User:PEA-2292/My sandbox
North Western Railway - Lines operated and worked
- a sub-section of the North Western Railway (NWR) page
The NWR was formed in January 1886 from the merger of the Scinde, Punjaub & Delhi Railway(SP&DR), the Indus Valley State Railway(IVSR), the Punjab Northern State Railway(PNSR), the eastern section of the Sind-Sagar Railway and the southern section of the Sind-Pishin State Railway.
The listings below are generally based on the “1937, History of Indian Railways”[1], and also where extra information is available from the “1918, Administration Report on Railways 1918” [2]
North Western Railway System.
The NWR owned and operated an extensive network of railways of mixed gauge, and was the description applied for the actual ‘NWR Proper’ lines plus a number of broad gauge (BG) and narrow gauge(NG) lines on behalf of other parties:-
- Broad gauge (BG) in 1918 was 4853 miles(7810km); and by 1937 was 6402 miles(10,303km)
- Narrow gauge(NG) in 1918 was 449 miles(722km); and by 1937 was 686 miles(1104km)
North Western Railway Broad Gauge (BG) .
The line lengths of the ‘NWR Proper’ (excluding lines on behalf of other parties) of Broad Gauge lines in 1918 was 3690 miles(5938km) and this had become 5769 miles(9284km) by 1937 divided into two sections :-
- NWR Commercial Section, 2559 miles(4118km) by 1918 and 5769 miles(9284km) by 1937as detailed below:-
- NWR Frontier(Military) Section, 1151(1852km) by 1918 and named the ‘NWR Strategic Section’, 1555 miles(2503km) by 1937 as detailed below:-
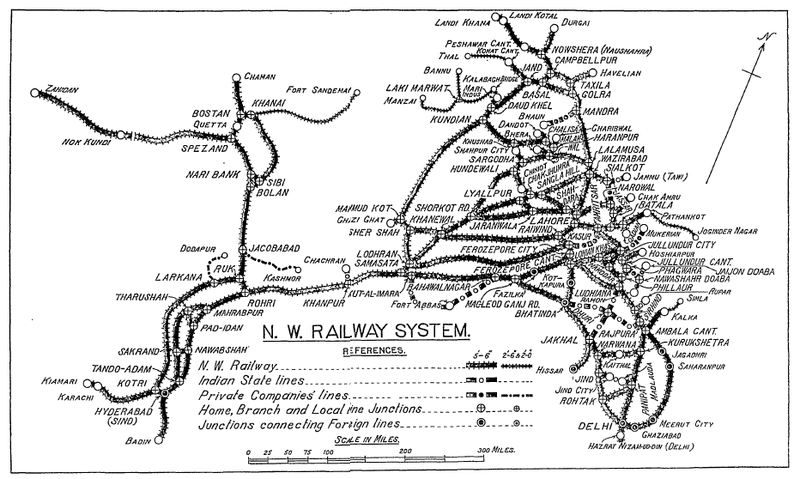
NWR Commercial Section BG
Broad gauge (BG), 2559 miles(4118km) in 1918; and 4184 miles(6733km) by 1937
Kiamari-Lahore Mainline
This NWR Mainline connecting Kiamari (near Karachi City) to Lahore, 757 miles(1218km) in 1937. Originally named the ‘Lahore-Karachi Mainline’, comprised:-
- ‘Kiamari-Karachi Section’, 3 miles(5km) from Kiamari-to Karachi City, opened 1889
- ’Kotri to Karach Section’, 108 miles(174km), was completed in 1861 by Scinde Railway, which became SP&DR 1870 and NWR 1886
- ‘Rohri-Kotri Section’, 189 miles(304km), from Rohri via Hyderabad and Rahoki Junction to Kotri was completed in 1900 with the opening of the Kotri Bridge over the river Indus. This making the former mainline (see below), which had opened in 1886 into the ‘‘Kotri-Rohri (via Ruk) Branch Line’
- ‘Rohri-Kotri (via Ruk) Branch Line’ from Sukkur via Ruk Junction, Larkhana and Sehwan to Kotri, completed in 1878. This line was formerly the mainline until the opening of the Kotri Bridge in 1900 to complete the NWR Mainline ‘Rohri-Kotri Section’ (see above)
- ‘Phulji Branch Line’, 3 miles(5km), from Phulji to Puranadera, opened as a branch to the ’Kotri-Rohri (via Ruk) Section’ opened by SP&DR in 1882; with short extension by NWR, 1902
