/read-contributions/life-back-then/350-breakup-of-the-north-western-railway-and-the-anglo-indian-community "Breakup of the North Western Railway and the Anglo-Indian community"] by Kenneth Hugh Staynor. indiaofthepast.org | ||
*[http://www.panoramio.com/user/4789607/tags/British%20Steam%20Locomotives Images of British Steam Locomotives used by North Western Railways] Ghilzai:panoramio.com | *[https://web.archive.org/web/20161118040346/http://www.panoramio.com/user/4789607/tags/British%20Steam%20Locomotives Images of British Steam Locomotives used by North Western Railways] Ghilzai:panoramio.com, now archived. | ||
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20170520190736/http://www.panoramio.com/photo/55027511 An old photograph of a Railway Inspection trolley with removeable sailboard used on NWR Hyderabad-Kotri, Sindh, Pakistan]. Ghilzai:panoramio.com, now archived. | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/northampton_museum/5044010710/in/set-72157625077918924 Photograph of Troops travelling by train] taken by Private J W Linley of the 2nd Battalion, The Northamptonshire Regiment compiled whilst serving in India 1923-1938. flickr.com/photos/northampton_museum | *[http://www.flickr.com/photos/northampton_museum/5044010710/in/set-72157625077918924 Photograph of Troops travelling by train] taken by Private J W Linley of the 2nd Battalion, The Northamptonshire Regiment compiled whilst serving in India 1923-1938. flickr.com/photos/northampton_museum | ||
===Historical books online=== | ===Historical books online=== | ||
*[http://archive.org/stream/quarterlycivill00offigoog#page/n192/mode/2up Some railway personnel in 1898]. Page 179 ''Quarterly Civil List for the Punjab: Corrected up to 1st October 1898'' Archive.org | *[http://archive.org/stream/quarterlycivill00offigoog#page/n192/mode/2up Some railway personnel in 1898]. Page 179 ''Quarterly Civil List for the Punjab: Corrected up to 1st October 1898'' Archive.org | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 09:19, 9 March 2021
| North Western Railway | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Line of route | ||
| Karachi to Quetta Karachi to Lahore Lahore to Delhi Lahore to Peshawar | ||
| Gauge / mileage | ||
| Broad gauge | 3186 miles (1905) 6861 miles (1947) | |
| Timeline | ||
| 1886 | Formed by merger of several railways, viz: Sind, Punjab and Delhi Railway Indus Valley State Railway Punjab Northern State Railway | |
| 1930 | Southern Punjab Railway merged into NWR | |
| Key locations | ||
| Presidency | Bengal | |
| Stations | see Major Stations Infobox below | |
| System agency | ||
| 1886 | State agency | |
| How to interpret this infobox | ||
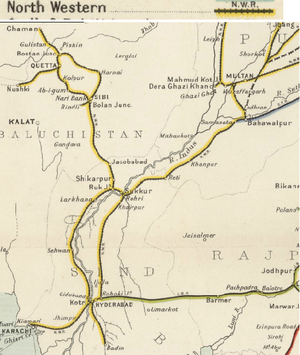

The North-Western State Railway (NWR) was formed in January 1886 from the merger of the Sind, Punjab and Delhi Railway, the Indus Valley State Railway, the Punjab Northern State Railway, the eastern section of the Sind-Sagar Railway and the southern section of the Sind-Pishin State Railway. [1]
History
The military and strategic concerns of Afghan-Indian border were such that Francis Langford O'Callaghan, was posted from the State Railways as "engineer-in-chief for a number of demanding railway projects, surveys and constructions on the north-west frontier" [2]. These were initially military and strategic projects and became part of the NWR network on formation in 1886. The Bolan Pass Railway Construction was completed in 1886. The Khwaja Amran Railway Survey in 1887 included the Khojak Tunnel and the Chaman Extension Railway[3]. The Khojak Tunnel opened in 1891 and the railway reached Chaman on the Afghan border.
Later renamed the North Western Railway, by 1905 it was the longest railway under one administration and the strategic railway of the north-west frontier. In 1947, one part became the nucleus of Pakistan's railways, with 4976 of the old system's 6861 miles lying within the new state; the part lying in India was reorganised and renamed as Eastern Punjab Railway.
North Western Railway - Lines operated and worked
See seperate page for full details NWR - Lines operated and worked
Comprising:-
- NWR Commercial Section
- NWR Frontier (Military) Section
- NWR Narrow Gauge System
- NWR System – BG Lines Worked as part of the NWR System
NWR Coal Supplies
From an early daate the NWR estabished their own collieries to supply coal for their operations.See separate pages for more information:-
- Khost Colliery - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1877 and closed on unknown date.