- ‘Lodhran to Rohri section’, 225 miles(362km), opened 1878 by Indus Valley State Railway(IVSR), which became NWR 1886, via Samasata (with an interchange to the ‘Southern Punjab Railway)
- ’Sukkur Bandar Branch Line’, 1.5 miles(2.4km), a branch from Sukkur on the ‘Lahore-Karachi Mainline’ to Sukkur Bandar, opened by IVSR in 1878
- ‘Khanewal to Lodhran Section’, 56 miles(90km), opened by NWR 1909, reducing the route length by 29 mile(46km) and making the former mainline, which had opened by IVSR in 1865, into the ‘Khanewal-Lodhran (via Sher Shar) Chord Line’ (see below)
- ‘Khanewal-Lodhran (via Sher Shar) Chord Line’, 85 miles(136km), from Khanewal to Multan, 1865; to Muzaffarabad , 1870; to Lodhran, 1878, formerly the IVSR Mainline, became NWR 1886. Became a NWR Chord Line In 1909 with the opening of the 29 mile shorter ‘Khanewal to Lodhran Section’ of the ‘Ghaziabad- Lahore Mainline’ (see above).
- ‘Lahore via Raiwind to Khanewa Section’, 177 miles(285km), originally the Punjaub Railway opened in 1865, merged to form SP&DR 1870, becoming NWR 1886.
Delhi-Peshawar Cantonment Mainline
This NWR Mainline connecting Delhi to Peshawar Cantonment , 639 miles(1028km) in 1937. Originally named the ‘Ghaziabad- Lahore Mainline’ and the ‘Lahore-Peshawar Mainline’ comprised:-
- ‘Delhi-Ghaziabad Section’, 13 miles(21km), opened in 1864 by the East India Railway(EIR) and transferred to NWR in 1925
- ‘Ghaziabad to Lahore Section’, 339 miles(546km), was part of the Scinde, Punjaub & Delhi Railway( SP&DR) until amalgamation into NWR in 1886. The line had been constructed in stages from Lahore to Amritsar in 1862 and via Jullunder, Ludiana, Ambala, and Meerut to Ghaziabad completed by 1870.
- ‘Lahore to Peshawar Section’, 288 miles (463km), was the ‘Punjab Northern State Railway’ (PNSR) until amalgamation into NWR in 1886. The first section from Lahore to Jhelum, opened 1873 as metre gauge(MG) and converted to BG, 1878; from Jhelum via Rawalpindi the onward connection to Peshawar, was made in 1883 with the completion of the Attock Bridge over the river Indus.
- ‘Tawi Branch Line’, was completed in 1890. The 26 miles(42km) from Wazirabad (a town on the ‘Lahore to Peshawar Section’, to Sialkot, opened 1884 by PNSR . Extended by NWR in 1890 by 9 miles(14km) to the ‘Frontier of Kashmir State’ where the Jammu and Kashmir Railway continued the railway a further 16 miles(26km) to the ‘Left Bank of the Tawi River near Jammu’. The 25 mile(40km)section is in some records referred to as the ‘Jammu-Sialkot Railway’. The complete line from Wazirabad to Jammu, a total of 51 miles(82km) was part of the NWR network until partition when the line was severed.
Raewind-Bhatinda Mainline
- ‘Raewind-Bhatinda Mainline’, 88 miles(141km), from Raewind (on the ‘Lahore Khanewa Section’ of the Mainline) via Kasur to Hussainiwala (on the northern bank of the River Sutlej), opened 1883 by Scinde, Punjaub & Delhi Railway(SP&DR). The Empress Bridge over the river was completed 1887 by NWR to Ferozepore and extended in 1899 to Bhatinda
Samasatta-Bhatinda-Delhi Mainline
- ‘Samasatta-Bhatinda Mainline’, 402 miles(647km), opened 1897 by ‘Southern Punjab Railway’(SPR) from Delhi via Narwana, Jakhal, Bhatinda to Samasata. Originally named ‘Delhi-Samasata Railway’
Delhi-Ambala-Kalka Mainline
- ‘Delhi-Ambala-Kalka Mainline’, 102 miles(164km) opened 1891 by the ‘Delhi-Umballa-Kalka Railway Company’ , from Delhi via Ambala(Umballa) to Kalka. Purchased by Government in 1926 and transferred to NWR.
NWR Branch Lines
- ‘Kotri-Dudu-Ruk Branch Line’, 210 miles(338km), opened 1878 from Kotri via Laki and Radhan to Ruk. This was original ‘[[Kotri-Rohri Railway| ‘Kotri-Rohri Railway’ - see separate page for details
- ‘Hyderabad-Badin Branch Line’, 62 miles(100km), opened 1904 from Hyderabad to Badin; dismantled during WW1 and reopened 1922
- ‘Sind Left Bank Feeder Railways’:-
- ‘Tando Adam-Nawabahah Branch’, 54 miles(87km), opened 1931
- ‘Sakrand-Tharushah Branch’,66 miles(106km), opened 1931
- ‘Padidan-Mehrabpur Branch’, 43 miles(69km), opened 1930
- ‘Sutlej Valley Extension’, 213 miles(343km), opened 1910 by ‘Southern Punjab Railway’(SPR), from Lodhran to Kasur; also named ‘[Kasur-Lodhran Railway]]’, dismantled 1917-18 during WW1 and reopened 1923-25. Worked by as part of the ‘NWR System’
- ‘Ludhiana Extension Railway’, 153 miles(246km), opened 1905-06 by SPR, comprising the ‘Ludhiana-Ferozepore Line’ and ‘Ferozepore-MacLeod Ganj Line’. Worked by as part of the ‘NWR System’
- ‘Jullundur Doab Extension’, 73 miles(117km), opened 1912-14 by SPR from Jullundur City to Ferozepur Cantonment. Worked by as part of the ‘NWR System’
- ‘Phillaur-Lohian Kilas Line’, 39 miles(63km), opened 1913 from Phillaur to Lohian Kilas. Also called the ‘Phillaur Branch Line’
- ‘Jullundur City-Nakodar Railway’, 20 miles(32km), opened 1914. Also called the ‘Jullundur-Nakodar Chord Railway'
- ‘Wazirabad-Khanewal Branch Line’, 201 miles(320km), from Wazirabad reaching Lyallpur, 1896; extended to Khanewal, 1900. Also named Khanewal-Wazirabad Railway’. Surveyed under the name Wazirabad-Multan Railway, 1892; when first section opened 1896 was named the Wazirabad-Lyallpur State Railway and became part of the NWR network.
- ‘Shahdara-Sangla Hill Railway’, 56 miles(90km), opened 1907, from Shahdara (6km north of Lahore on Mainline) to Sangla (an intermediate station on the ‘Jech Doab Branch Line’)
- ‘Jakhal-Hissar Railway’, 50 miles(90km), opened 1913 from Jakhal to Hissar
- ‘Narwana-Kurukshetra Branch’, 53 miles(85km), opened 1909-10 from Narwana to Kurukshetra
- ‘Jind-Panipat Railway - British Section’, 15 mile(24km), opened 1916 from Panipat to “2¾ miles from Madhuka” as part of the ‘Delhi-Umballa-Kalka Railway’ . The line connected to the ‘Jind-Panipat Railway - Indian State Section’, 26 miles(41km). Both sections funded by Jind State Durbar. Originally worked by EIR until 1926, then by NWR
- ‘Rohtak-Panipat Branch’, 44 miles(71km), opened 1928 from Rohtak to Panipat
- ‘Jullundur Cantonment-Hoshiapur Branch’, 23 miles(37km), opened 1913 from Jullundur Cantonment to Hoshiapur
- ‘Pathankot Branch Line’, 67 miles(107km), a branch from Amritsar via Dinanager to Pathankot, opened 1884 by SP&DR, became NWR from 1886.