- Dandot Colliery - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed 1911.
- Sharigh Colliery - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed on unknown date.
- Bhaganwala Colliery - owned and worked by NWR, opened in 1894 and closed 1899.
NWR Sleeper Supplies
See separate pages for further information
- Changa Manga Forest Operation. By 1884 the NWR found itself starved of sleepers that were vital in running services on its network. This operation had been established in 1864 and started supply of sleepers in 1884
- Marala Sleeper Works, opened 1917, closed and transferred 1922-23
- Dhilwan Sleeper Works, opened 1923
NWR Quarries
- Paikhel Quarry Railway, owned by NWR, in use 1939-42
FIBIS resources
See separate pages for more information:-
- FIBIS Gallery Album Railways/NWR/H V O WATERS Collection He served as a travelling Inspector of Coaching and Goods Accounts, NWR 1907-1917. Includes a
- map of the railway network. To enlarge, click on the icon at the top left hand corner of the map.
Records
An on-line search of the India Office Records (IOR) records held at the British Library relating to this railway [4] gives several entries, the most relevant as follows: -
- L/AG/46/34; “Records of the India Office relating to the North Western State Railway”; 1893-1924
- L/F/8/18/1419; “North Western Railway, Book of contracts relating to lines worked by the NorthWestern Railway Office of the Chief Examiner of Accounts”; date unspecified

Personnel
There are no staff agreements for NWR personnel held at the British Library in the India Office Records.
North Western Railway Personnel gives details of NWR staff from several sources:-
- “India Civil List 1890” [5] and the " India List and India Office List, 1905" [6] for Public Works Department Railway Branch or State Railways personnel deployed to NWR gives a number of entries. The most notable of these have been listed.
- "Grace's Guide ” for notable personnel [7]
- "National Archives from the RAIL collection” [8]
Associated Auxiliary Force
- North-Western Railway Battalion. Includes mention of armoured trains
Institutions
- North Western Railway School, Fairlawn, Mussoorie.
- Picture of the teachers and students of St. Andrew School, Pakistan Railways (then NWR) at Lahore, set up in the late 19th century panoramio.com, now archived.
Recommended reading
- Berridge, Percy Stuart Attwood. Couplings to the Khyber: the story of the North Western Railway. Newton Abbot: David & Charles, 1969.
Good coverage of the largest Indian railway system, especially from a civil engineering perspective. Lacks a bibliography and poorly annotated. [Slides of the photographs used form a collection deposited at the Cambridge South Asian Archive together with copies of the North Western Railway Magazine, the monthly staff magazine edited by the author.]
- North Western Railway Magazine.
Monthly staff magazine. Some editorial content published in Urdu . No BL holdings. 2 copies (November 1942, December 1945) are held in the Berridge Papers, Cambridge South Asian Archive.
External links
- Terry Case, North Western Railway. Includes a section about Hal Waters (refer photograph album above)
- "History of Northern Railway", Northern Railway.
- Quetta to Lahore by Rail 1925 All Things Pakistan, now an archived website
- "Breakup of the North Western Railway and the Anglo-Indian community" by Kenneth Hugh Staynor. indiaofthepast.org
- Images of British Steam Locomotives used by North Western Railways Ghilzai:panoramio.com, now archived.
- An old photograph of a Railway Inspection trolley with removeable sailboard used on NWR Hyderabad-Kotri, Sindh, Pakistan. Ghilzai:panoramio.com, now archived.
- Photograph of Troops travelling by train taken by Private J W Linley of the 2nd Battalion, The Northamptonshire Regiment compiled whilst serving in India 1923-1938. flickr.com/photos/northampton_museum
Historical books online
- Some railway personnel in 1898. Page 179 Quarterly Civil List for the Punjab: Corrected up to 1st October 1898 Archive.org
References
- ↑ " Administration Report on the Railways in India – corrected up to 31st March 1918"; Superintendent of Government Printing, Calcutta; page 106; Retrieved 20 Dec 2015
- ↑ Institution of Civil Engineers "Biographical Dictionary of Civil Engineers in Great Britain and Ireland - O'Callaghan, Francis Langford "; Retrieved on 9 Jul 2016
- ↑ "The Imperial Gazetteer of India" v. 21, p. 14.; Retrieved on 13 Jul 2016
- ↑ “British Library Archives and Manuscripts Catalogue” - Search; Retrieved 30 May 2016
- ↑ Fibis Records, scans of original ”
- ↑ " India List and India Office List, 1905" Retrieved on 30 May 2016
- ↑ “Grace’s Guide”; Retrieved 30 May 2016
- ↑ “National Archives” ”; Retrieved 30 May 2016