- ‘Batala-Qadian Railway’, 12 miles(19km), opened 1928 from Batala to Qadian
- ‘Verka-Narowal Railway’, 39 miles(63km), opened 1920-27 from Verka to Narowal
- ‘Jassar-Chak Amru Railway’, 27 miles(43km), opened 1927 from Jassar to Chak Amru
- ‘Shahdara-Narowal Railway’, 48 miles(77km), opened 1926 from Shahdara to Narowal
- ‘Wazirabad-Suchetgarh Railway, 36 miles(58km), opened 1894 from Wazirabad to Sialkot and extended to Suchetgarh in 1890
- ‘Shorkot Road-Qila Sheikhupura Railway’, 137 miles(220km), opened 1909-11 from Shorkot Road to Qila Sheikhupura. Originally named the ‘’Shorkot Road-Chichoki Mallian Branch Line’, from Shorkot Road (on the ‘Wazirabad-Khanewal Branch Line’ ) via Jaranwala to Chichoki Mallian (an intermediate stop on the ‘Shahdara-Sangla Branch Line’) .
- ‘Lyallpur-Jaranwala Railway’, 21 miles(34km), opened 1927 from Lyallpur from Jaranwala
- ‘Shorkot Road-Malakwal Railway’, 140 miles(225km), from Malakwal (on the NWR Sind-Sagar Railway) via Sarodha, opened by NWR, 1903 ; extended to Shorkot Road, 1906 to join the ‘Wazirabad-Khanewal Branch Line’. Originally named the ‘Jech Doab Branch Line’
- ‘Chak Jhumra-Hundewali Railway’, 43 miles(69km), opened 1928-29 from Chak Jhumra to Hundewali
- ‘Sargudila-Khushah Railway’, 28 miles(45km), opened 1929 from Sargudila to Khushah
- ‘Taxila-Havelian Railway’, 35 miles(56km), opened 1913 from Taxila to Havelian. Originally named ‘Havelian Branch Line’, from Sarai Kala (Not identified, thought to be Taxila Junction, 15 km NW of Rawalpindi, on the ‘Lahore-Peshawar Mainline’, to Havelian,
- ‘Moghalpura-Lahore Cantonment West Railway’, 2.2 miles(3.5km), opened date unstated from Moghalpura to Lahore
- ‘Sirhind-Rupar Railway’, estimated 55 km from Sirhind (on ‘Ghaziabad- Lahore Mainline’ between Ambala and Ludhiana). Constructed by NWR as part of a dam construction project and in operation before 1927
NWR Military/Strategic Section
Broad Gauge(BG), 1151(1852km) in 1918 described as the ‘NWR Frontier(Military) Section’; by 1937 this had become 1555 miles(2503km) and described as the ‘NWR Strategic Section’.
‘Baluchistan Railways’ is the sub-heading used in the 1937 Report comprising:-
- ‘Ruk-Chaman Mainline’. Recorded in the 1916 Report as the ‘Sind-Pishin State Railway’, 337 miles(542km). The ‘Quetta Link Railway’ was order by the British Government in 1876 as a strategic railway. The section from Ruk Junction to Sibi opened 1880, constructed by the SP&DR and named the Kandahar State Railway, merged into NWR 1886; extended from Sibi via Mushkaf and Bostan 1887; to Killa Abdulla, 1888; reaching Chaman 1892 . The section from Muskaf through the Bolan Pass was a major challenge as described in the page ‘Bolan Pass Railway Construction’, the track was twice washed away and finally opened after reconstruction in 1887. Recorded in the 1937 Report as the ‘Ruk-Chaman Mainline’, 310 miles(499km)
- ‘Sebi-Bostan (Harnai Route) Branch Line’, 134 miles(216km), originally named the ‘Sibi-Bostan Loop Line’, 109 mile(175km), from Sibi to Quetta, opened 1882 and 1887, dismantled and realigned 1897; extended to Bostan, 1887; Bostan Chord opened 1898.
- ‘Spezand-Zahidan Branch Line’, 440 miles(708km, original section named the ‘Quetta-Nushki Branch Line’, 88 miles(141km),opened on November 15, 1905. An extension NWR Military Section from Spezand Junction near Quetta to Nushki. The line was extended to respond to Military demands and was completed to Duzdap (Zahidan) by 1927. See ‘Trans-Baluchistan Railway’ and ‘Nushki Extension Railway’ for details.
- ‘Bhaganwala Branch Line’, 11 miles(18km) from Haranpur to Bhaganwala, opened 1895. Listed in the “1918 Admin Report” under the ‘NWR Frontier Section’, not listed in the “1937 History of Railways”
- ‘Warcha Quarry Branch Line’, 8 miles(13km) from Gunjyal to Warcha, opened 1918. Listed in the “1918 Admin Report” under the ‘NWR Frontier Section’, not listed in the “1937 History of Railways”
- ‘Ghazi Ghat Branch Line’ 10 miles(16km), opened 1887 from Mahmud Kot to Ghazi Ghat. Listed in the “1918 Admin Report” under the ‘NWR Frontier Section’, not listed in the “1937 History of Railways”
N.W.F.P Railways BG
This abbreviation is the heading in the 1937 Report – exact meaning unknown
- ‘Peshawar Cantonment-Landi Khana Mainline’, 37 miles(60km). The first section named ‘Peshawar-Jamrud Branch Line’, 11 miles(18km), opened 1901 from Peshawar to Jamrud. Extended in 1925-26 from Jamrud via Kotal to Landi Khana, worked as part of NWR. This formed the first part of the ‘Khyber Railway - see separate page
- ‘Nowshera-Durgai Railway’, originally opened 1901 as narrow gauge(NG) , 40 miles(64km) from Nowshera to Durgai. Owned by State, worked as part of NWR. Converted to BG 1921-22
Punjab Railway Branch Lines BG
This is the heading used in the 1937 Report
- ’Sind-Sagar Line’
- ‘Lala Musa-Kundian Branch Line’, 157 miles(414km) from Lala Musa to Malakwal, following the east bank of Indus River, opened 1880 by Sind-Sagar Railway as metre gauge(MG) converted to BG 1886 on the amalgamation into NWR. The line was extended from Malakwal to Kundian in 1887
- ‘Shershah-Campbellpur Branch Line’, 309 miles(497km), opened in stages. From Shershah (where the line connected to the ‘Lahore-Karachi Mainline’) to Kundian , opened 1887-90. The ‘Kundian-Campbellpur Section’, 119 miles(191km) from Kundian via Daud Khel to Jand opened 1892-99; Jald to Basal opened 1881 and extended to Campbellpur 1899, later renamed Attock
- ‘Daud Khel- Mari Indus Branch Line’, 6 miles(10km), opened 1892 from Daud Khel to Mari Indus. This branch linked to the ‘Shershah-Campbellpur Branch Line’ at Daud Khel (see above) and was originally named the ‘Mari-Attock Railway’
- ‘Malakwal-Bhera Branch Line, 18 miles(29km), from Malakwal via Miani to Bhera, opened 1880-82 as a metre gauge(MG) line and named the ‘Bhera Branch Line’; converted to BG 1887
- ‘Charlisa-Dandot Branch Line’, 7 miles(11km), from from Chalisa Junction via Khewra Salt Mines to Dandot, opened 1888 as a metre gauge(MG) line; converted to BG 1887-89. Originally named ‘Dandot Light Railway’ as a metre gauge(MG) line; converted to BG 1887-89
- ‘Jand-Kohat Branch Line’, 39 miles(63km), 7 miles(11km) from Jand to Khushalgarh opened 1881 as BG line; the 32 miles(52km) extension to Kohat was first opened 1902 as part of the ‘Khushalgarh-Kohat-Thal Railway’ 2ft 6in/762mm narrow gauge(NG), the section as far Kohat was converted to BG, 1908.
NWR System – BG Lines Worked as part of the NWR System
Based on the “1937, History of Indian Railways”[3], and also where extra information is available from the “1918, Administration Report on Railways 1918” [4]
See separate pages for details
- ‘Amritsar-Patti -Kasur Railway’, BG, 55 miles(88km), opened 1906 from Amritsar to Patti, and named ‘Amritsar-Patti Railway’; the ‘Patti-Kasur Railway’extended the line to Kasur, a further 27 miles(43km), 1910. A Private Company formed in 1905, with Managing Agents Messrs. Killick, Nixon & Co, Bombay, worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’
- ‘Hoshiarpur Doab Railway’(HDR), BG, Private Co., three sections opened 1915-17, total 91 miles(146km). Network of lines all worked by NWR as part of ‘NWR System ‘
- ‘Jullundur-Mukerian Section’, BG, 45 miles(72km), opened 1914-15 from Jullundur City to Mukerian
- ‘Phagwara-Rahon’, BG, 26 miles(42km), opened 1915-16 from Phagwara to Rahon
- ‘Jaijon Extension Railway’, BG, 20 miles(32km), opened 1917 from Nawanshahr to Jaijon
- ‘Jammu and Kashmir Railway - Indian State Section’, BG, 16 miles(26km), opened 1990 from ‘Frontier of the Kashmir State’ to the left bank of the Tawi River near Jammu Indian State Section’ as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Jind-Panipat Railway - Indian State Section’, BG,26 miles(41km) from Jind City to “2¾ miles from Madhuka” where it connected to the ‘Jind-Panipat Railway - British Section’, 26 miles(41km). Both sections opened 1916 funded by Jind State Durbar. Originally worked by EIR until 1926, then by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Khanpur-Chachran Railway’, BG, 22 miles(35km), opened 1911 from Khanpur to Chachran . Owned by Bahawalpur Durbar; worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Ludhiana-Dhuri-Jakhal Railway’, BG, 79 miles(127km), opened 1901 from Ludhiana via Dhuri to Jakhal . Managed, maintained and worked by NWR under an Agreement with the Princely Maler Kotla State]Durbar and the Jhind State Durbars as part of the ‘NWR System’. The line was used by ‘Sind Punjab Railway’(SPR) linking the ’Delhi-Samasata Mainline’ at Jakhal with 'Ludhiana Extension Railway' at Ludhiana.
- ‘Mandra Bhaun Railway’, BG, 46 miles(83km), constructed by NWR, opened in 1915-16 from Mandra to Bhaun. Private Co. formed 1913, with Managing Agent Killick, Nixon & Company. Worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Rajpura-Bhatinda Railway’, BG, 108 miles(173km) total, opened 1884 from Rajpura to Patiala as the ‘Rajpura-Pattiala Railway’, extended to Bhatinda 1889. Owned by Patiala Durbar and worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Sialkot-Narowal Railway,’ BG, 38 miles(61km), opened 1915-16 from Sialkot to Narowal. Constructed by NWR for the ‘Sialkot-Narowal Railway Company’ and worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Sirhind-Rupar Railway’, BG, 31 miles(50km), opened 1928 from Sirhind to Rupar. Private Co. Funded by Patiala Durbar and worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
- ‘Bahawalnagar-Fort Abbas-Kut Al Imara Railway’, BG, 152 miles(245km). The ‘Bahawalnagar-Fort Abbas Section’, 70 miles(112km), opened 1928 and extended to Kut Al Imara in 1931. Worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’.
NWR Narrow Gauge System
Based on the “1937, History of Indian Railways” [5]
See separate pages for details
- ‘Kalka-Simla Railway’, Narrow Gauge(NG) , 59 miles(95km), opened 1903 from Kalka to Simla. Constructed and funded and initially worked by the ‘Delhi-Umballa-Kalka Railway Company’ . Taken over by Government of India(GoI), 1906 and made over to the NWR from 1907[6].
- ‘Kangra Valley Railway’, NG mountain railway, 103 miles(km), opened 1929 from Pathankoft to Jogindar Nagar. Constructed by ‘State Agency . Worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’ [7]. One section closed in 1942 (reopened 1954).
- ‘Trans Indus (Mari Indus-Kalabagh-Bannu) Railway’, total 157 miles(253km), the section from Laki Marwat to Manzai classified as a ‘NWR Strategic Line’ [8]. It comprised the following railways:-
- ‘Trans Indus (Kalabagh-Bannu) Railway’, NG , 88 miles(142km), opened 1913 from Kalabagh to Bannu . This classified as the ‘Main Line’. The ‘Bannu Railway Survey’ is recorded as “ under survey in 1909” by NWR on behalf of Government of India(GoI
- ‘Laki Marwat via Pezu to Tank Strategic Line’, NG, 47 miles(76km), opened 1916, worked by the NWR as a ‘NWR Strategic Line’
- ’ Tank via Kaur to Manzai Strategic Line’, NG, 22 miles(45km) , opened 1921-22, worked by the NWR as a ‘NWR Stategic Line’
- ‘Mari Indus Railway’, NG , 22 miles(35km), opened 1922 from Tank via Kaur to Manzai , worked by the NWR as a ‘NWR Military Line’. Note the locations of Kaur and Manzai have not been identified
- ‘Zhob Valley Railway’, NG, total 174 miles(282km). An unspecified section opened 1917 as ‘assisted siding of a private company’ . ‘Acquired by the State’ with the ‘ ‘Khansi to Hindabagh Section’, 43 miles (69km) opened 1921 as part of the ‘NWR System’. Extended from Hindabagh to Killa Salfullah in 1927, a further 39½ miles(63km) and from Killa Salfullah to Port Sandeman, Zhob in 1929, a further 88½ miles(143km) [9].
- ‘Kohat-Thai Railway - Military Line’, NG, 62 miles(100km) opened in 1903 from Kohat to Thai. Originally part of the ‘Khushalgarh-Kohat-Thal Railway’, opened 1903 as a narrow gauge (NG) military railway;. The section from Khushalgarh to Kohat was converted to BG in 1908 and became part of the ‘Jand-Kohat Branch Line’ (listed in ‘NWR Branch Lines’ [10].
- ‘Jacobabad-Kashmore Railway’, NG , opened 1914, 77 miles(123km) from Jacobad to Kashmor. Constructed by the ‘ Upper Sind Light Railways Jacobabad-Kashmore Feeder Company. Worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’ [11]. Purchased by GoI, 1945
- ‘Larkana-Jacobabad (Sind) Light Railway’, NG , opened 1921, 53 miles(85km) from Larkana via Shahdadkot to Dadaur. Constructed by the ‘Sind Light Rail Company with Managing Agents Forbes,Forbes, Campbell & Co, Karachi. Worked by NWR as part of the ‘NWR System’ [12].
- ‘Nowshera-Durgai Railway’, originally opened 1901 as narrow gauge(NG) , 40 miles(64km) from Nowshera to Durgai. Owned by State, worked as part of NWR. Converted to BG 1921-22 and classified ‘N.W.F.P Railways’ see heading above [13].
Foreign Lines worked by NWR
- ‘Aden Railway’, MG, opened 1915-16. Constructed as a military railway, worked by NWR under designated 'Engineer-in-charge'. Closed 1929, dismantled 1930
References
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 150-151, pdf 187 and 190; Retrieved 13 Sept 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report for Railways” pages 106-7 (pdf115-6); Retrieved 13 Sept 2020
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 157-171, pdf 196-210; Retrieved 13 Sept 2020
- ↑ “Administration Report for Railways” pages 111-120 (pdf 119-128); Retrieved 13 Sept 2020
- ↑ US Archive .org pdf download of ‘History Of Indian Railways, constructed and in progress’, 31 March 1937 by ‘The Government of India - Railway Department’ page 172-178, pdf 211-218; Retrieved 13 Sept 2020
- ↑ ibid page 172 pdf 211
- ↑ ibid page 173 pdf 212
- ↑ ibid page 174 pdf 212
- ↑ ibid page 174 pdf 213
- ↑ ibid page 176 pdf 215
- ↑ ibid page 176 pdf 215
- ↑ ibid page 178 pdf 218
- ↑ ibid page 174 pdf 212